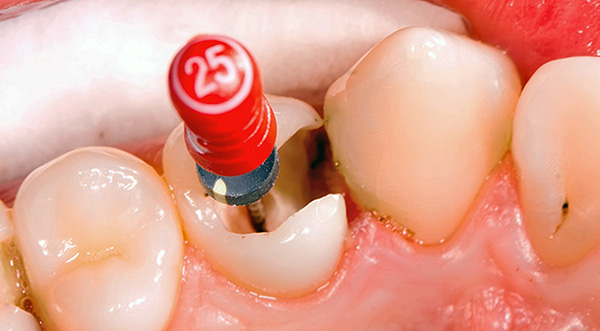
Often, after treatment of pulpitis, patients are surprised to find that the tooth continues to hurt - it hurts to press, bite, or it can even just whine without any external influences. It would seem that there is still sick - because the nerve is removed!
Unfortunately, post-filling pain after treatment of pulpitis is a frequent phenomenon, and not always the problem goes away by itself within a few days. Sometimes people suffer for months before finally realizing that excruciating pain will not disappear without medical help.
Let's see why such a problem may arise, what causes it usually causes and, most importantly, how to act in a given situation ...
Pain after treatment of pulpitis as a variant of the norm
It should be understood that treatment of pulpitis - The procedure itself is quite traumatic. Many experts draw an analogy with surgery, since the dentist-therapist first opens the tooth,after which it removes natural soft tissues from the pulp chamber (inflamed or necrotized neurovascular bundle), and then replaces these tissues with artificial filling material (so that there are no voids in the tooth in which bacteria could multiply).
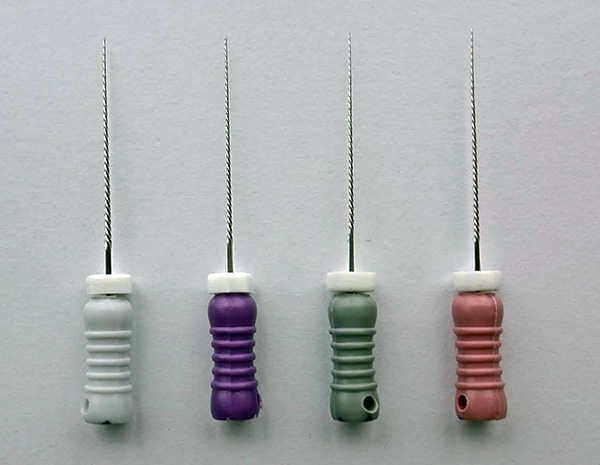
Since the roots of the teeth are long enough, the doctor uses special dental needles (so-called files) - each needle has a certain length and thickness, and is designed to clean the canals of the tooth from the remnants of the inflamed pulp. During operation, the needle is brought almost to the top of the root of the tooth, and sometimes it is also removed outside of it, injuring soft tissues adjacent to the root.

Read more about the procedure of removal of the dental "nerve" in a separate article: How to remove a nerve from a tooth and what problems may arise..
Also a mandatory step in the treatment of pulpitis is flushing the channels with fairly concentrated solutions of disinfectants, the classic of which is sodium hypochlorite solution.
All this is a kind of stress to the tissues surrounding the tooth, and recovery from injury requires some time. Each case is individual, but on average, the pain after treatment of pulpitis lasts no more than 5-7 days, subsiding day by day. All this time, the tooth is really painful to press or bite at it during a meal. In addition, in the first days after treatment, body temperature may rise, as the body's natural response to local inflammation in the background of injury.
The recommendations of dentists for this period are standard - use pain medication. However, doctors often do not say what to do to the patient, if the pain in a week has not passed and improvements are not observed.
The nuances that patients usually do not speak
If, after the treatment of pulpitis, the tooth hurts for more than a week, this is a reason to be alerted. Like other doctors, certain errors can occur in the work of the dentist, leading to complications, and such errors can occasionally occur even among doctors with 30 years of experience.
To better understand the essence of the possible causes of post-filling pain and the criticality of a situation for the future fate of the tooth, let's look at possible medical errors in more detail.
Overheating tooth tissue
In most cases, the removal of carious tissues of the tooth, for example, against the background deep cariesIt is carried out with the help of mechanical rotating instruments - burs (sometimes with a laser). During this procedure, there is a strong heating of both the tool itself and the hard tissues of the tooth.
If the workplace does not provide sufficient cooling of the working area with water (fortunately, this rarely happens), then there may be overheating of the soft tissues adjacent to the tooth and their thermal burn. Because of the anesthesia, the patient will not even feel this during the treatment.
Depending on the severity of the burn, pain after treatment of pulpitis can last an average of 7 to 14 days. For the further fate of the tooth is, as a rule, not critical.
The doctor did not cure all the channels of the tooth.
In endodontic treatment, the doctor needs to create access to all root canals of the tooth - to do this, you must find and open all of them. Different people in the teeth with the same sequence number may have different number of channels, and may also have different number of branches.
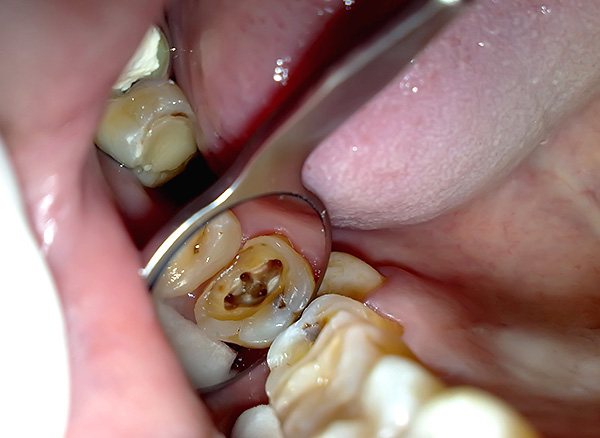
On a note
The anatomy of the root system of a tooth can be compared with a tree.In the roots of teeth, pulp fills special channels, and, as a rule, their number corresponds to the number of roots, but often there are additional channels.
Root canals have an orifice (beginning) communicating with the crown, and an apical part (on the final root segment), on which there is an anatomical hole - the tip, through which communication with the surrounding gum and jaw bone tissues takes place.
So, it is unacceptable to leave at least one channel with the infection inside. It should be understood that in this case the inflammation center will not go anywhere - it will remind of itself after the treatment of pulpitis, that is, the tooth will hurt. Night pain may not be, but it will take a long time to bite on a tooth, and pathology can turn into a chronic form to form cysts on the tooth root.
The photo below shows a distant tooth with a cyst on the root:
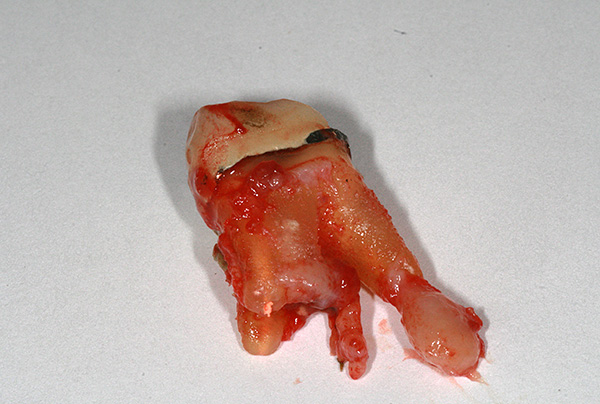
Leaving such a focus of infection without treatment is impossible, that is, in this case, the problem is crucial for the future fate of the tooth. An untreated tooth canal left untouched will sooner or later force the patient to see a doctor, and sometimes the only option is to remove the tooth in the face of exacerbated periodontitis.
Break off the tool in the channel
Breaking off in the channel of a dental instrument (a piece of a file is usually broken off) is one of the most unpleasant complications of treatment for both the doctor and the patient. Leaving the tool in the channel, if not removed, is fraught with an unfavorable forecast - tooth extraction in perspective the next few years.
In addition, after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth can last for a long time - up to several weeks (although in some cases the pain can go away within normal periods, in just a couple of days, but this still does not indicate the absence of infection in the area of the broken instrument).
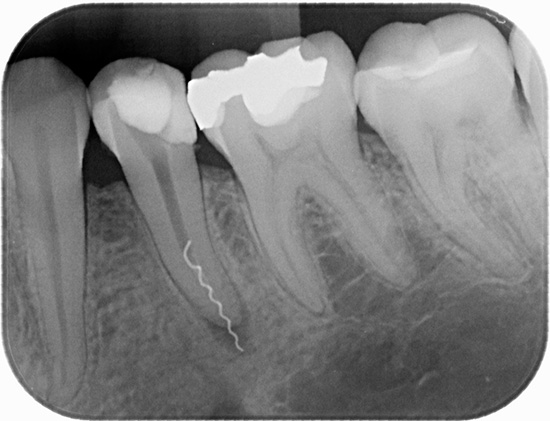
Why does the dental file used to clean the channels sometimes break? The most common reasons for this are:
- Application of excessive force when working with a file;
- Non-compliance with the principles of working with the tool - certain angles of inclination of files;
- Too long work with already deformed tool. Each file is designed for a certain number of manipulations, but sometimes doctors neglect this, in time without changing the file to a new one when processing the channel.
If the file is broken at the very beginning of the channel processing, then it is not so bad, because the doctor can relatively easily remove the broken part with the help of special ultrasound tips. If the file is broken closer to the end of the channel, then the fragment can be very difficult to get.
On a note
The use of a dental microscope helps a lot with this work, but not all clinics have such equipment. Therefore, the doctor sometimes technically can not extract a piece of the file from the canal, and is forced to seal it as it is - that is, with a fragment inside the canal (not everyone is willing to admit his mistake, plus the inability to correct it, sending the patient to another clinic).
The photo below shows a piece of the instrument extracted from the root canal:
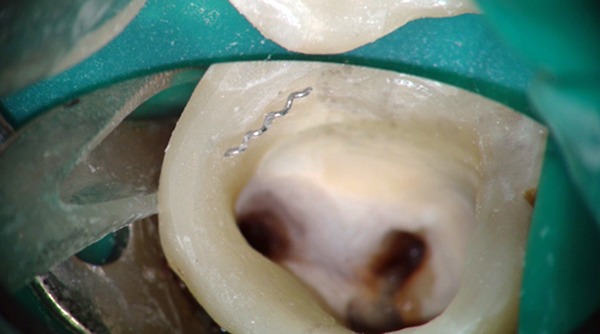
However, it’s still necessary to get the debris, because the part of the tool remaining in the channel blocks a certain segment of the root and does not allow to complete its processing - a non-treated infection site is formed, which can lead to tooth extraction in the future.
The output of the filling material for the top of the tooth root
A modern and widely used material for canal filling is gutta-percha pins. They correspond to the labeling of the files with which the canal is prepared, and are fitted to the length of the root, very little before reaching the anatomical opening of the outlet to the underlying tissues.
On a note
Gutta-percha is a natural resin, similar in chemical composition to the composition of natural rubber. Its molecular chain is longer, so it is less plastic than rubber. It is widely used as a non-absorbable filler for filling root canals.
Another variant of the filling material is various pasty cements, which harden inside the tooth canal after a short time.
In dentistry, they use bioinert materials, that is, they are assumed to be harmless to the body. However, if the filling material is brought out of the root, it can cause inflammation of the surrounding tissues - like a splinter in the finger.
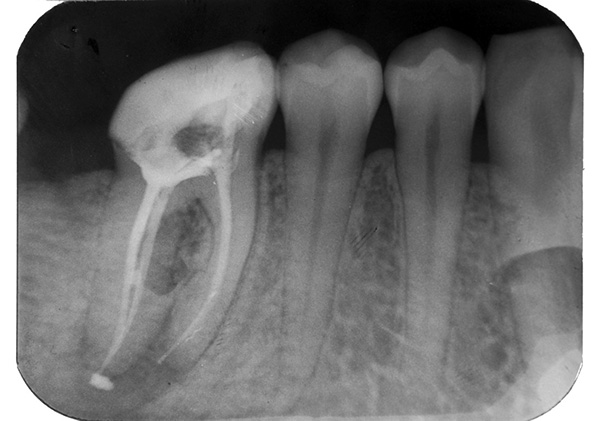
In case of excessive removal of filling material for apex, post-filling pain can be very long. Sometimes pain when pressed on a tooth can persist for months.
In such cases, the tooth must be re-cured, because if the error is not corrected, the problem may not completely disappear and within six months (in addition, a cyst may form at the root).
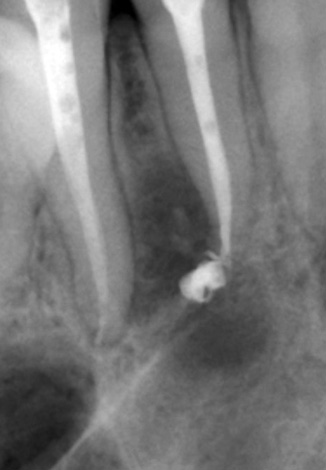
Feedback:
"Hello! Six months ago, she treated pulpitis, removed the nerve in the 12th tooth. When the anesthesia was gone, there was severe pain. In the picture, the outflow of the root is approximately 2 mm beyond the root. A month and a half later, hell was unzipped. The pain was a little less, but not to such an extent that it could be tolerated.
For the next 3 months, calcium was set and washed. The pain algorithm was the following: when the procedure was performed and immediately after it was carried out there was severe pain for 7-10 days (it was impossible to eat, eat and drink through the straw, it was impossible to touch the tooth). Then the pain subsided a little, for 5-7 days, and then again increased in intensity. So it goes 3 weeks, they wash me again, put calcium. All the same, in the same scenario.
Replaced the doctor. The new doctor decided to replace calcium for the fourth time and put more iodoform. For 4 times the pain was less than for all these times of treatment. But it didn’t go completely ñ neither chewing nor biting was possible, that is, the pain remained anyway, but it could already be tolerated. In general, the tooth did not stop hurting.And the doctor decided to put on a gutta-percha and a permanent filling anyway. Put. And as in the usual scenario: the first 7 days - it hurts a lot, then less than a week, and then the pain increases again ... "
Olga, Moscow
And this is just one example of the many cases in which post-filling pain after the treatment of pulpitis when removing filling material for the root tip lasts a very long time.
Fracture of the tooth root
Fracture of the root of the tooth is a rare and difficult to diagnose complication of endodontic treatment (it is not always possible to recognize it on a regular X-ray). Root canals can be sealed according to all the rules, but sometimes during work, a microcrack can occur at the root, which can only be seen on CT.
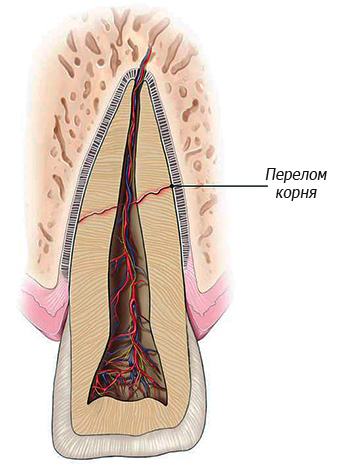
Fracture of the tooth root in most cases is an absolute indication for tooth extraction.
By the way, the removal of the tooth root is not a pleasant procedure. You can read more about it, as well as visually see some moments in the photos in this article.
In very rare cases, a root fracture can be cured with the help of various techniques of bonding fragments together. But this is not always feasible.
The fracture does not heal itself, and inflammation of the soft tissues soon forms around it. It is impossible to chew on such a tooth, the slightest strain will cause severe pain.
After treatment, pulpitis painful bite on the tooth
In all the above-described cases, after the treatment of the canals of the tooth, pain can be observed when biting on the tooth, and sometimes it even creates the feeling that the entire side of the jaw is in pain.
In rare cases, against the background of acute pain, a sensation may arise that the tooth has begun to move out of the gums. In dentistry, there is even a term - “the feeling of a grown tooth”. A similar sensation arises in patients due to periodontitis - a disease that is a complication of pulpitis (inflammation and suppuration of the tissues adjacent to the tooth root occur).
If we talk about the acute phase of the disease, the pain during chewing will be very strong, it can also "itch" and hurt the gums for a long time around the tooth. If the process is chronic, then these feelings will not be so pronounced. Periodontitis can develop in the absence of treatment of pulpitis, and (in much rarer cases) after improper treatment of pulpitis.
Oversize the seals - what will happen if nothing is done?
The dental system is very sensitive to any changes in it, so even if the doctor has treated the pulpitis according to all the rules and with minimal trauma to the tooth tissues, discomfort and even pain during biting due to filling is still possible for the time being, as for fillings on the chewing surface molars.
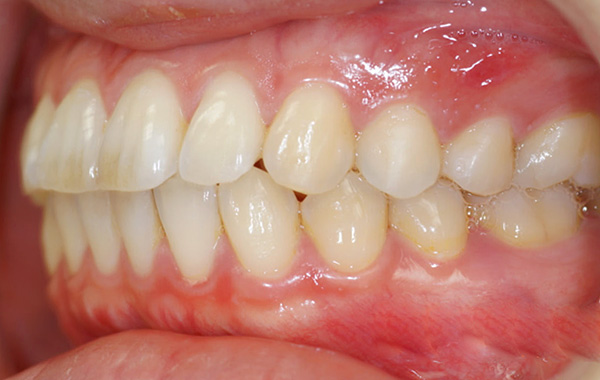
After treatment, the teeth sometimes close in slightly different, not quite familiar. The feeling of discomfort from a new filling can normally be from 5 to 7 days.
If the patient feels discomfort longer than this time, if the tooth interferes in the bite and there is a feeling that it is higher than the rest of the teeth, then without the intervention of the doctor this can lead to various problems - ranging from loosening the tooth itself (since it has an increased load) and ending with problems with the temporomandibular joint.
Here are some possible consequences of excessive overestimation of the bite fillings, which sometimes arise with time:
- Difficult, painful opening of the mouth;
- Pain when chewing (in some cases, the pain may be given to the ear);
- Clicks in the jaw joints when opening the mouth;
- Accelerated erasing of individual teeth;
- Regular headaches.
- Constant stress on the tooth can also cause traumatic periodontitis.
On a note
In most clinics today, dentists use light-cured materials for dental fillings. This is due to their high strength, durability and aesthetics. Seals from such materials are not erased for a long time when chewing, so you should not expect that the seal will soon be erased, and the problem will disappear by itself. Correctly remove the excess fillings in height can only be a doctor using a drill.
After treatment, pulpitis swollen cheek
Here it is important to understand that the swelling of the cheek that occurs after the treatment of pulpitis is a clear sign of inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the tooth (and sometimes in addition of the jaw bone). This condition may be accompanied by general malaise and weakness, a rise in body temperature, inability or difficulty in eating because of severe pain.
Normally, swelling of the cheek after endodontic treatment is not observed at all. The temperature can actually rise (up to 38-38.5 degrees), however, if severe edema is observed at the same time, high fever and pain in the treated tooth are a warning sign.
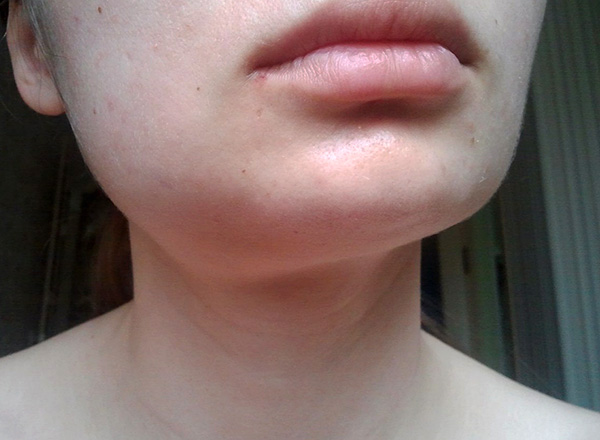
Such situations are quite dangerous, so do not wait and lose time, believing that the next day the swelling will resolve and the temperature will pass. This may not happen, moreover, the situation can significantly and rapidly worsen (up to phlegmon - deadly spilled purulent inflammation). Therefore, an immediate appeal to the doctor at least for reinsurance and inspection will be the most appropriate solution.
In no case should the swollen cheek be heated, it will only worsen the condition. Also, do not sleep on the side of the swollen cheek, so as not to aggravate the swelling.
If you notice a "pimple" (abscess) or fistula on the gum, near the place where the treatment of pulpitis was performed, it cannot be opened or cleaned by yourself. It is necessary to consult a doctor again and correct the treatment (most likely, a center of inflammation appeared on the root of the tooth, and pus, by melting the gum tissue, made its way into the oral cavity).
As you can see, the possible causes of tooth pain after treatment of pulpitis can be many, and without additional examination it is usually difficult to say what exactly is the source of pain.If the pain does not pass more than a week from the moment of treatment, or there is significant swelling of the cheeks, or other complaints that were not there before the visit to the doctor - in such cases, you need to go for a second appointment to clarify the situation.
Why a toothache hurts after canal treatment: comments by a dentist
Useful video about the appearance of toothache after tooth filling