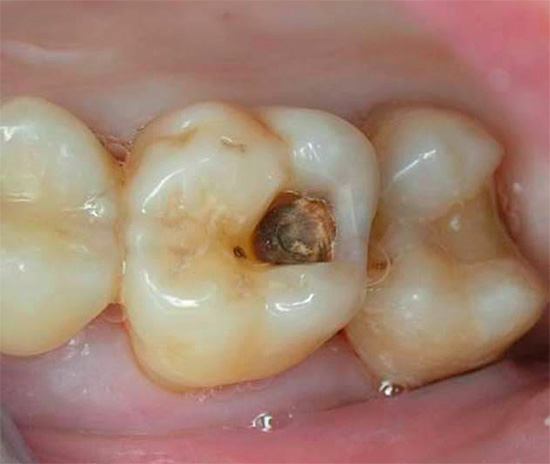
Today, almost every person at a certain stage of his life at least once faced with the problem of caries, which is often accompanied by varying degrees of severe toothache (and some have suffered such periodic pains for years, drowning them out with pills). However, few people know that if nothing is done, then in the last stage of destruction with deep caries, in addition to various painful sensations (from sweet, hot, cold, from solid food) there are serious risks of development pulpitis and periodontitis. Such complications of deep caries often cause pain of such strength that everyone who has ever experienced them remembers this for a lifetime.
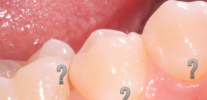
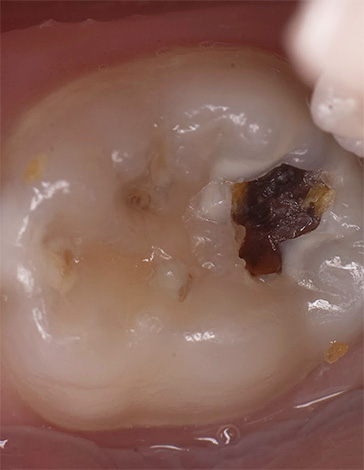
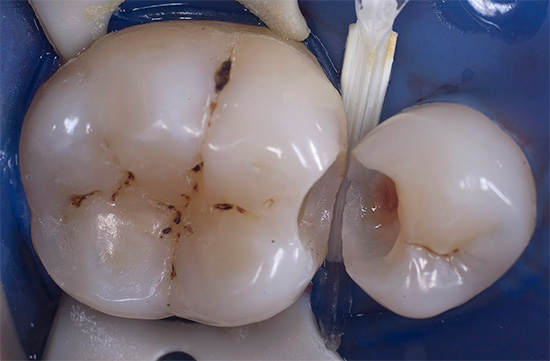
The photo below shows an example of deep caries, in which the pulp chamber of a tooth can be struck with a high probability:
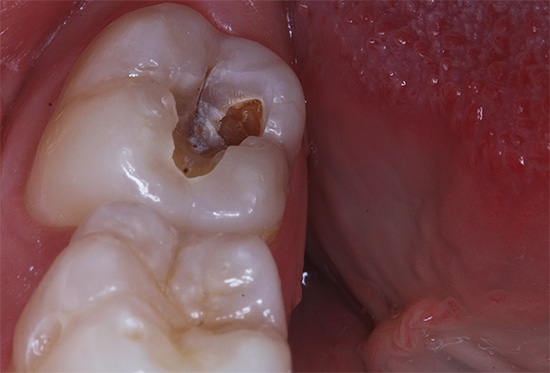
By what symptoms can we understand that deep caries has already formed in the tooth,how to distinguish it from other types of carious lesions and complications, why a bad breath develops during deep caries and what you need to know about treatment in such a situation — we'll talk about these and many other interesting nuances further.
It is interesting
People were familiar with deep caries from antiquity, which is confirmed by the deplorable state of the jaw bones and teeth, often found during excavations. In the Middle Ages, it was believed that the disease was caused by “dental worms”, which need to be removed with a red-hot iron - as you understand, such procedures did not give a special therapeutic effect. Attempts to treat deep caries were made long before that (several thousand years ago in ancient Rome), but some success was achieved only after the appearance of the first primitive drill of Morrison in the middle of the 19th century.
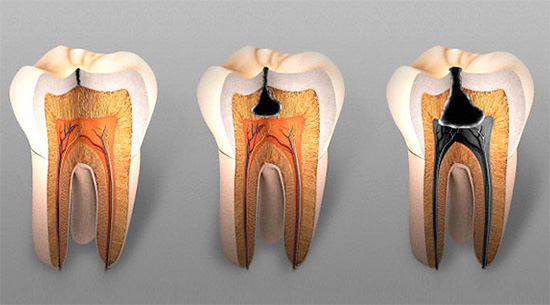
The main forms of deep caries
Depending on the course of the disease, there are acute and chronic forms of deep caries.
Acute deep caries characterized by short-term pain from a variety of stimuli. Often the cavity has a deep and narrow entrance with a wide base.If you could scrape the walls of such a cavity with something hard (and dentists do it regularly at receptions), you would notice that softened infected and pigmented dentin is always abundantly separated from the walls of the cavity.
On a note
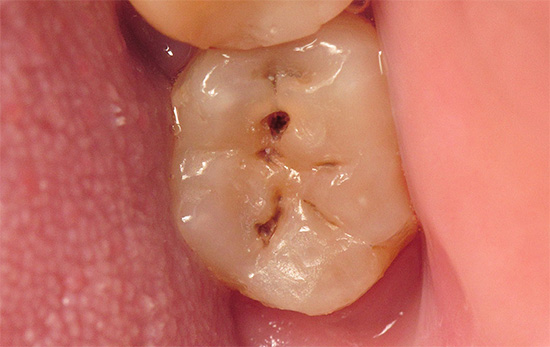
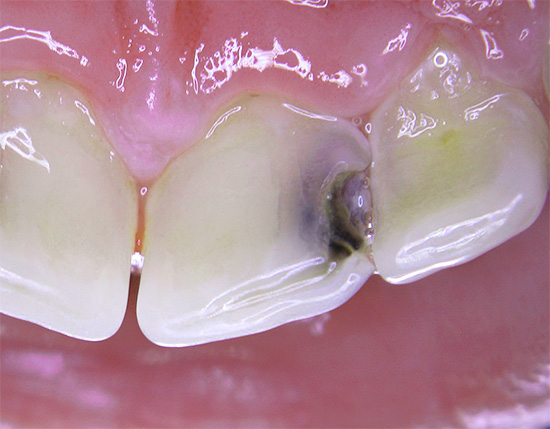
Since the deep carious cavities can accumulate food debris for a long time and rot there, it is often accompanied by the appearance of an unpleasant smell from a person’s mouth - even though he seemingly brushes his teeth twice a day.
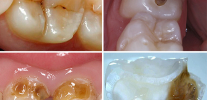
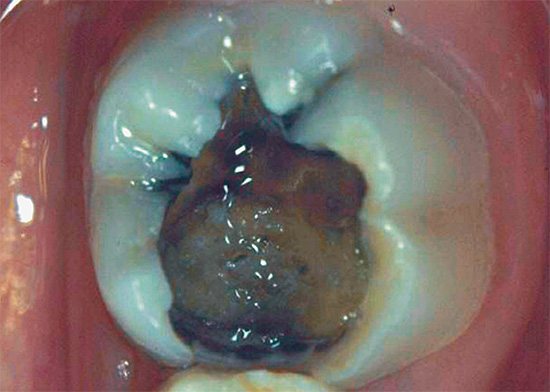
The photo below shows an example of such a deep carious cavity:
Chronic deep caries, unlike the acute one, has a sluggish current, therefore, it can often not manifest itself by any symptoms due to the deposition of replacement dentin at the bottom of the carious cavity, which prevents its irritation with food or drinks. Often the bottom is dense and even slightly polished. Otherwise, chronic caries is called "paused."
It is interesting
Researchers in the field of caries studies believe that even an acute form of deep caries can occur without specific symptoms.Even in the presence of a deep cavity with softened dentine, it can be covered with a “shell” of enamel and stay in a place difficult for external irritants, for example, on one of the contact walls of the tooth near the gum (that is, in the interdental gap). Only after breaking off or splitting off a significant part of the enamel above the carious cavity is possible the classic manifestation of acute deep caries with a characteristic clinic.
Signs of deep caries that are unlikely to “leave anyone indifferent”
Since deep caries is the last stage of carious destruction, it has a characteristic clinic only (the same goes for diagnostics and treatment methods). In real life, it is quite difficult to determine the stage of destruction of hard tooth tissues: medium and deep caries often have few differences.
The following characteristic symptoms of deep caries can be distinguished:
- Pain when taking hot and cold (that is, from temperature factors);
- Pain from sweet foods, sour foods, or salty (chemical factors);
- Pain when hard food enters the carious cavity of the tooth (mechanical factor).
Such a deep caries clinic is typical for most cases. When a sweet tooth or a cold one hits a painful tooth, a sharp pain occurs that lasts exactly as long as the stimulus acts.
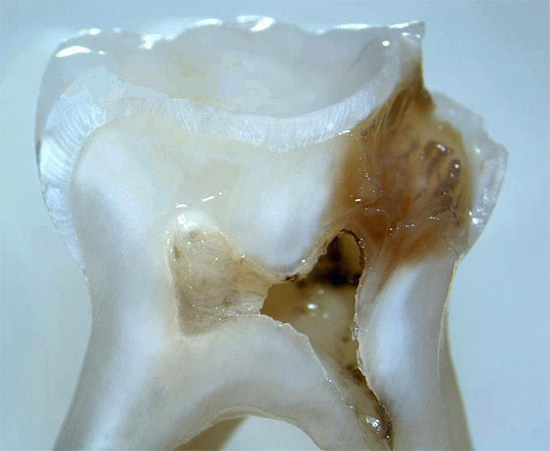
Unfortunately, short-term pain for many people is a great opportunity not to go to the doctor and wait a little longer. And they are really waiting for months - until the emergence of acute pain characteristic of pulpitis or periodontitis, when without strong toothache pills, there can be no longer a full life.
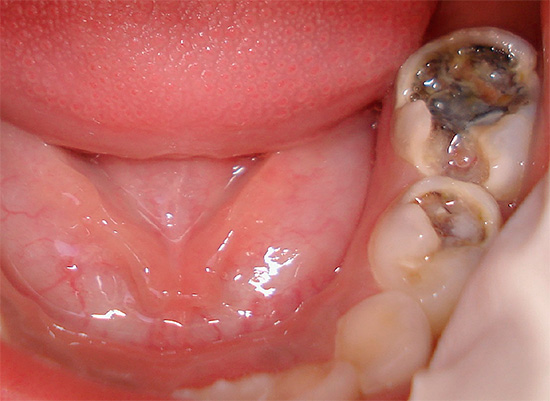
Photo of a tooth with a deep carious cavity, which led to the development of pulpitis:
Feedback
About a year ago, I felt that my lower molar tooth on the left began to break down and began to react strongly to the cold. I didn’t particularly hurt, so I didn’t go to the dentist, but after a couple of months, the tooth began to react to literally everything: candy, hot tea, milk from the refrigerator, and even fruit and chewing meat. According to these symptoms, I was diagnosed with deep caries and I was lucky that the treatment cost one visit. But the doctor warned me that after the treatment it was necessary to ensure that pain did not reappear in the tooth. Thank God, but he hasn’t been disturbed for a year.
Elizaveta, Pyatigorsk
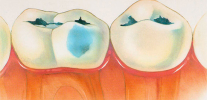
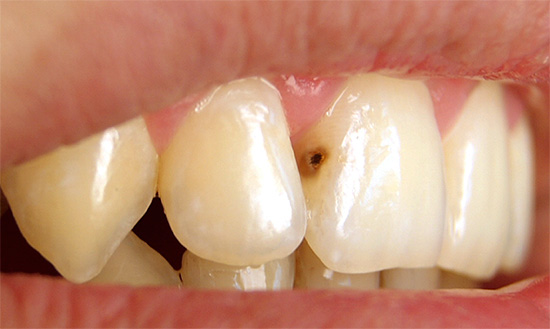
Photo of deep caries on the front tooth:
Self-diagnosis for correct diagnosis
If you want to make sure that the pain in your tooth is associated with deep caries, and not with something else, then you can try to conduct an independent differential diagnosis. First of all, you need to make sure that it does not pulpitis: with caries, the dental nerve is still intact, and with pulpitis, the bacteria have already made their way into the pulp chamber and slowly destroy soft tissues here. Accordingly, in the first case, the treatment will threaten only with the installation of a seal, and in the second, it will be necessary to remove the “nerve”, clean the canals, fill them, etc., that is, the procedure will be much more complicated (and expensive).
- In acute pulpitis, pain is acute and spontaneous (especially at night), that is, they arise on their own, unlike deep caries, in which pain arises only from external stimuli.
- With deep caries, the pain from irritants quickly passes, and with pulpitis, the tooth aches for a long time.
- At chronic forms of pulpitis the carious cavity can communicate with the pulp chamber, therefore, when food gets in, there are often severe pains that do not last for a long time.
Dentist advice
Of course, only a doctor should make an accurate diagnosis. However, since we undertook a self-test ... There is another way to make a diagnosis of deep caries: you can temporarily close the deep carious cavity with a cotton ball (if possible). If the pain disappears during the day or becomes insignificant, then you are most likely to have deep caries. In case of complications of caries (pulpitis or periodontitis), the pain after closure of the cavity from external stimuli with a cotton swab remains at the same level or even increases.
Modern diagnostic methods
At the reception at the dentist, you can make the correct diagnosis with 100% accuracy by applying various methods of differential diagnosis of deep caries.
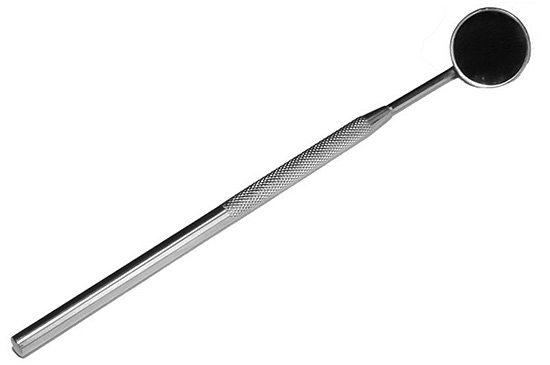
Visual diagnostics. It is perhaps the most common form of diagnosis and is carried out, as a rule, with the use of a dental mirror and probe. It estimates the depth of the cavity, its shape and the hardness of the dentin on the bottom and walls.
Usually with deep caries, the sensing is painful all over the bottom. The pulp chamber (the place where the dental “nerve” is located) has not been opened.In the acute form of pulpitis, probing is often painful only at one point, and in chronic forms, the pulp can even be opened, and the “nerve” can be bleeding painfully when probing.
The photo shows the tools used for the visual diagnosis of deep caries:

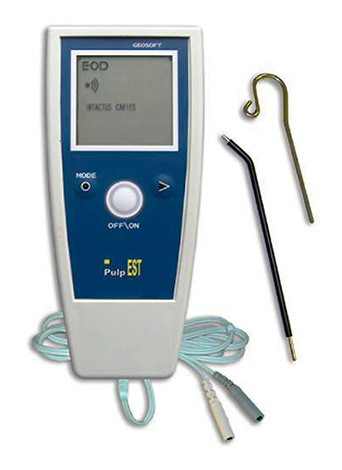
Electroodontodiagnostics (EDI) or, alternatively, electroodontometry. This method is a very informative way to determine the state of soft tissues inside a tooth using weak electric currents.
The doctor assesses the strength of the current to which the tooth reacts during the procedure. With deep caries, during the course of EDI, the tooth begins to react to current from 2 to 6 μA, less often - 10 μA.
In acute forms of pulpitis, the tooth reacts only at a current strength of more than 15-20 μA, and in chronic forms - more than 50-60 μA. A periodontitis tooth is sensitive to current from 100 μA and above. Electro-monitoring devices: for example, EOM-1, OD-2M, OSM-50, etc.
The photo below shows the device for EDI:
From the observations of the dentist
When conducting EDI deep caries, the value of excitability of the nerve is often determined by the strength of the current, equal to 15-20 μA. Generally speaking, this is a transitional form, when latent inflammations can begin in the pulp chamber, or they may not exist.In such cases, according to the caries treatment protocol, the doctor conducts all activities related to cleansing the carious cavity from necrotic tissue and does not put a permanent filling, limited to a temporary dressing without medication for up to 1-2 weeks.
The patient is warned that if the tooth is closed by a temporary filling, the next day will be sick, you should immediately come for the treatment of pulpitis. If the tooth does not react to anything over the period of the test, then on the next visit a permanent filling will be performed with a diagnosis of “deep caries”.
X-ray - allows you to find hidden deep carious cavities. The so-called contact X-ray is the most popular at the present time, when an aiming image is taken, covering 1-3 teeth. Such data can be obtained on modern devices - viziografah. For informational content, often problematic teeth (teeth) are increased in the images, which makes it possible to estimate the depth of the carious cavity.
The photographs below show an x-ray image of the teeth with a hidden deep carious cavity:
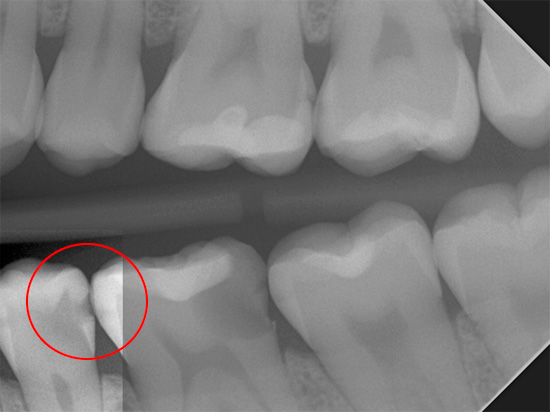
X-rays easily pass through tissues softened by caries, and a dark spot of a certain area is visualized in the image in proportion to the size of the carious cavity. The message of such a “spot” in a photograph with a pulp chamber almost always indicates inflammation of the “nerve” and the development of a complication of deep caries - pulpitis.
Methods for the treatment of deep caries and materials used in this
Treatment of deep caries has its own characteristics. The exceptional proximity of the dentin at the bottom of the cavity to the pulp chamber of the tooth requires the dentist to adhere to the following rules:
- Mandatory anesthesia (anesthesia) of the tooth. Without a “shot”, treatment cannot be performed, since the depth of the cavity and the proximity of the pulp cause different pain patterns when the tooth is processed with a drill, sometimes very strong.
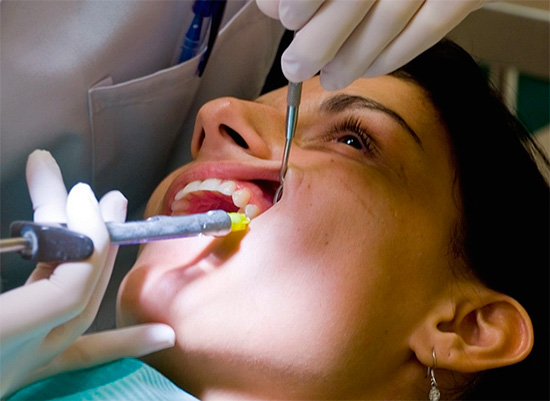
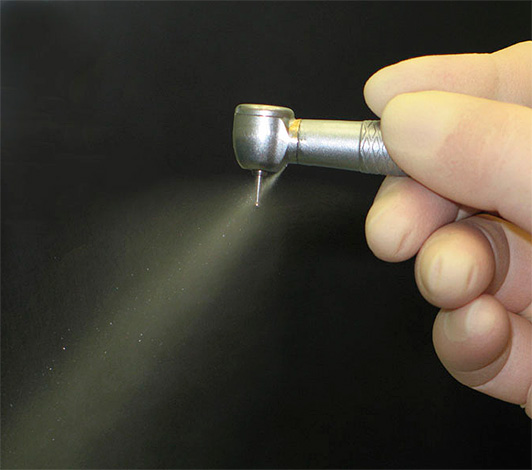
- Mandatory air-water cooling when processing a cavity with a drill. At the same time, a 4-channel turbine tip with improved water supply qualities should be used. Modern modified versions of tips have numerous channels for jet feeding of water to a tooth and even the possibility of lateral cooling of a tooth.The better the tooth cools when it is processed, the less risk that it will accidentally overheat, and in the future under the permanent filling complications arise.

- Treatment of the tooth with the use of special paste-pads to relieve possible inflammation, restore the layer of tissue (new healthy dentin) over the “nerve”, bactericidal effect and prevent complications of caries in the form of pulpitis. Most often, in the treatment of deep caries, therapeutic pads based on calcium hydroxide (Calcin, Calmecin, Calcipulpe, Dycal, etc.) are used. Eugenol based gaskets are sometimes used (zinc-eugenol cement, Cavitec, Eugespad, etc.). Rarely used combined formulations of drugs.
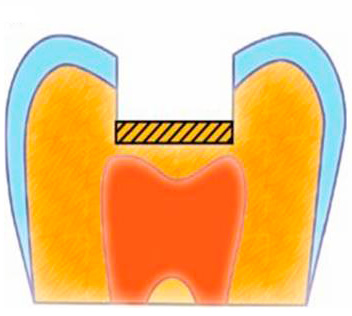
The main stages of carious cavity treatment with deep caries are:
- disclosure of the carious cavity and removal of the overhanging edges of the enamel
- cleansing from softened and infected tissues by hand or machine
- the formation of the cavity under the material that will be used for permanent fillings
- medical treatment of the formed cavity with weak antiseptic solutions (for example, 2% chlorhexidine)
- filling with pre-selected material.
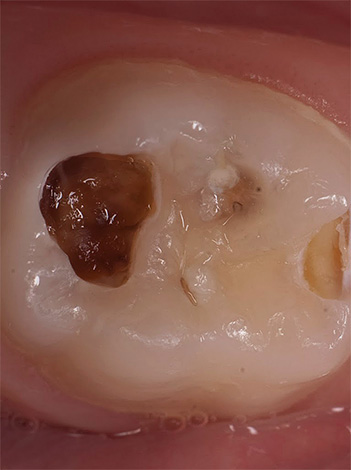
The photo below shows an example of an already formed cavity during the treatment of deep caries:
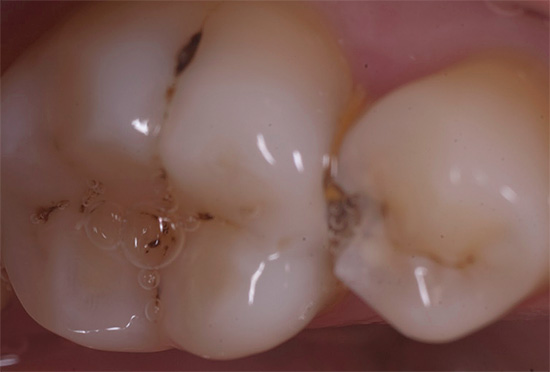
Opinion dentist
Currently, there are two different positions about the use of medical pads for the treatment of deep caries (pads are needed to protect the pulp chamber of the tooth from the toxic effect of filling materials). Many dentists are of the opinion that it is possible and necessary to install a medical gasket for the prevention of complications. Another dental school, as opposed to the first one, argues for not using medical pads, but to limit only to insulating materials (for example, based on glass-ionomer cements) and immediately put modern filling materials in one visit.
Most dentists do not deny the fact that it is not forbidden to put a medical pad with deep caries under a temporary seal for the required duration of treatment (from several days to 2-3 weeks), until its therapeutic effect has a positive role. And in the second visit, the dentist is already boldly delivering a permanent filling.
Modern materials used as fillings for deep caries:
- composites
- glass ionomer cements (limited)
- compomers
- Ormoker (organo-modified ceramics)
and some others.
Most modern materials suggest the use of glass ionomer cements (JRC) as insulating gaskets, since they emit fluoride for a long time in the tooth tissue, providing an additional anti-caries effect.
The deeper - the more expensive?
Currently, the pricing policy of most dental clinics is determined in many respects by the depth of carious lesions, since with deep caries more expensive material is consumed than, for example, with average. And some companies to determine the cost of treatment are guided only by the location of the deep carious cavity according to the classes according to Bleck (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5).
Most often, the emphasis is on the depth and area of the lesion, so the last stage of the carious process will have to be paid more than the first three. That is why the treatment of caries should be started not at the stage when it already threatens to develop into pulpitis, but when the first signs of the disease are detected (stain, roughness, the slightest pain).
Still waiting for the pill to relieve toothache again? In the meantime, the bacteria are getting closer and closer to the pulp chamber of the tooth, and after all they will ruin everything if they get there. So do not hesitate, and run to the dental clinic!
But what awaits you in the treatment of deep caries ...
Methods for the treatment of deep caries