Surprisingly, many parents are still convinced that the milk (temporary) teeth in a child do not have to be treated, unlike permanent ones. Irresponsible moms and dads claim that they do not cure caries in their children only because these teeth will soon fall out anyway. There are frequent cases that do not heal promptly and pulpit milk teeth, even despite the strong pain in a child.
Such an idea of the optional treatment of milk teeth is absolutely wrong, moreover - this is a very dangerous ignorance!
Pulpitis temporary teeth in children in most cases develops on the background untreated caries. When the baby tooth begins to hurt, the child experiences no less agony than adults with pulpitis of permanent teeth. Sometimes parents are looking for ways to help the child with improvised methods, most often with “chemistry” (pain pills), which often simply do not help, but most importantly - they do not solve the problem itself.
Depending on the immunity of the child, pulpitis in the baby tooth without adequate treatment can turn into complications (periodontitis, periostitis, and others) both in a few months and in a day. There were cases when the baby died from complications of pulpitis due to blood poisoning, when it took only a few days from the first pulping toothaches to severe swelling of the face and the subsequent death.
To avoid serious problems, it is necessary to treat caries in children in time, but if you have already tightened and pulpitis started - you should treat it immediately, do not suppress pain with pills and wait until the tooth deigns to fall out by itself.
Symptoms of acute pulpitis of milk teeth
In children acute pulpitis in milk teeth is less common than chronic, but it shows itself more aggressively than in a constant bite. The acute form is subdivided into serous and purulent stages, which determine the condition of the baby, the nature of the pain, and the intensity and duration of the attacks.
Acute serous pulp of the baby tooth is similar in clinical picture to acute focal pulpitis in permanent teeth. As a rule, the first pain occurs at night.Often a child complains of pain during a meal.
In acute serous pulpitis in the pulp tissues an inflammatory process develops, leading to oxygen starvation (hypoxia) of the pulp. As a result, a so-called serous exudate or serous fluid appears, which fills the channels.
In such cases, the pain is often one-time in nature, affecting temporary teeth with unformed or absorbable roots. Already after 4-6 hours after the first painful episodes appear, the acute serous pulpitis passes into a purulent stage, which almost always makes caring parents turn to a pediatric dentist.
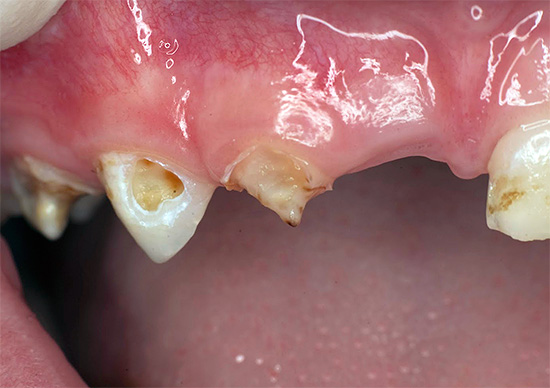
The severity of the purulent form of pulpitis, as well as serous, is largely determined by the formation of the roots of the baby tooth, the reactivity of the child’s body (immunity), the activity of the microbes causing inflammation of the “nerve” inside the tooth and some other factors. For example, sometimes the pain is not pronounced, if the child has a good immunity, the microbes inside the tooth are weakened and there is pus output through large carious cavitywhich communicates with the pulp chamber
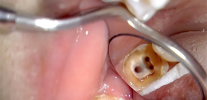
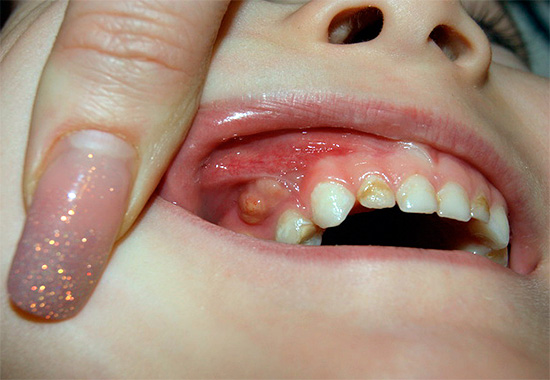
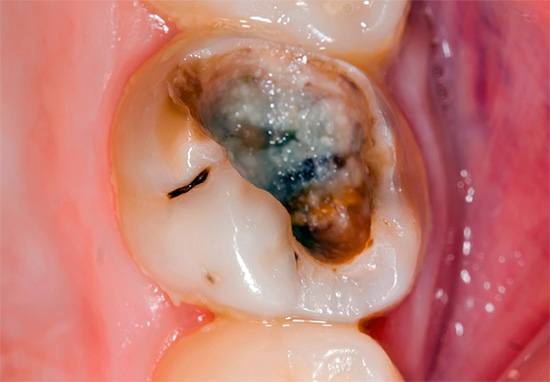
The photo shows a pulpit milk tooth with a deep carious cavity:
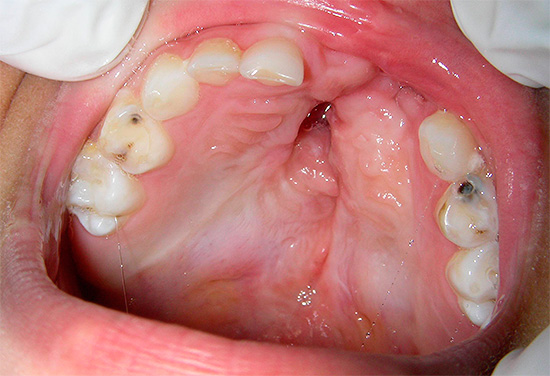
However, most often the clinic purulent pulpitis is bright. It is not similar to the clinic of the acute form of pulpitis in an adult, and often occurs with characteristic signs of periodontitis: fever, purulent exudate in the canal, severe pain during chewing.
Among symptoms severe prolonged pains with short intervals between attacks prevail. Often, an acute pain attack in a baby tooth occurs during a meal due to temperature fluctuations. Sometimes the baby can not specify exactly what kind of tooth hurts, as the pain can give to the adjacent teeth, to the upper jaw.
If parents do not go to the dentist in time for the treatment of pulpitis of the baby tooth, then the child's general state may gradually deteriorate: the temperature rises, sleep is disturbed, the baby may refuse to eat because of constant pain. Touching a tooth can be very painful, the gum around it also becomes painful.
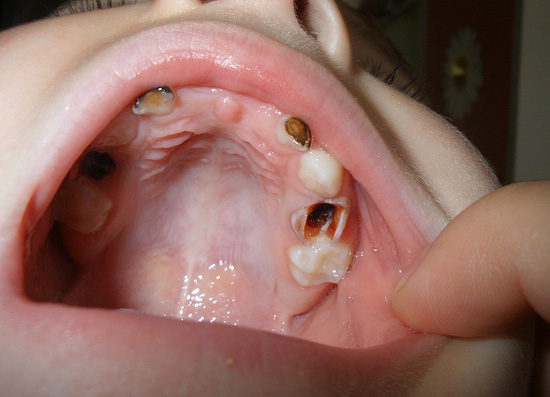
From the practice of the dentist
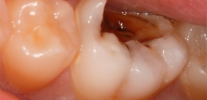
When they come to the reception with pulpic pain, there is almost always a deep carious cavity in the milk tooth. Sensing its bottom and extracting softened carious dentin can be very painful.At the opening (with or without anesthesia) of the layer that closes the “nerve”, a drop of pus is released from the cavity, but there may still be live pulp in the depths. At the same time, it often bleeds painfully.
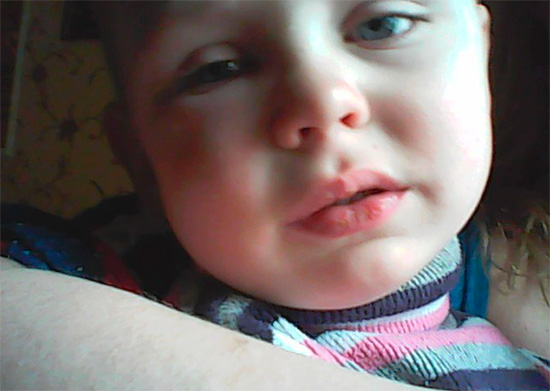
Acute purulent pulpitis is sometimes complicated by periodontitis, lymphadenitis, and also periostitis (“flux”), and often in a very short period of time, sometimes within a day. Some of these complications are often accompanied by severe intoxication, when all the systems of a weakened child’s body suffer and even the death of the baby appears.
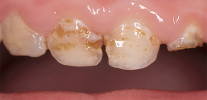
Photo of the flux on the child's gum:
Traditional approaches to the treatment of temporary pulpitis in children
Given that acute pulpitis of a baby tooth is such a state of inflammation of the “nerve” that can lead to very tragic consequences, the first priority of treatment is to eliminate such risks. On the one hand, the removal of the tooth is the easiest, but the removal is almost always a trauma for the fragile psyche of the baby, it is a surgical operation and, in the end, possible violations of the permanent bite in the future.
Let's look at how baby teeth are treated for pulpitis in children's dentists in some budget organizations: hospitals or clinics at the place of attachment.For the treatment of pulpitis of temporary teeth, there is still used an antediluvian method of devital amputation, which, however, is still popular in some private clinics.
This method is to some extent sparing for the child's psyche, since it does not require the impact of tools on the canals of the milk tooth. Instead, the first visit to the opened “nerve” is placed arsenic paste for a period of 24 to 48 hours, or devitalizing paste that does not contain arsenic, for up to 7 days or more.
During the second and subsequent visits (1-2), “pumping” into the beginning of the canals of the milk tooth with a killed pulp of resorcin-formalin mixture, and then paste. The paste effectively mummifies the infected pulp, thereby preventing its putrefactive decomposition. Usually in the third or fourth visit a permanent filling is established on a temporary tooth.
On a note
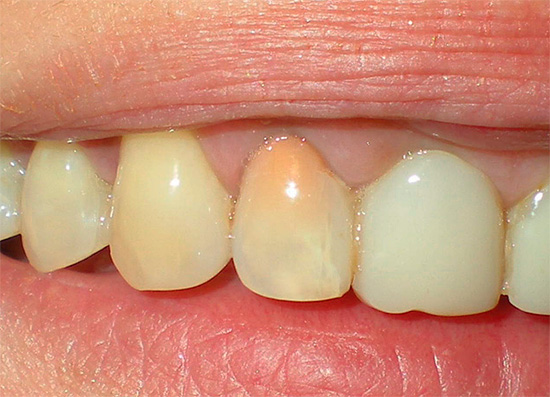
Almost every dentist in Russia has directly or indirectly encountered and often continues to experience results. treatment of pulpitis in adults and children using the devital method, during which resorcinol-formalin paste was used.After such treatment, the teeth after some time are painted in any shade of red: from pink to dark red and brown.
Due to the fact that over the years, this paste creates a "plug" in the canals of permanent teeth, it is almost always difficult to re-condition such a tooth or it is not possible. Dentists-surgeons who specialize in removal, encountering such teeth, warn patients in advance that there are serious risks of a complex and lengthy removal, as the resorcin-formalin paste, in addition to the “narrowing of the canals” for a long-term existence, also coats the root of the tooth with the surrounding his "bone". Often in such situations, the root of the tooth crumbles and leaves the hole in small pieces.
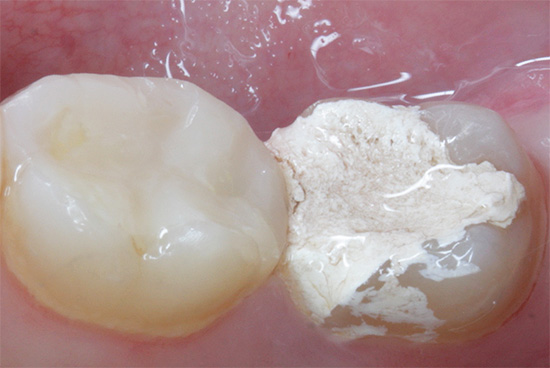
The photo shows what a permanent tooth looks like already in an adult a few years after the treatment of pulpitis using resorcin-formalin mixture:
Modern methods and means of treatment of milk teeth pulpitis
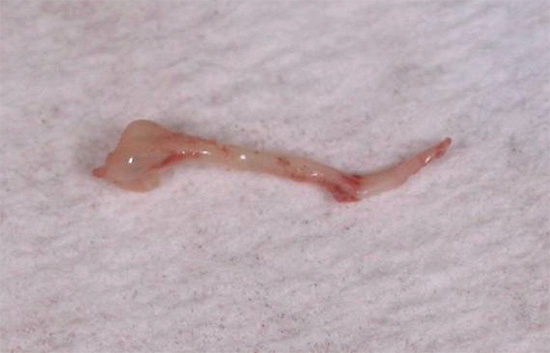
For calm children who can withstand long-term treatment of pulpitis of milk teeth with formed roots, vital or devital extirpation is used (treatment in two or three visits).In the first case, the “nerve” is immediately removed from the canals, and during devital extirpation, the devitalizing paste is first placed on the exposed pulp on the first visit to kill it.
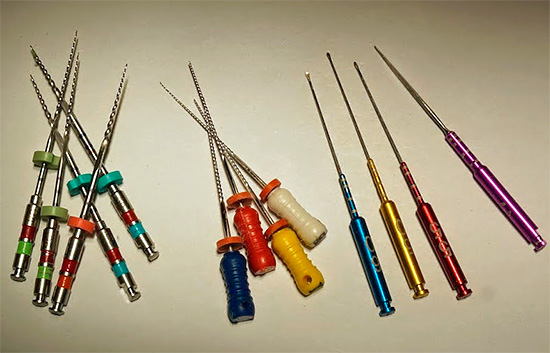
Photograph of a removed dental "nerve":
After a thorough mechanical and medical treatment of the canals of the milk tooth with the extraction of infected pulp and the creation of sterility, the canals are sealed with a paste that has an anti-inflammatory effect and with time absorbs with the roots when changing a temporary tooth. Pediatric dentists often use zinc-Eugenol paste as a root filling, but the paste that foreign colleagues prefer Magipex has also recommended itself well.
Studies have shown that only a good cleaning of the root canal system leads to a normal result, keeping the milk tooth from re-activating the infection in it until the physiological change. However, there is a mass of supporters of an equally effective and modern method: vital amputation, which involves only partial removal of the upper (coronal) part of the “nerve”, and a special medicine is installed on the root pulp.

Previously used preparations based on eugenol paste and calcium hydroxide have been successfully replaced with Swiss-made Pulpotec (Pulpotec) and its Russian counterpart Pulpodent (VladMiva), which have a long-lasting anti-inflammatory, antiseptic effect and hermetically closes the root stump of the pulp.
On a note
Pulpotek powder contains iodoform (strong antiseptic), polyoxymethylene (for surface protein denaturation) and zinc oxide, and liquid - dexamethasone acetate (anti-inflammatory effect), formaldehyde (antiseptic and mummifying action), and also phenol and guaiacol antiseptic.
The drugs can not only keep the root pulp in a viable state, but also prevent the development of pain during and after treatment. Unlike resorcin-formalin paste, Pulpotec and Pulpodent do not stain the tooth and are not so toxic for the body, reducing the number of visits to the child to a minimum.
The specificity of the treatment of pulpitis of the milk tooth with unformed roots
In order to better understand how to treat pulpitis of a baby tooth with unformed roots, you should first understand the terms.Unformed roots are the roots of a temporary tooth that have an open tip after the eruption of a baby tooth. The complete formation of the roots usually lasts several years, as well as their resorption during physiological change of teeth.

If an infection from the carious cavity enters the pulp chamber, pulpitis can develop, which should be treated immediately in order to avoid the development of complications that pass to the germ of a permanent tooth.
A feature of the choice of the method of treatment of pulpitis in the case of unformed roots is the impossibility of using methods of extirpation, that is, the complete extraction of the pulp and the processing of the channels along the entire length of the root. That is why children's dentists prefer biological and amputation treatment methods for such cases.
Let us first consider the biological method of treatment of pulpitis of the primary tooth (conservative). This method involves the preservation of the entire pulp in a viable state, however, it has many contraindications and requires adherence to an ideal aseptic and antiseptic during operation, in order to avoid repeated pain.
First, under anesthesia, the carious cavity is cleaned of necrotic tissue, and medical paste (usually based on calcium hydroxide) is applied to the bottom of the cavity or directly onto the exposed pulp for several days. After the cessation of pain, a permanent filling is placed on the milk tooth.
Due to the biological method of treatment, the tooth remains alive, that is, the stored pulp allows you to supply its tissues with nutrients, maintaining high strength. But the tooth with the removed “nerve” becomes more fragile over the years and prone to breaking off the walls bearing the seal.
Amputation methods for the treatment of pulpitis of milk teeth with unformed or resorbable roots are very popular among dentists. The essence of such methods follows from their name - infected pulp is simply amputated, removing from the pulp chamber.
At the same time, “ancient” methods of devital amputation by the resorcin-formalin method, as well as modern vital methods (under anesthesia and without arsenic) amputation techniques with a therapeutic coating of root pulp with antibiotics, enzymes, calcium-containing preparations, etc., can be used.The pulpotec and pulpodent drugs are also suitable for the treatment of pulpitis of milk teeth with unclosed root tips.
On the photo - arsenic containing temporary filling in the tooth:
It is interesting
Devital amputation is a method of treating pulpitis, initially involving the “killing” of the pulp and then its mummification with potent and often toxic pastes. To cure pulpitis with this “old” method, you need not one visit, but three and even more. Long-term results, taking into account many years of experience with this method, are often negative.
Possible errors in the treatment and how they threaten the child
During treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth in children, medical errors are more common than in adult dentistry. This is due to the specifics of the children's reception, when the child often prevents the doctor from carrying out all the necessary manipulations with due accuracy and in full. To minimize the severity of errors and for violent children, pediatric dentists may resort to a devital amputation by the resorcinol-formalin method, since in another way the child simply does not allow to save the baby tooth before its physiological change.

In pediatric dentistry, in the treatment of pulpitis of a baby tooth, there is, for example, such an error as an incorrectly set paste for pulp devitalization. The most difficult result of such an error is transferred if the paste is arsenic. If the child does not allow the tooth to be processed with high quality, then it is put by the doctor not on the opened “nerve”, but on the soft bottom of the prepared cavity, because of which often not only does not work, but also causes even more severe pain. Emergency care in this case is setting the paste again.
There are cases when the devitalizing paste is placed next to or directly on the gum, since in children the carious cavity is often occupied by an overgrown gum or close to the gingival papilla. This results in severe pain, and on arrival of the child to the doctor, a burn caused by the components of the paste is detected on the gum. Prevention of such a complication is the observance of the technique of setting the paste, and when receiving a burn it is required to prescribe anti-inflammatory wound-healing gels or pastes.
During the canal treatment in the baby tooth, pulpitis may cause bleeding due tothat root tips may not be formed or have already been slightly resorbed, and the dentist may forcefully move files outside the root to process the canals (special needles), injuring adjacent tissues. It is difficult to stop bleeding even with special preparations.
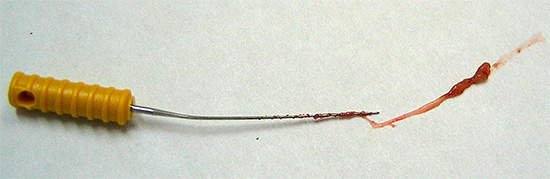
Sometimes an inexperienced doctor can make such mistakes as root perforation and tool breaking off in the tooth canal. Since the canals in the milk teeth are almost always very wide, the percentage of such complications is very low, but the severity is the same as in the case of permanent teeth in an adult. As a result of perforation of the tooth root and breaking off of the instrument in the canal, periodontitis or periostitis may later develop due to inflammation of the tissues around the root.
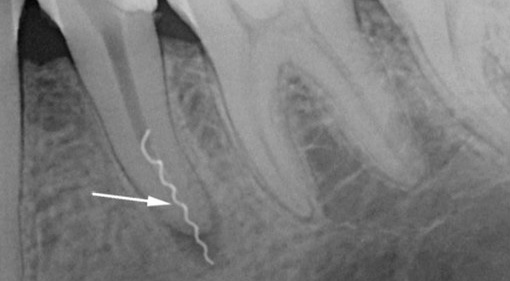
To prevent these complications, the pediatric dentist removes a piece of the instrument from the canal in an affordable way, and perforations is covered with a special material, for example, “ProRoot MTA”. In some cases, in the absence of the necessary equipment and materials, the doctor simply mummifies the channels with the resorcin-formalin method.
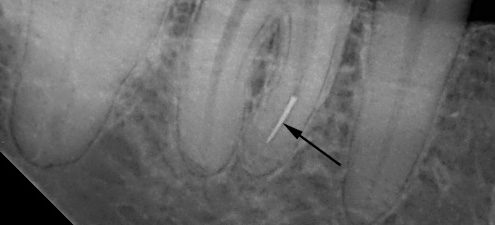
The photo shows an example of a tool broken off in the canal of a tooth:
How to prepare a child for treatment
In order for a child not to be afraid to treat his teeth (even with severe pain during pulpitis), it is necessary to carry out the first preventive visit to a pediatric dentist long before that. The success of the first visit depends equally on the dentist and the parents of the baby.
The visit should be exploratory in nature. During it, the child gets acquainted with the new situation of the office, the tools, showing only curiosity, not fear, but even preparation for such a visit is required.
Before going to the dentist follow the following recommendations:
- talk to your child before a preventive visit in 1-2 days before he hears “horror stories” from peers;
- tell your child only positive impressions;
- Do not emphasize the importance of the event, because taking care of your health is a normal procedure;
- tell about the future visit to the dentist, as about meeting a new friend;
- play "in the dentist" with the whole family: set an example that you are not afraid of the doctor yourself;
- Do not use scary dental words;
- Do not deceive the child that it will not hurt, it is better to say that it may be unpleasant at first, but then the tooth will not hurt;
- do not experience fear and panic yourself, then it will not be transferred to the baby;
- The best option for a visit to the dentist is the morning when the child slept well, ate well and is active;
- It is better if you go to the dentist with your favorite toy so that the child constantly pulls something in his hands;
- let the doctor find contact with your child without your help;
- if the child resists, interferes with the reception, then you should not intimidate, threaten, beg, etc.
- you should try to win the trust of the child, so if the situation is out of control, then it is better to postpone the appointment for the next time.
If a child is initially uncontrollable and anxious, often falls into hysterics, then he should be prepared with medication, relieving him of the upcoming stress. For this ideal non-prescription drug Tenoten Children's. 20 minutes before the treatment of caries or pulpitis of milk teeth, give the child one tablet under the tongue for resorption.
Under high or moderate stress, Tenoten removes tension, causing inhibition of mental processes. As a rule, after 20-30 minutes, the child gives all the necessary manipulations.
To make the child feel comfortable in the dental chair, you need to early age start an appeal to the dentist for the purpose of prevention. With an adequate level of hygiene, timely preventive examinations and quality control of teeth cleaning, you can avoid not only pulpitis, but also caries, and save the baby's teeth before their physiological change.
Interesting video about the importance of the treatment of pulpitis of milk teeth
Some more helpful clarifications from the doctor regarding pulpitis of milk teeth.