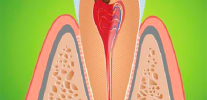
In acute inflammation of the so-called dental "nerve" (pulp) as a result of infection in the closed pulp chamber from the carious cavity, an acute form of pulpitis is diagnosed.
In turn, acute pulpitis, as a disease, is divided into two forms: focal and diffuse. Focal pulpitis is also otherwise called serous, because it appears as the initial stage of acute inflammation of the neurovascular bundle inside the tooth, which is accompanied by the accumulation of serous fluid in the channels. In fact, this is the result of the body's immune response to the invasion of bacteria into a previously sterile pulp chamber.
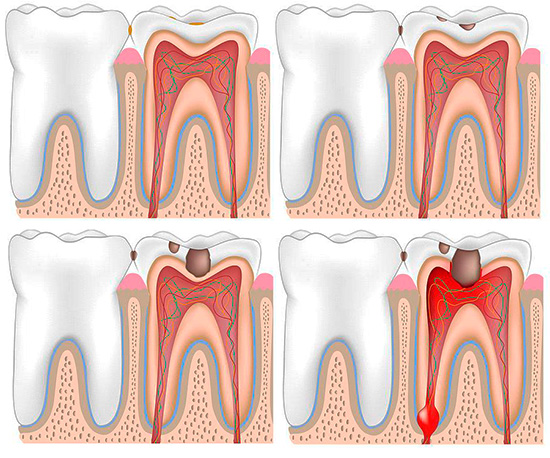
As the immune response intensifies, purulent exudate begins to accumulate in the channels - the result of the death of leukocytes and pathogenic bacteria. As a result, purulent pulpitis (also called acute diffuse pulpitis) develops, which causes a person to severe pain.
In most cases, the pulp chamber does not have a message with a carious cavity, that is, it is closed tightly, so the fluid accumulating inside the tooth begins to literally squeeze the “nerve”. This not only leads to the emergence of severe pain, but, in addition, acute purulent pulpitis often manifests itself with symptoms that make it very difficult to diagnose and follow treatment in the dentist’s office.
There are cases when a doctor simply cannot find a bad tooth and does not know which one to treat - as a result, treatment of healthy innocent teeth is carried out one by one. And, unfortunately, in such an unpleasant situation, anyone can now get with pronounced symptoms of purulent pulpitis.
In order not to appear among such “lucky ones”, let's get acquainted with the problem in more detail and consider it, so to speak, from all its angles ...
Why is purulent (diffuse) pulpitis sometimes so difficult to find a bad tooth?
The first and perhaps the most important aspect of the problem is the difficulty in determining a diseased tooth by a dentist. And here the patient may have a quite reasonable question: why the doctor,who has been studying his profession for more than 5 years, cannot find an ordinary, seemingly pulping tooth that hurts terribly and requires immediate treatment?
The fact is that of the acute forms of pulpitis, purulent (diffuse) is the most unpredictable. Most people with this diagnosis come to the doctor with complaints that "everything hurts." There is such a strong pain that it becomes difficult to indicate exactly the aching tooth.
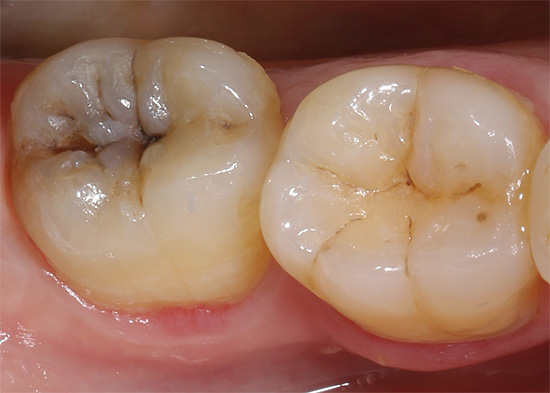
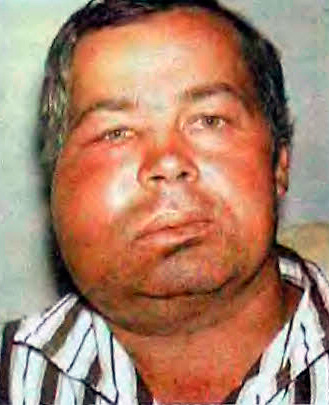
The photo below shows an example of how the dentition looks, in which one of the teeth is affected by purulent pulpitis. But which one? ..
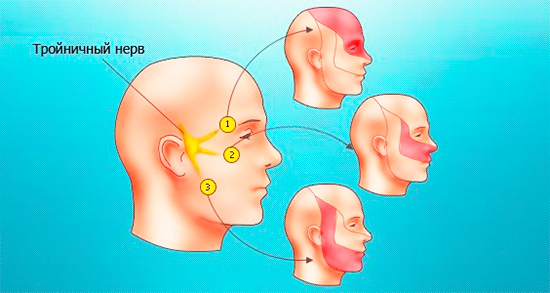
Why there are such difficulties in diagnosis? The fact is that, as noted above, the accumulation of purulent exudate leads to a strong squeezing of sensitive pulp tissue between the walls of the channels. Impulses along the nerve fibers are transmitted to the brain, responding to pain. At some point, the signals from the squeezed “nerve” tissue become so intense that the pain begins to “shoot” along the branches of the trigeminal nerve, in other words, in different areas of the maxillofacial region (sometimes the ear, part of the face, head, and throat can ache) .
A case from the practice of the dentist therapist
When I worked 5 years ago in Ryazan, a patient (37 years old) approached me with a sharp pain in the tooth that had been tormenting her for 5 days, but on the day of the visit she became so intolerable that it was no longer possible to wait. I have seen cases before when a patient points to a healthy tooth, but you treat someone who is standing next to carious cavity and always guess, but there was something completely different.
The woman complained of a sharp pain in the tooth, which "gives" to the head. At the same time, both the upper and lower jaw hurt, and the patient pointed to the upper tooth on the right, although I did not find signs of at least one broken tooth in this area. Since there was a seal on the last right upper tooth, I started with it: I removed the nerve from the canals and sealed them in the first visit.
The next time a woman came in with the same sharp pains. At the same time, she urged me to cure the nearby tooth, as she would not suffer another “night with her circles of hell”. After the canal treatment, the next appointment was prescribed, but I'd rather not come to it, since the woman, exhausted by the strongest pain in the tooth, rushed at me almost with her fists. I had to reassure her for a long time: she no longer believed in the success of the new upcoming procedure.
After a detailed examination of all the teeth in the lower jaw on the left, a wisdom tooth affected by caries (the eighth) was found. The woman continued to insist that lately the pain has intensified in the upper teeth, but with the anesthesia, I was allowed to at least treat the carious cavity in the wisdom tooth and put arsenic paste on it to devitalize the nerve. The very next day, she brought me a bunch of gifts for the fact that the pain was completely gone: neither the head nor the jaw reminded me of myself.
So I first encountered one of the most difficult to diagnose diseases of the tooth - acute purulent pulpitis (diffuse). The result of this was the useless treatment of two innocent teeth.
In the future, I had to deal with such cases more than once, however, even taking into account my previous experience, there were not always damaged teeth, standing somewhere far from the location indicated by the patient. There were cases that all the teeth in the row turned out to be whole and (or) with fillings, and again we had to find a pulpous tooth using the scientific “spear” method, as it was only possible to dream of modern diagnostic methods and devices in our clinic…
Symptoms of acute purulent pulpitis
Comparing the case histories of acute serous (focal) and acute purulent pulpitis (diffuse), only a slight resemblance can be found, for example: in both cases, acute paroxysmal pain, which can occur without irritant and is worse at night. With both of these acute forms of pulpitis, almost any irritant (sweet, hot) can cause the symptoms long-lasting pain in the tooth, even despite the elimination of the stimulus. However, with acute serous pulpitis, seizures usually do not last long (no more than 20 minutes), and with purulent - they can last for hours.
Acute focal pulpitis lasts no more than 2 days, passing into the purulent phase of acute diffuse pulpitis, which lasts up to 2 weeks. The dentist easily conducts a differential diagnosis of these two forms of acute pulpitis on the basis of only one symptom - the ability to accurately determine a diseased tooth:
- if the patient easily points to the tooth that is disturbing him, this is the serous form of pulpitis;
- if the patient finds it difficult to say exactly where the pain is located, and complains of long-lasting attacks, radiating (irradiating) to the maxillofacial area and the head area, then this is with a high degree of probability the purulent phase of pulpitis.
From the upper teeth, the pain "shoots" in the temple, brow and cheekbones, as well as in the teeth of the mandible. With diffuse pulpitis in the lower jaw, the pain "gives" to the back of the head, to the submandibular part, and sometimes to the temple and teeth of the upper jaw. In case of purulent pulpitis of the front teeth, the symptom of pain radiating creates the sensations of “sick teeth” on the opposite side of the jaw.
Feedback
Literally that week I turned to a dentist with strong bouts of pain in the lower molar, which could not be tolerated. Generally, I do not like to go to the doctors, especially to visit the dentist, but on the third day from the occurrence of the first symptoms in the tooth began something that is beyond words.
If the day before I knew exactly where it hurts and that it hurts, then on that ill-fated day I had to drink pills with handfuls, because the damn pain went beyond the jaw and began to “pierce” my head, then the whole jaw, then the upper teeth.When I could not tolerate this nightmare, I literally ran to the doctor. It’s good that I even remembered where everything had gone from and pointed the doctor to the tooth that had started to hurt itself a couple of days ago. And it was the case that my friend, by mistake, the surgeon removed the wrong tooth. This is only because he, like me, had pains everywhere, and the beater was not long to figure it out: where he was shown, he pulled.
And I just removed the nerve and put a seal. Now everything is fine. I hope that there will be no more such a nightmare.
Innokentiy, Oryol
Modern methods of treatment of purulent pulpitis
It’s rare for anyone to endure acute pain with purulent pulpitis - usually after a couple of days of torment everyone begins to realize that without the help of a dentist, only pain pills he can not do. And the sooner such an understanding comes, the better, since this acute form of pulpitis is successfully and easily treated with the use of modern methods and approaches.
Dentist comment
If someone is still confused by the word “purulent” in combination with pulpitis, then I hasten to rejoice with the fact that the contents of the root canals at this stage of the disease are filled with a quite lively and “moderately plump” nerve.And the same pus that must flow from the canal is a slightly different story concerning another disease.
The main thing is to understand the difference: in acute purulent pulpitis, live pulp (tissue) is surrounded by an inconspicuous eye (with rare exception) liquid, and in acute purulent periodontitis, the “nerve” has long died and decomposed sufficiently so that when the pulp chamber is opened, one or more drops of pus appear from the hole .
So it is better to treat another living tooth with acute pulpitis, until it has accumulated so much pus that innocent gum can be selected as a reservoir, which will swell.
Treatment of acute serous (focal) pulpitis can be carried out by a biological method with the preservation of the entire pulp in a viable state, but in dentistry of different levels almost always resort to pulp removal from canals, their subsequent washing and sealing. On the one hand, it is simpler (the doctor does not need to specify the stage of pulp inflammation and carry out complex diagnostics), but on the other hand, it is safer for the patient’s health and more advantageous for his pocket. On the financial issues in the treatment of acute pulpitis will still be detailedset out just below.
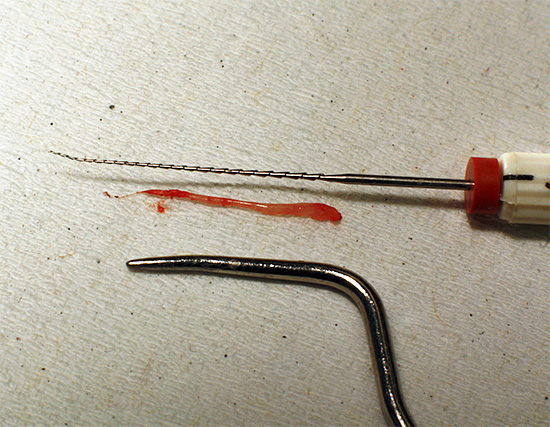
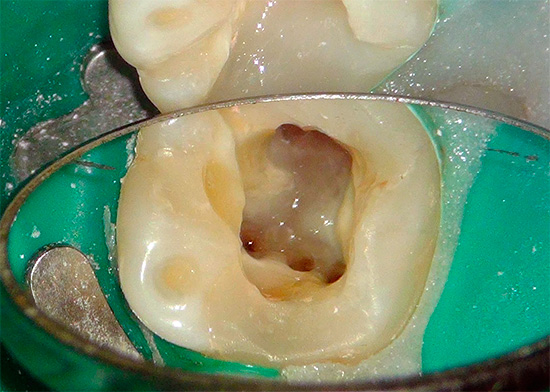
Acute purulent pulpitis is treated by common methods of vital and devital extirpation. Devital extirpation involves setting up a devitalizing paste for the first visit to a tooth, which kills the “nerve” in a few days.
On the photo - “nerve” removed from the tooth:
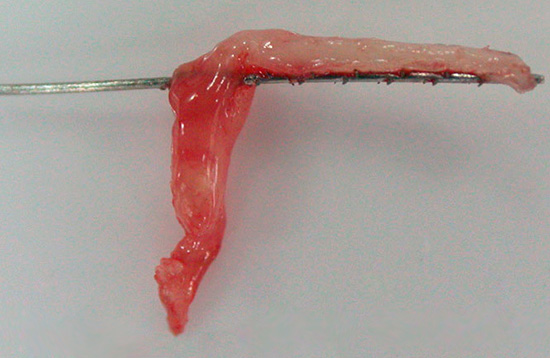
Some people are scared away by the scary word “arsenic”, but in reality, in the hands of a professional, arsenic paste does not lead to the terrible consequences that are widely known among people: severe pain, tooth decay a few months before the foundation, burns of the gums, etc. d. However, those same professionals have long since switched to alternative pastes that do not contain arsenic anhydride.
Moreover, in the treatment of acute pulpitis, preference is often given to the vital extirpation of the pulp, when the neurovascular bundle does not need to be killed beforehand:
- High-quality local anesthesia is done with a domestic or imported (more often) anesthetic;
- The pulp chamber is opened, amputation of the “nerve” coronal part and extirpation (extraction) of the root are performed;
- Channels are flushed with effective antiseptics (sodium hypochlorite, hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, etc.);
- Then the channels expand to the size and conicity that is required under the future "root filling";
- At the next stage of treatment, the canals are sealed to a physiological narrowing (apex), that is, without reaching the radiological tip. The choice of material for canal filling is the creative approach of each doctor, based on clinical experience, the clinical situation during the work, the financial possibilities of the client and other factors.
- Temporary restoration or imposition of a temporary seal. In some cases, this stage is omitted, and a permanent filling is immediately applied, although there are still debates on the issue of the feasibility of a single-stage tooth restoration immediately after intracanal treatment.

Why it is impossible to treat purulent pulpitis folk remedies
The answer is simple: because such treatment with a high probability will lead to tooth loss. Our ancestors well understood that it is not always possible to relieve a person from suffering with the help of lotions and conspiracies.
Although there were many cases when, after the use of traditional medicine, a decaying tooth never again had an effect and rotted to the root, which gradually began to loosen and fell out no worse than a baby tooth.
Opinion dentist
Many doctors are interested in the riddle of prayers and some folk remedies for toothache: why sometimes grandmother plots really help relieve pain, what happens to a tooth at this moment and how long it does not manifest itself again.
From my point of view, such methods of alternative medicine are associated with the transition of the acute process into chronic formand the latter often proceeds without symptoms of acute pulpitis, which has a beneficial effect on the emotional state of a person. It's nice when the tooth does not hurt, even if it starts to crumble slowly.
Therefore, there are still old women who slyly smile when talking with the dentist, and pass their gift from generation to generation, flaunting, however, with decaying root-roots, which in general are in a state of dying. It seems to me that for modern society rotting teeth that do not hurt are, at least, wild.
Dentists offer a good solution in this situation: not to treat acute pulpitis using traditional methods, hoping for true healing, and only temporarily get rid of the pain with available painkillers when it is difficult to get a doctor in the near future.
It is important to understand that a timely appeal to a professional dentist for help saved a lot of teeth from the surgeon’s forceps. In addition, every year there are cases when, without the special help of a dentist, people simply died from odontogenic infections. It can spread throughout the body, resulting in sepsis (blood infection) or, for example, odontogenic mediastinitis (inflammation of the mediastinum).
Sometimes, severe complications are only the result of undue delay and treatment of acute pulpitis with traditional methods that did not help. Not always conspiracies, propolis, garlic or beets are as effective as some traditional healers position them ...
When treatment of purulent pulpitis can empty your wallet
In a private clinic, it is often advantageous for a doctor to treat the tooth canals with any form of pulpitis, since treatment of each channel is charged separately. While maintaining the same pulp in a viable state, the dentist cannot use all the charms of numerous items of the price list, and, in addition, at the wrong diagnosis and technique of this method of treatment, the patient also has complications in the form of repeated pain and shouts: “Return my money!”

In general, acute purulent pulpitis has such symptoms that allow not the most conscientious doctors in private clinics to treat the channels in many teeth, even healthy ones, at once.
Imagine a situation: a person is dealing with severe sharp pains that make the whole jaw hurt. The doctor calmly finds the pulpit tooth (the benefit of modern equipment in most private clinics makes it easy to do this), and at the same time reports that next to him there is also a problem in the tooth, which in mutual connection gives such "delights of life".
The fact is that on the adjacent tooth can only be small carious stainwhich can either be sanded or processed and put a seal. But canal treatment is 2-3 times more expensive, especially since at the end of intracanal treatment there is the same filling that was originally intended.Sometimes it reaches the point that even more than 3 teeth are subjected to intracanal treatment at once, and the reason is the acute purulent pulpitis of one tooth and the uncontrolled desire of a private dentist (often not from a good life) to earn themselves and their family an extra piece of bread.
What can you do when the prices for canal treatment for pulpitis and periodontitis in private clinics grow steadily every year, and high-quality intra-canal, albeit useless for a given tooth, therapy allows you to keep a tooth for life, albeit in a dead state .
In a state institution, a “divorce” for money manifests itself in a different way, but almost always it is not associated with multiple useless treatment of the canal teeth, because the doctor, due to constant haste, sometimes does not even have time to do what is required of him in this clinical situation. The result is often a tooth healization, no longer in the state, but in the same ill-fated private clinic. Such a vicious circle.
In order not to be mistaken with the choice of the clinic and doctor, it is useful to initially survey acquaintances, friends and relatives, read reviews on websites, find out the doctor’s work experience and the degree of equipment of the clinic.And if you have found a good doctor, then hold on to him, not allowing casual dentists in random clinics to “hang out” on your teeth.
Be healthy!
Interesting video: what awaits you in the treatment of pulpitis in the clinic
Symptoms of pulpitis and why it can hurt the whole face

Hello.I have a specific question: tell me, if the nerve overheated during preparation and, without noticing it, they immediately filled, then at least after some time pus can develop in the tooth and outside the tooth, i.e. in periodontal? The fact is that a brother was put a seal a week ago without removing the pulp. Here, in a week the face was swollen. The doctor justified that before him someone had not completely removed the nerve. That's why the tooth festered.
Hello! If a tooth has been treated for caries (medium or deep) and the doctor has dealt with a “live” tooth, then we are talking about the occurrence of periodontitis. And not always the reason is overheating - there is also a chemical effect of the material in violation of the technique of working with it and excessive vibration when working with a bad tip. Overheating is also often the cause of the death of the pulp, especially when working without water cooling. To notice overheating of the tooth during the work is almost impossible.
As for the minimum in time: in general, there is no such thing in such situations. I would say that the average problem develops within 1-2 months, although everything is individual - it may well arise even in a few days.
I do not know how much this justifies the doctor, but I know quite a few cases when dentists treat tooth decay, which in reality already has an inflammatory process in the pulp, but at a given moment of time behaves relatively calmly. Just a week from pulpitis, which was mistakenly treated as caries, the problem can also turn into purulent periodontitis.
If a tooth in the canal to the doctor you mentioned is not treated, it means that the dentist is trying to justify himself by talking about the partial removal of the nerve before him. But again, I repeat that I have cited above some nuances that do not allow considering the issue so straightforwardly and unambiguously in the context of just one overheating of the carious tooth.
Hello, tell me, is it possible to cure a healthy molar tooth, around which a purulent pocket has formed? Maybe you can make a cut in the gums and treat from there?
Hello! First you need to find out exactly what you called the "purulent pocket." If we are talking about purulent inflammatory process due to periodontitis, then the dentist-therapist determines the tactics of possible treatment.In the event that the “purulent pocket” is the same pathological gingival pocket with suppuration against the background of periodontitis in the acute stage or exacerbation, then it is better to analyze the tactics with a periodontist dentist. If you do not have this specialist in your area, then a dental surgeon or maxillofacial surgeon will do. If treatment is possible, it is carried out in a complex way: from curettage of periodontal pockets, to gum plastics, splinting of teeth with mobility, selective grinding and the use of pastes, ointments and gels to eliminate microbial factor and inflammation. I'm not talking about the preliminary professional hygiene of the oral cavity: the removal of stone and plaque from all teeth. Sometimes in such teeth it is necessary to remove the “nerve” and treat the canals - this is according to the situation.
If treatment is limited to only one incision, without conducting a complex therapy, then it will either be ineffective or just postpone the final part of the tooth - removal.
Hello! They treated the pulpitis, they said that it could hurt for some time. It's been almost 2 weeks, and it hurts. The doctor is on vacation, waiting. Tell me, please, what could be the reason?
Hello! Pain for almost 2 weeks in a treated tooth is not the norm. However, with small errors of the doctor during the treatment of pain channels during bite sometimes pass only within a month (when it comes to insignificant removal of material beyond the apex of the tooth root, most often based on epoxy resin, which is now popular as a sealer). It is possible to understand how “slightly” the sealer is derived from the image, the benefit is that this material is contrasted.
Of the complications after the treatment of pulpitis, when a tooth hurts for a long time, the following can be noted:
1. A failed channel or channels;
2. Perforation of the tooth wall;
3. Significant removal of material for apex (also gutta-percha);
4. Break off the tool in the channel;
5. Creating a false channel.
There are other problems. In order to roughly know what's wrong with your tooth, it is important to have on your hands a couple of pictures in different projections
Hello! A year ago, the wisdom tooth was sealed (sixth, lower jaw). After a while, the floor of the tooth with the filling broke off, and five days ago it began to hurt.The pain increased, even painkillers did not help, inflammation appeared. I went to the doctor in a private clinic, and the dentist said that it was necessary to remove, because the tooth was incorrectly healed. The procedure was carried out, but after a day the inflammation remained, the left lower jaw hurts, the cheek is slightly swollen. I rinse with chlorhexidine and apply Metrogil Denta Gel as prescribed by the doctor. The dentist warned that the pain will remain for some time. Tell me, how long does the inflammation persist after tooth extraction and why did the pain remain?
Hello! The inflammatory process on the background of injury usually lasts for 1-2 weeks, and all this time pain may be observed to varying degrees of severity. If we are talking about sharp pains after tooth extraction, then they are stopped in the first days by analgesics. Although often acute pain does not happen. Aching pains are the norm at the stage of healing of the hole and are individual in nature. It all depends on the quality of the removal, the body's defenses and pain threshold. The fact that you comply with the recommendations of the doctor is commendable, but do not forget also that it is useful to make a check-up inspection of the hole by the doctor 3-4 days after the extraction of the tooth.