Often the teeth begin to hurt at the most inappropriate time - many people are well aware of this the hard way. Often the symptoms of pulpitis will be taken aback during long holidays, at work, on vacation, and it is not always possible to immediately consult a doctor for help. It is impossible to predict at what point deep caries, as the most common cause of pulpitis, the inflammation of the dental “nerve” with the appearance of characteristic symptoms, it can happen at any time.
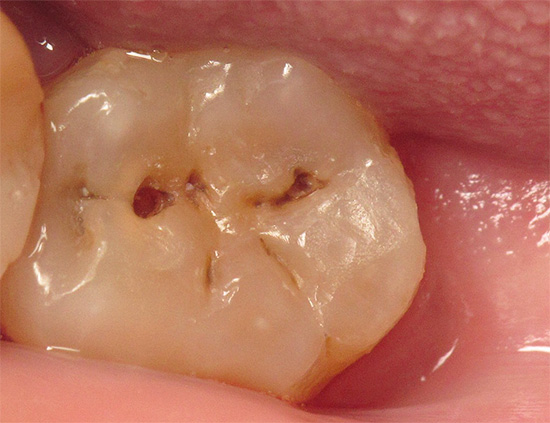
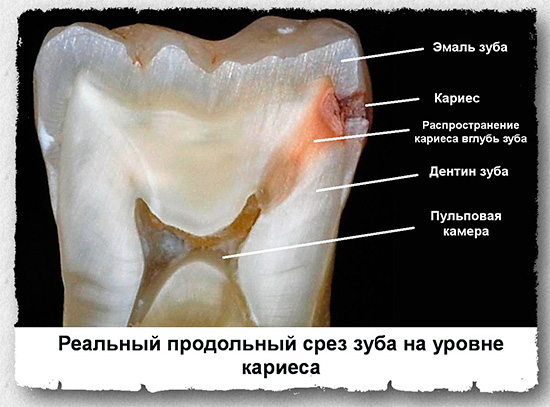
It is important to bear in mind that if it is not timely addressed to the clinic, pulpitis often turns into purulent formswhen you can tolerate tooth extraction and expensive prosthetics, or even irreversible processes for the general human health, sometimes bordering on life and death.
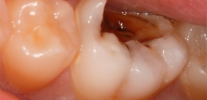
The photo below shows a tooth removed due to complications after pulpitis:
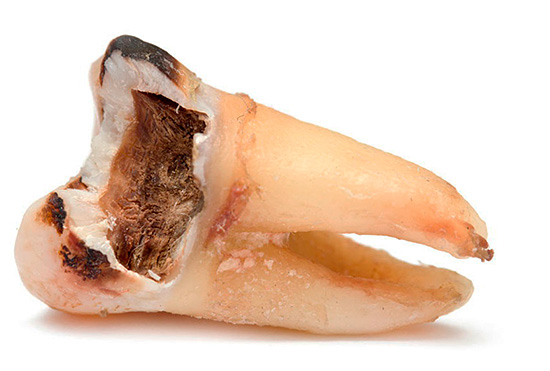
But how to distinguish the symptoms of pulpitis from other diseases of the tooth (say, from severe pains with deep caries), what complications can threaten and whether there are ways to prevent them - this and many other things will be discussed further.
Characteristics of pulpitis, like inflammation of "living" tissue
In order to better understand the root causes of various symptoms of pulpitis and to imagine in advance what can wait for you during future treatment, it is necessary to first deal with what, and what is actually inside a tooth can, in principle, hurt. The definition of pulpitis itself greatly clarifies this issue.
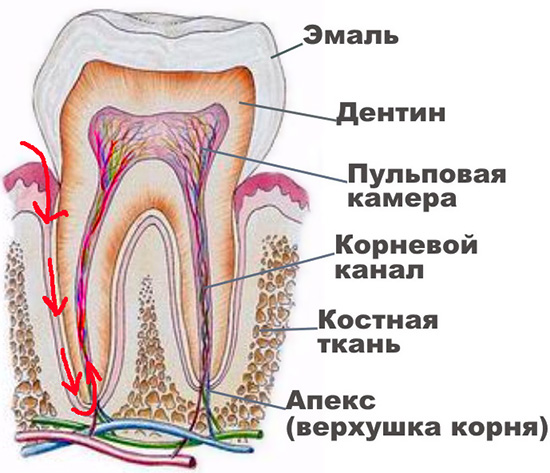
Pulpitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the so-called pulp chamber, or, otherwise, in the dental “nerve” (neurovascular bundle). And this process is associated in most cases with the activity of microorganisms: as a result of untreated deep caries, pathogenic microflora sooner or later penetrates the thinned dentin into the soft tissue of the pulp with the appearance of characteristic signs of tooth pulpitis.
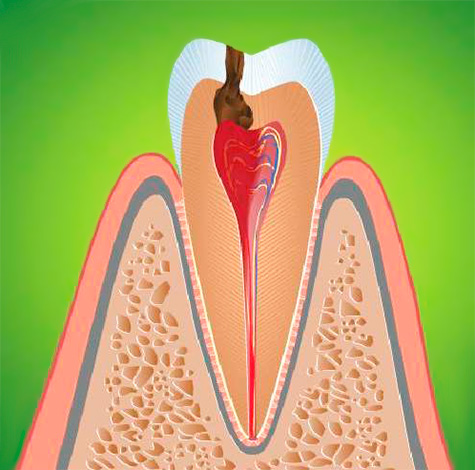
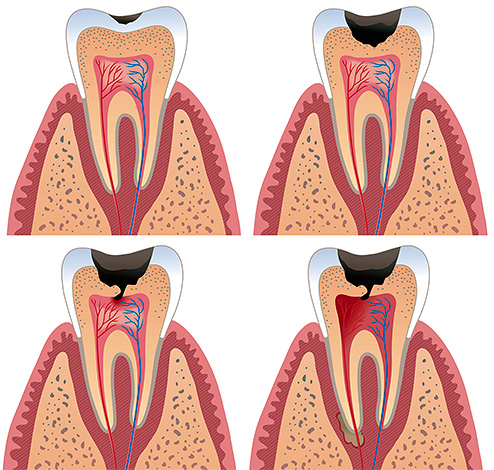
Inflammation in the pulp proceeds according to the same laws as in any other tissue. Against the background of the aggressive effects of bacteria and their toxins on living tissue, gradual cell death occurs, which activates inflammation factors.If we could observe this picture under a microscope, then its meaning would be as follows:
- to fight infection, immunity sends cells (leukocytes) to destroy the source of damage to the pulp;
- the result of this struggle is structural changes in the pulp tissue, up to its complete necrosis (necrosis) and the appearance of a characteristic clinic of chronic or acute pulpitis.
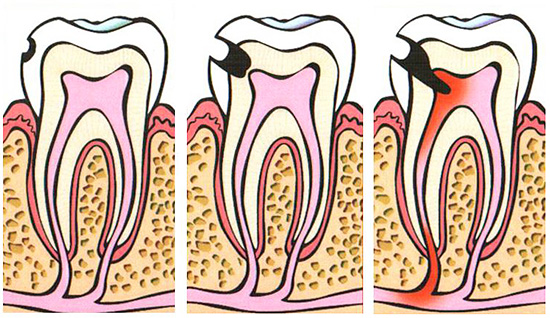
The soft tissues inside the tooth cannot recover on their own, but the process can turn into a long-lasting chronic with limited inflammation from the surrounding root tissues - this helps protect them from diffuse purulent fusion.
In the picture below, this process is shown schematically:
Question: Why does pulpitis sometimes cause a strong bad breath?
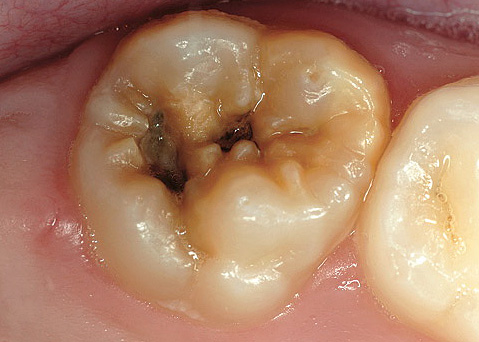
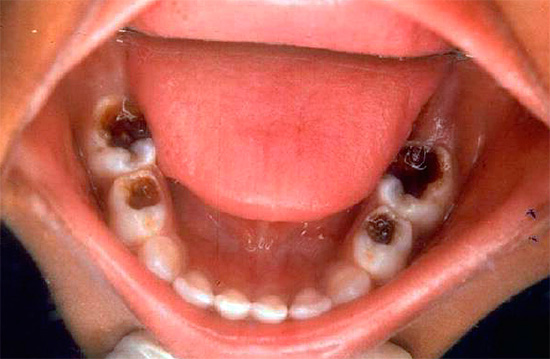
With a deep carious process, food particles accumulate on the walls and bottom of the carious cavity, and there is often little or no self-cleaning of the cavity. The result of the gradual decomposition of organic residues is the appearance of putrid odor from the mouth - this symptom often accompanies deep caries.Moreover, if pulp necrosis occurs, then the smell of rotting dental “nerve” also joins the smell of rotting food residues. And the more carious cavities (especially with pulpitis), the more pronounced are the signs of bad breath from the mouth, making it difficult to communicate normally with people.
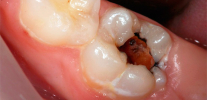
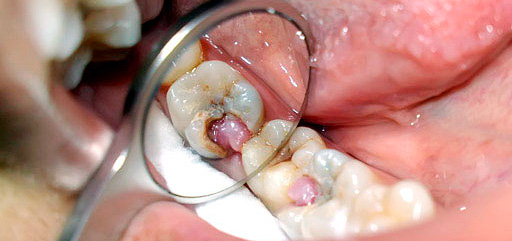
Photograph of a tooth with a deep carious cavity, which at any time can cause pulpitis:
Classic symptoms of pulpitis
There are many pulpit classifications, but the easiest to understand is that which most dentists use to make an accurate diagnosis and determine a treatment plan. According to this classification, the division of all pulpitis is made into acute and chronic forms.
Acute pulpitis is of only two types: focal and diffuse, and chronic - three: fibrous, hypertrophic and gangrenous. There is also a category of pulpitis in the stage of its aggravation.

A characteristic symptom of acute forms of pulpitis is spontaneous paroxysmal pain, often occurring at night, which in duration often fall into 2-3 weeks.With these forms of pulpitis, the dental “nerve” remains covered with carious tissues, and there is no external communication with it. The pain is intense: it is cutting, shooting, tearing, brings great pain, often forcing to use painkillers.
The appearance of painful symptoms in acute pulpitis is also provoked by external stimuli (cold, hot, sweet), but, unlike caries, such pains do not disappear for a long time even after the removal of such an irritant.
The principal difference between acute focal and diffuse pulpitis is determined by the characteristic clinic. In acute focal pulpitis, you can accurately indicate the aching tooth, and during diffuse pulpitis, pain radiates (gives) along the branches of the trigeminal nerve. For example, pain from the lower teeth is directed to the ear, back of the head and even to the temple. A sick upper tooth “shoots” in the zygomatic region, in the region of the eyebrows, often the pain radiates to the opposite jaw.
Chronic forms of pulpitis often occur, bypassing the acute stage. Almost always the pain is aching in nature, and often such a pulpitis can occur even without symptoms.
Chronic fibrous pulpitis has symptoms characterized by aching pains when eating hot and solid foods. Asymptomatic course is also characteristic of this species. Sometimes with fibrous pulpitis, the pulp chamber is opened, that is, it communicates with the oral cavity.
Chronic hypertrophic pulpitis is extremely rare, mainly in pediatric dentistry. The main clinical features of this pulpitis is the growth of the pulp due to the formation of new tissue or, as it is called, “wild meat”. Moreover, often the entire carious cavity is occupied by this tissue, which causes pain when eating, especially hard food.
At chronic gangrenous pulpitis symptoms depend on whether the pulp chamber, where the pulp of the tooth is located, is closed or has already been opened. When the camera is closed, the pain is strongly pronounced, they can even be spontaneous, but more often - strong aching from the hot. With an open cavity, gangrenous pulpitis gives a blurred clinic, so the final diagnosis can only be made at a dental appointment.
Question: Does the temperature occur during pulpitis?
Most often, there is no elevated temperature during pulpitis, and this symptom characterizes more periodontitis, periostitis and other complications. However, in some cases, the immune system may respond with a slight increase in temperature within subfebrile (37.0 ° -38.0 °), especially in children. Most often, the temperature may occur when signs of pulp necrosis appear (chronic gangrenous pulpitis).
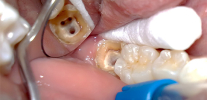
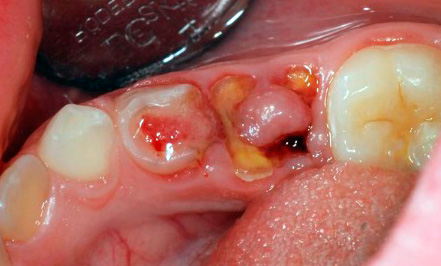
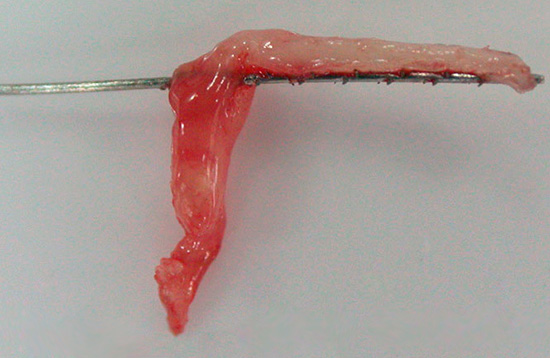
The photo shows a dental “nerve” extracted from the pulp chamber:
The main difficulties of diagnostics and devices used for this
To diagnose pulpitis, you should contact an appointment with a dentist who will conduct a number of additional studies. In addition to studying the symptoms of pulpitis, the following methods are also used:
- The so-called objective method using a dental mirror and probe;
- Thermometry;
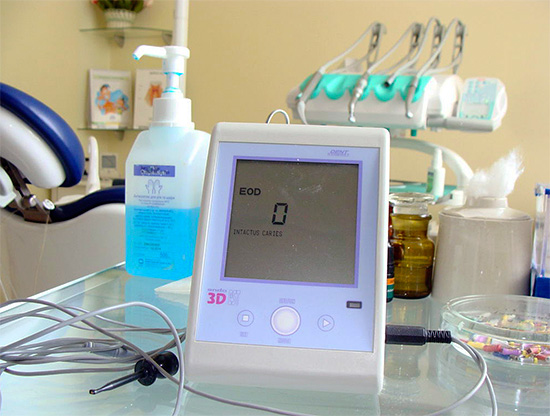
- Instrumental Diagnostic Method (EDI);
- Radiodiagnosis.
Almost 70-80% of information on the shape of the pulpitis of the tooth can be gleaned on the basis of an assessment of symptoms and a study of the carious cavity when examined by a dental mirror and when probing.The data of objective research allow us to distinguish pulpitis from deep caries, various forms of periodontitis, etc.
Probing makes it possible to understand whether the pulp chamber of the tooth is opened, whether its probing is painful, whether the opened “nerve” is bleeding, whether the tooth is changed in color, is there any pain in it during percussion (tapping the tooth with the blunt end of the probe handle) - all this also has importance for accurate diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
From the practice of the dentist
An experienced dentist can make a preliminary diagnosis of pulpitis based on the symptoms and the appearance of the carious cavity, and even determine its type, which in practice does not currently matter in principle (except for gangrenous forms of pulpitis, where special medical treatment of the tooth canals is required). In order to prove the presence of a cavity cavity with a pulp chamber, dentists of old quenching can carry out probing with great force, causing a sharp pain when the tip of the probe hits the tissue of the pulp that has not yet died. Such methods of differential diagnosis due to the not very humane approach are not acceptable in moderndentistry.
A frequently used diagnostic method is thermometry. This is a test of the tooth's reaction to cold and hot. If the tooth pulp has already died, the tooth will not react to cold water. The reaction to temperature stimuli in pulpitis is more pronounced than in caries, and does not go away for a long time after removing the temperature stimulus.
EDI or electrical diagnostics. Perhaps this is the most informative method in such a diagnosis, allowing not only to distinguish pulpitis from other tooth diseases (caries, periodontitis), but also pulpitis among themselves (acute types of pulpitis, chronic). Its principle is based on the use of devices capable of acting on a tooth with weak electric currents. At the same time, a healthy “nerve” reacts with insignificant painful sensations already at a current strength equal to 2-6 μA.
When a painful reaction to the current of such force is diagnosed with caries. The exception is deep caries, when the tooth can begin to respond to a current of 20 μA. In any case, pulpitis, as a rule, react to currents above 20-25 μA. And the occurrence of the reaction at 100 μA indicates already complete destruction of the pulp and the occurrence of periodontitis.Acute forms of pulpitis respond to currents of up to 40-50 μA, and chronic forms up to 90-100 μA. Gangrenous pulpitis in the destruction of the coronal part of the nerve is determined at a current of 60-80 μA.
Radiodiagnosis - is quite informative method. For example, by the nature of changes in the bone structure around the root (roots) of a tooth, it can be understood that we have signs of pulpitis, not periodontitis, and also we can determine the approximate boundaries of the carious cavity and suggest a violation (opening) of the pulp chamber. It is important to confirm or refute the diagnosis of deep caries.
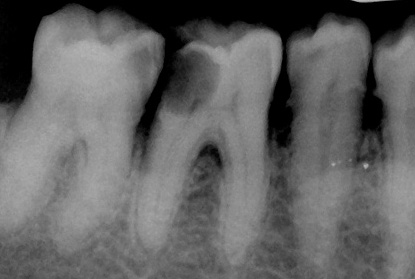
In chronic forms of periodontitis, as a rule, changes in the bone tissue around the root are significant, and in acute pulpitis there are no such changes at all (with chronic gangrenous pulpitis a small expansion of the periodontal gap is sometimes possible).
Symptoms of rare types of pulpitis
Traumatic pulpitis. It differs from the classical forms of pulpitis by the cause of the appearance: the neurovascular bundle is damaged due to a tooth injury. As a result of the traumatic factor, inflammation of the tooth begins, sometimes with the addition of infection from the oral cavity.
Despite the possibility of infection, in its pure form, such pulpitis are non-infectious, but cause quite typical clinical symptoms: severe pain from irritants (cold, hot), as well as spontaneous and paroxysmal pain. Traumatic pulpitis is common in childhood and adolescence, as well as in asocial categories of the population.
Retrograde pulpitis is a rare form of pulpitis, sometimes causing confusion at the dentist’s reception when there is no cavity and symptoms of pulpitis (bouts of pain, night and long-term pain) are present. In such cases, the infection inside the tooth enters through a hole at the top of the root.
Common causes of retrograde pulpitis are:
- Sinusitis
- Periodontitis
- Osteomyelitis
- Actinomycosis
and etc.
Concrete pulpitis is also a rare form of pulpitis, in which there is no infectious factor in the development of spontaneous or prolonged aching pain in the tooth. Inflammation of the pulp develops as a result of its prolonged compression by concretions — the wall deposits that are present in some people in the dental canals.
Most often in old age, the lumen of the channels is narrowed by denticles or petrification - salt deposits. The clinical signs of concreto-pulpitis are often blurred: there may be long aching spontaneous pain, or only from irritants (hot).
To the note: How to find a bad tooth in case of retrograde or calculous pulpitis ...
Unfortunately, in most clinics there is no EDI, which allows you to check which teeth are healthy and react to a current of 2-6 μA, and which bad tooth is already 20 μA or higher. Radiodiagnosis can sometimes help only with calculi pulpitis, where areas with signs of blockage of channels are detected by accumulations of salts. Almost always the bone tissue around the root with pulpitis is not affected.
In large dental centers and research institutes, equipment for EDI is available, and in most clinics they can search for a causative tooth based on patient complaints, pulpitis clinics, but in fact using a “tyke” method, when a patient can partially help a doctor by pointing out approximately to a sick tooth.Sometimes at the same time, 1-2 healthy and innocent teeth are treated, but it is worth emphasizing that for any doctor meeting with retrograde or calculitis pulpit is a very rare phenomenon that during all of its practice may not occur at all.
Signs of dangerous complications of pulpitis
Complications of pulpitis may occur as a result of the lack of tooth treatment, or not competent to conduct it. The first category of cases occupies the main position according to statistics, since a long-term localized infection in the “nerve” of a tooth sooner or later turns into a purulent process, which often causes serious complications.
The number of such fairly frequent complications include:
- Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root of the tooth (ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth in the hole), often manifested by a purulent process with an increase and swelling of the gums near the patient's tooth or fistula on the gum, from which pus flows into the oral cavity.
- Periostitis, also called “flux” in the people. This inflammatory process under the periosteum of the jaw.
- Osteomyelitis is a purulent inflammation that develops already in the bones of the jaw itself, most often against the background of untreated periostitis.
- Abscess - limited purulent inflammation, accompanied by fever, intoxication of the body and serious consequences.
- Cellulitis is a very terrible complication of an abscess, when a purulent infectious process spreads through the jaw tissues, soft tissues of the face and can cause death.
- Sepsis - against the background of reduced immunity, high aggressiveness and the spread of infection in the jaw, intoxication or infection of the whole body can occur with serious consequences.
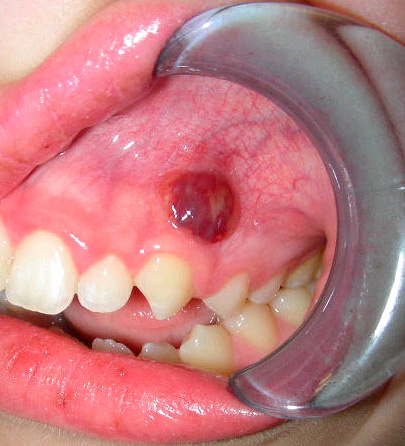
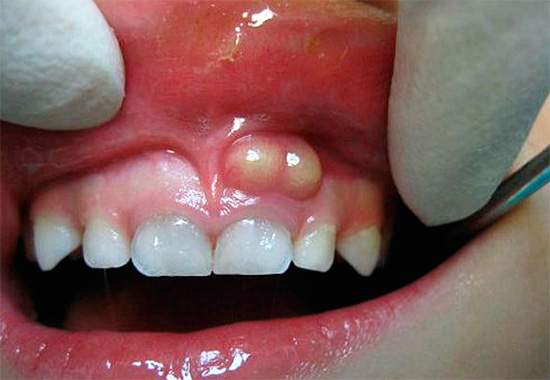
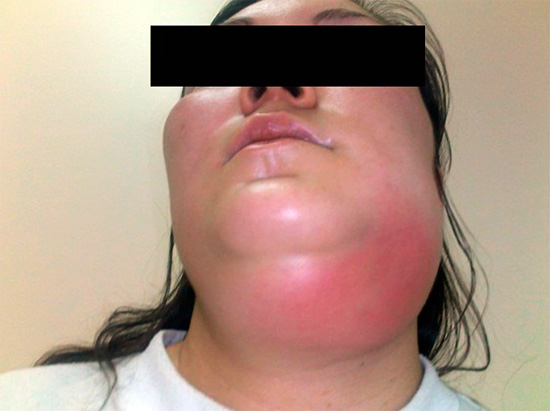
In this case, the list of complications of pulpitis is not complete, but even he gives a good indication of how dangerous it is not to treat pulpitis at the first signs of its appearance.
After treatment of pulpitis, there are sometimes complications, especially when contacting low-budget organizations with unqualified and not experienced doctors, but they are not as widespread as the first category of complications.
Question: Why is it easier to treat canals with pulpitis of the upper front teeth?
When the symptoms of pulpitis of the front tooth appear, most people turn to the dentist for help. Since all the upper front teeth from canine to canine have only one,most often wide channel, then in almost 100% of cases the risks of complications during and after treatment of pulpitis of the tooth minimized. Usually, canal treatment takes 2 times less time than intracanal treatment of posterior teeth (they have many roots, as well as a high percentage of complex anatomy of the canals).
See, for example, interesting nuances of treatment of pulpitis in the three-channel teeth.
First aid for pulp pain
If the symptoms of pulpitis of the tooth interfere with work or rest, but it is problematic to get to the dentist in the next day, then it is not forbidden to help yourself by choosing either popular methods of getting rid of pulp painor medications.
Common folk methods:
- rinsing the mouth with warm decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, oak bark, mint, lemon balm, valerian - until the attack completely disappears or a significant reduction in its severity;
- rinsing with warm soda-salt solutions (usually a teaspoon of soda and salt is diluted in a glass of warm water);
- rinsing the mouth with vodka or keeping it near the diseased tooth for a while. This method of treatment has age restrictions.

Common medications to alleviate the painful symptoms of pulpitis:
- Use conventional painkillers for oral administration (Ketorol, Ketanov, Pentalgin, Nise, Dexalgin and others) in therapeutic doses. Prior to their reception, you should consult (remotely) with a physician or dentist, as there may be side effects, contraindications or individual intolerance.
- Alcohol tinctures of eucalyptus or valerian. They are suitable for both applications and treatment of the carious cavity. When this is achieved a certain anti-infective and analgesic effect.
Often, propolis is also used to close the carious cavity with an open “nerve” as a temporary filling. If there is no allergy to this drug, then it is perfect for temporary use.
And finally, a tip: Is it possible to warm a tooth at the first signs of pulpitis?
In case of acute toothache, it is not recommended to warm the sore spot outside. A warm water bottle, scarves and warming compresses will stimulate inflammation, turning it into a purulent process literally overnight.Heating always aggravates the infectious process, which cannot be said about the warm rinses of the oral cavity itself. Therefore, it is not necessary to put a sore cheek on the battery to reduce pain - the opposite effect is obtained.
Interesting video: treatment of pulpitis under a microscope
What is important to know about pulpitis