In simple terms, the distal bite is such bite anomaly, in which the teeth of the upper jaw are strongly pushed forward in relation to the teeth of the lower jaw. Well, if expressed by the language of orthodontists, distal bite is considered, in which the first molars of the upper and lower jaws close in the second class of Angle, that is, the reduced lower jaw is located behind the dominant upper jaw.
Generally speaking, such an arrangement of jaws is not a rare occurrence, and occupies about 30 percent of the prevalence among the European population of the Earth.
Let's see what, in fact, distal occlusion is bad, what are the reasons for its occurrence, and whether it is necessary to engage in general prevention of the development of distal occlusion and treatment, if it is already formed ...
Types of distal bite and problems created by it
First of all, it should be borne in mind that the distal bites are, so to speak, different - respectively, and the problems in people with this anomaly are also different.
When diagnosing distal occlusion, orthodontists distinguish two subclasses: the difference is due to the position of the front teeth, namely the incisors, and the inclination of the incisors often greatly influences the course of the pathology and the treatment tactics of the patient.
For example, in the first subclass of the distal occlusion or, as it is also called, the horizontal type of the distal occlusion, the incisors of the mandible rest with their cutting edges on the palatal surfaces of the upper incisors, which, in turn, are inclined towards the upper lip.
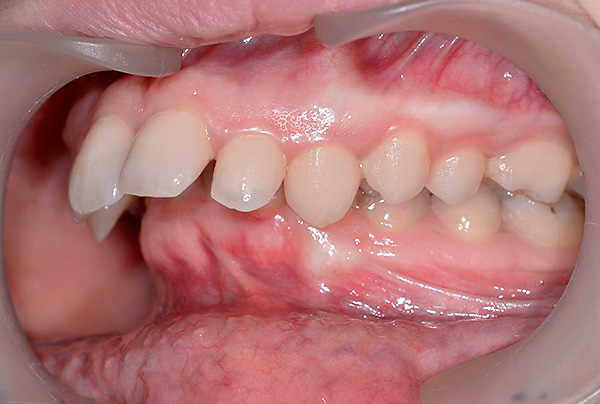
In grade 2, subclass 2 or, in other words, a vertical type of distal occlusion, the cutting edges of the lower incisors rest against the palatine tubercle of the upper incisors, while the upper central incisors are inclined towards the oral cavity. Sometimes the upper front teeth rest against the gum, as a result of which they injure it (traumatic bite).
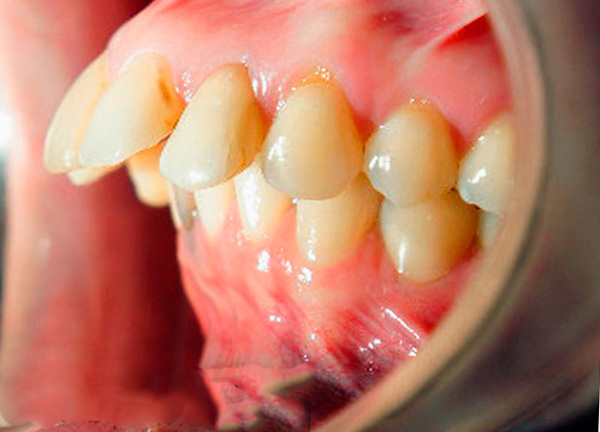
The inclination of the incisors affects not only the shape of a person’s face, which can eventually become far from normal, but also the specific problems that often accompany the distal occlusion.
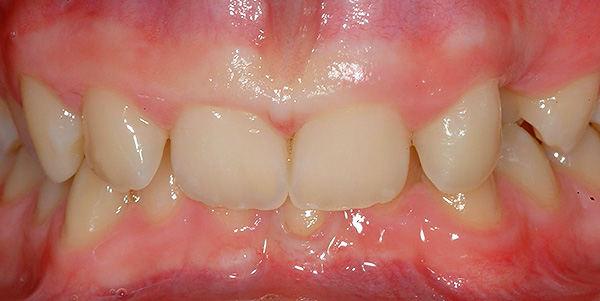
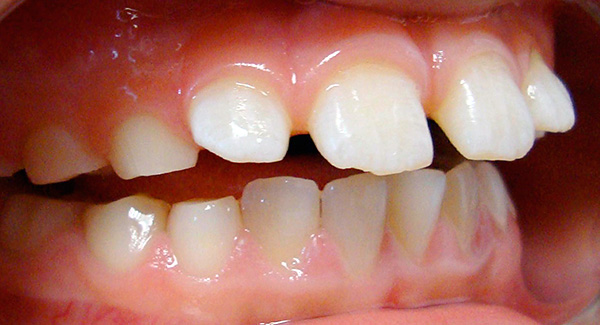
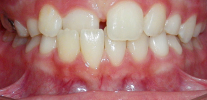
For example, the formation of an open bite in the front section (first class II subclass), that is, when the upper front teeth protrude forward, leads to violations of sound pronunciation, difficulty in eating, and sometimes to problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
The photo below shows an example of an open bite:
In the second subclass of class II, the situation is reversed: a deep bite is formed in the anterior section, that is, the front upper teeth sink inward. Patients mark a lisp, in some cases, children complain of injury caused by lower incisors when in contact with a soft palate - such wounds do not heal for a very long time, as soft tissues are permanently injured when chewing.
Among other common problems accompanying the distal occlusion, patients note problems with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ): pains when opening the mouth, pains during chewing, headaches, crunching and clicking in the joint. These disorders of the joint arise from the incorrect position of the head of the mandible in the articular fossa, the compression of the articular ligaments, the overstressing of the masticatory muscles. Over time, with inadequate treatment, the symptoms may progress, forcing the person to resort to regular pain medication.
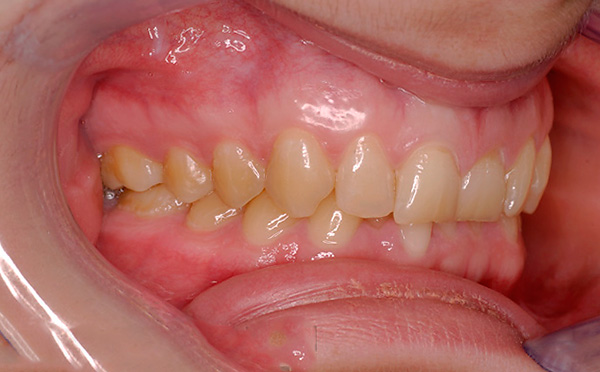
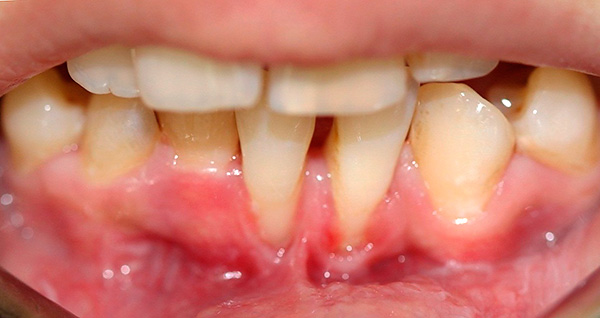
Gingival recession and wedge-shaped defects are also frequent consequences of the distal occlusion: due to the incorrect position of the jaws and teeth, the involuntary overload of the masticatory apparatus and compensatory loss of the soft tissues of the gums occur. In turn, all this leads to the sensitivity of the teeth when brushing, when taking cold, sour and solid foods.
In the photo - gum recession at the base of the lower teeth:
On a note
The unpleasant consequence of the long-term presence of the distal bite, especially in childhood, is the development of psychological problems - in particular, low self-esteem: the child is embarrassed by his appearance due to incorrectly standing teeth, afraid to smile. In the absence of timely adequate treatment (bite correction), such psychological problems can accompany a person in the future throughout his adult life.
In addition, over time, if the distal occlusion is not treated, complications such as premature abrasion of teeth, their pathological mobility and premature prolapse are sometimes observed.
How can a patient's face change due to distal bite (facial signs)
With the development of distal occlusion, the face of a person usually undergoes corresponding changes, and far from being for the better. However, such changes are largely reversible: after treatment, the profile of the face in most cases returns to a state close to the physiological norm - in other words, a person begins to look prettier (this is clearly seen when comparing photos before and after the treatment of distal bite).
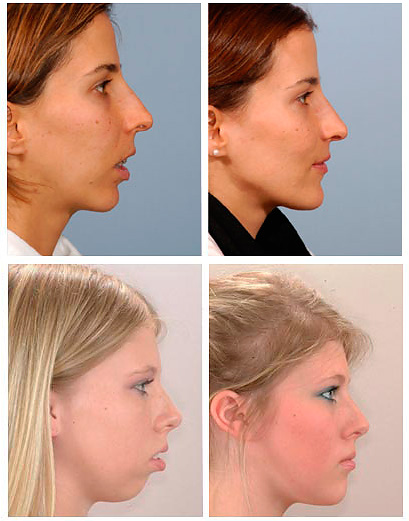
So, what usually gives the distal occlusion immediately when looking at a person's face:
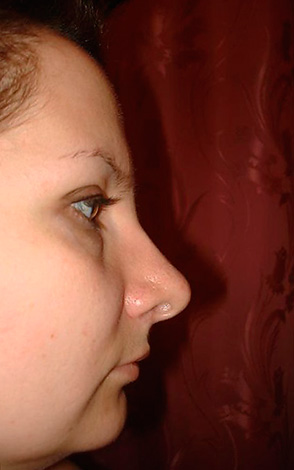
- Concave profile - the so-called "bird's face." It arises due to the fact that the lower jaw is in a posterior position relative to the upper one, as a result of which a visible step is created between the upper lip and the base of the chin. The photo below shows an example of such a profile:
- Depending on the inclination of the incisors, the upper lip at the distal occlusion can either be pushed forward when the lower lip is lagging and straining, or a lower lip can be observed when the lower lip is pushed forward slightly. The second option is to compensate for open bite in the anterior part of the dentition, when the patient, in the presence of a sagittal gap (the space between the teeth of the upper and lower jaw), is forced to strain the lower lip to close the mouth;
- A characteristic feature of the distal occlusion may also be a well-defined tense chin fold — with a medium and large sagittal slit (3-6 mm and more), the chin crease is constantly in tension with the patient's mouth closed.
On a note
Sometimes, for a complete understanding of the clinical picture and treatment tactics, an orthodontist can conduct specific clinical tests, for example, the Ashler-Bitner test, which allows us to determine which of the jaws is “to blame” for abnormal bite.
For the test, the doctor remembers or photographs the profile of the patient at rest, and then asks to push the lower jaw forward, to the physiological position of the first molars. If the profile of the face improves, the cause of the formation of the distal occlusion is underdevelopment and incorrect position of the mandible, and if the profile deteriorates, the problem is caused by the lack of growth of the maxilla. If the profile of the face improves first and then deteriorates, then the distal occlusion is due to the imbalance in the growth of both jaws.
Causes of pathology
Let's see why distal occlusion arises at all - what reasons lead to the fact that the position of the jaws along with the tooth rows begins to deviate from the norm.
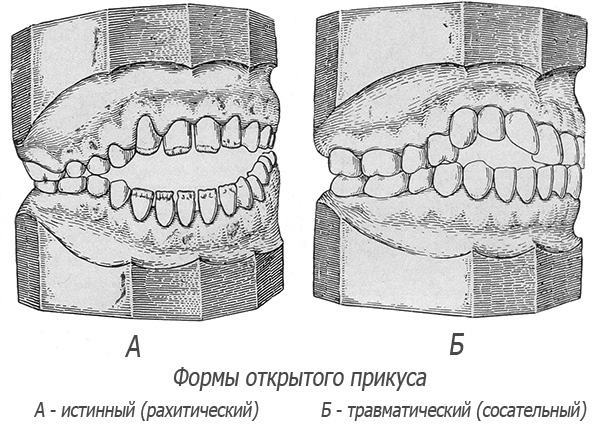
- Endogenous diseases suffered by a child in early childhood can lead to the development of distal occlusion. For example, rickets causes changes in the bone structures of the whole organism, strongly influencing the process of their development. Thus, the lower jaw in children who have had rickets is usually reduced in size compared with the norm. The picture shows the so-called rachitic bite (open);
- Diseases of the nasopharynx, an increase in the pharyngeal tonsils, frequent colds, curvature of the nasal septum - all this causes the child to breathe through his mouth, which, in turn, has a direct effect on the occlusion. Due to frequent oral breathing, the upper and lower jaws are displaced in the anteroposterior direction, the tongue descends to the bottom of the oral cavity, creating an open bite in the anterior section and a distal bite in the lateral portion of the dentition;
- Injuries of the maxillofacial area: falls, strong blows to the area of the child's face during the period of active growth can slow down or completely disrupt the development of the jaw bones, especially the lower jaw.Since the bone tissue in children is still quite soft, even a minor blow from the point of view of an adult can cause the lower jaw to shift to the back position and reduce its relative size in the near future with the formation of the distal bite;
- Harmful habits - chin beating with a fist, sucking fingers, pencils and other foreign objects. If this is an everyday involuntary repetitive process, then it becomes a kind of orthodontic force directed "in the wrong direction." In particular, this causes the lower jaw under the action of pressure to gradually move backward, while, among other things, an open bite forms: the front teeth of the upper and lower jaws lean towards the lips, a sagittal slit appears;

- We must not forget about the factor of heredity - bite, like other phenotypic features (eye color, hair color), is inherited by the child from the parents. Sometimes the discrepancy between the size of the jaws is due to the fact that one jaw developed like a father’s, and the other developed like a mother’s child;
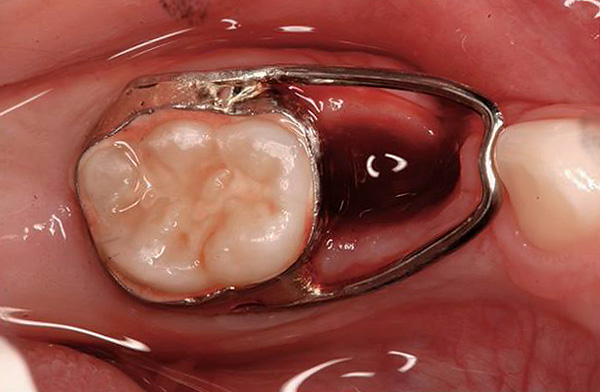
- Tooth extraction in childhood due to caries and its complications provokes the displacement of neighboring teeth towards the remote one, because nature does not tolerate emptiness.Thus, sometimes whole groups of teeth are shifted to replace the space that has appeared. To avoid this phenomenon (and if you still need to remove the tooth), a pediatric dentist sends the child to the orthodontist for the manufacture of a special apparatus that saves space for the further eruption of permanent teeth in its place;
- Later, weaning from the nipples can also cause distal bite. The sucking reflex in infancy contributes to the growth and development of the lower jaw, but if the nipple sucking lasts more than 1-1.5 years, then this is already beginning to cause harm. The lower jaw shifts back while sucking the nipple; under the action of the lips and tongue, the front teeth of the upper jaw bend forward, forming an open bite;
- The presence in the diet of the child only soft food leads to a decrease in the size of the jaws, because the dental system of the child does not feel the proper load, which is necessary to stimulate the growth and development of the jaw bones. As a result, narrowing and flattening of the jaws, especially the lower jaw, occurs.
Principles of treatment of distal occlusion in children
Myogymnastics is a very effective way of treating the distal bite in children - provided that the child regularly performs exercises.
The first exercise in myogymnastics: you need to push the lower jaw as far as possible - so that the lower incisors overlap the upper ones. In this position, you need to hold the jaw for a few seconds. Exercise is performed until the feeling of fatigue in the muscles.

The second exercise: to raise the tongue before contact with the palatal surfaces of the upper teeth.
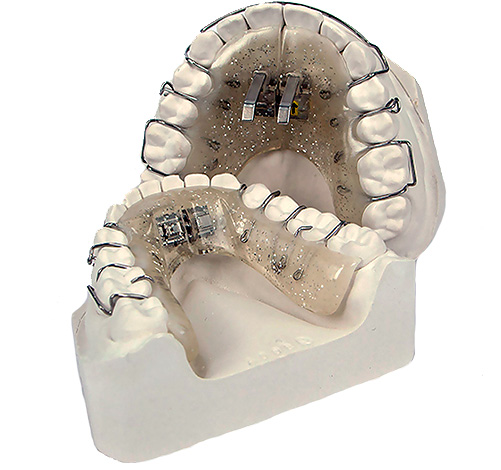
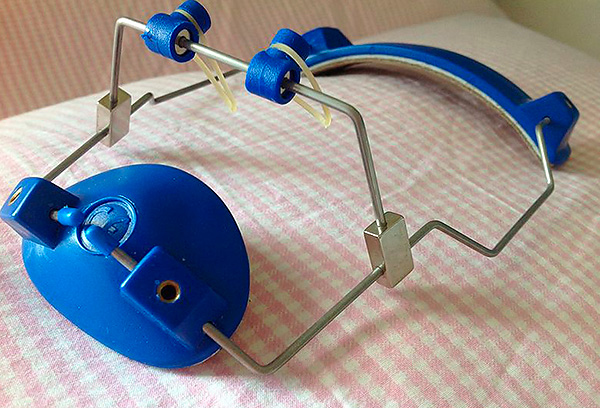
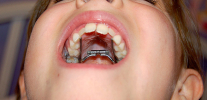
In combination with the use of special removable devices, treatment of the distal occlusion can be greatly reduced in time, and the result achieved will be as stable as possible. For example, in the early replaceable bite (milk), removable devices with a screw are used to expand and control the growth of both jaws. An example of such a device is shown in the photo below:
The doctor may also suggest that the child wear a silicone maxillary splint that relaxes the muscles and pushes the lower jaw to the correct front position. These devices include trainers, LM-activators.
On a note
Removable orthodontic appliances are effective both in the milk bite and in the period of tooth replacement.For example, with a distal bite in a 10-year-old child, the use of trainers, proofreaders and other silicone tires can serve as a preparation for the active orthodontic treatment stage on the bracket system, thereby shortening the wearing period of braces.
Removable devices are able to provide the desired therapeutic effect only with strict adherence to the wearing regimen prescribed by the doctor. For example, the mode of wearing silicone devices is usually 2 hours a day and all the time at night.

In the relatively “adult” age of a child (8-10 years old) orthodontists use Twin block devices - this is a system consisting of two plates, which, forming a block between themselves, push the lower jaw forward.
On a note
For the manufacture of the apparatus with paired blocks, in addition to removing the impressions, the stage of determining the constructive bite is important. To do this, the doctor asks the patient to push the lower jaw forward until reaching the first-class state of the molars. The orthodontist fixes this position with the help of wax bite patterns, or with the help of silicone material. Then these templates along with the models are sent to the laboratory for the manufacture of the device.

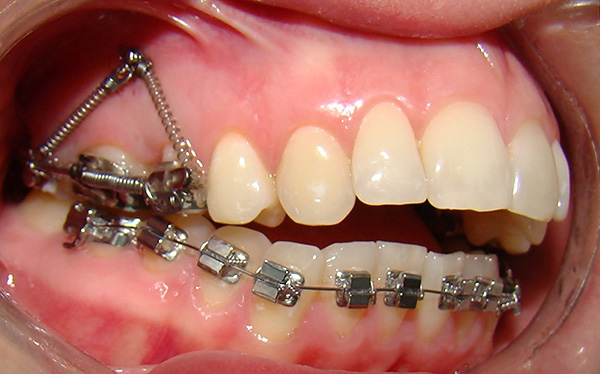
Sometimes an orthodontist prefers to partially fix braces on already erupted permanent teeth: the brace system allows you to align the teeth and place the teeth in the correct position. On the bracket system it is more convenient to move the 6th and 7th teeth with the help of springs to the back position - to distalize them to the position of the I class according to Angle (to the norm).
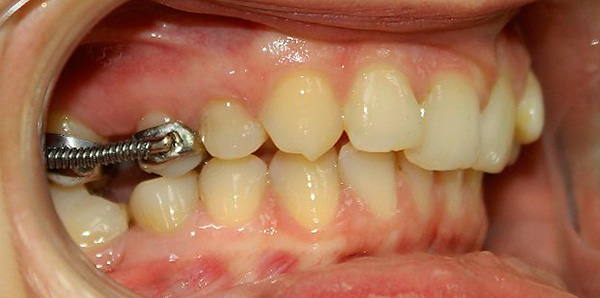
In children and in adults at the final stages of treatment of the distal occlusion, if the correct position of the lower jaw has not been achieved, the orthodontist may suggest wearing the device Gerbst and its modifications. This unit consists of two spring modules: the upper part of the module is fixed to the 6th teeth of the upper jaw, and the lower part is fixed either behind the canine or to the premolar of the lower jaw. The springs push the lower jaw forward, while the upper jaw moves slightly to the back position.
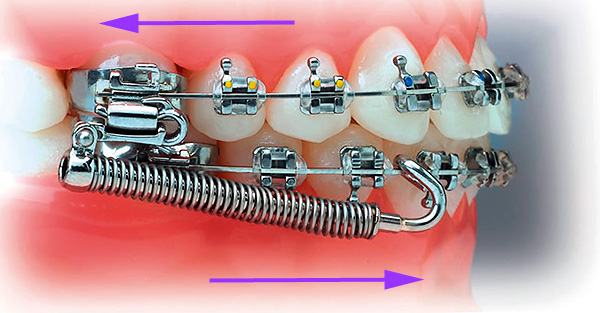
Treatment of distal occlusion in adults
In adults, depending on the severity of the pathology, several stages of orthodontic treatment of distal occlusion can be distinguished. The first stage is preparation for fixing the active equipment (system bracket).To reduce the treatment time on the braces, as well as to finally achieve a stable and expected result, orthodontists begin treatment with fixing various frame devices.
For example, today Distal Jet is quite popular:
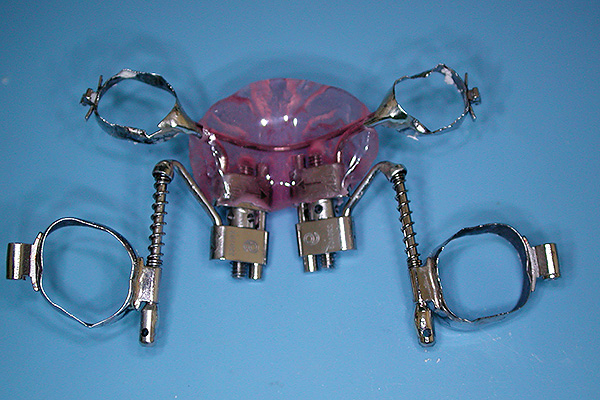
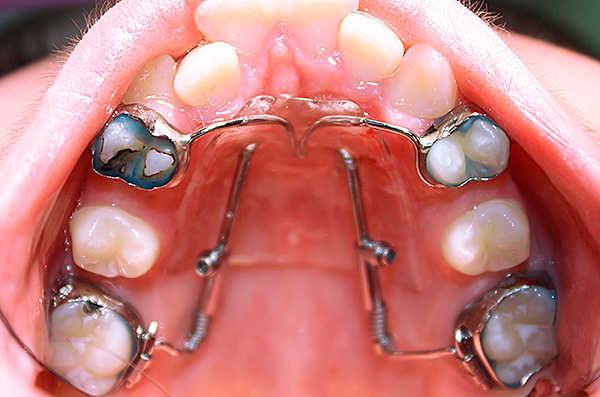
Such an orthodontic apparatus allows the first molars of the upper jaw to be moved to the posterior position, until the molar ratio is achieved in the first class of Angle, that is, to the norm.
Elements of construction include:
- Rings pre-assembled by the doctor for molars and premolars;
- The palatine byugel is the arc elements that run from the rings on the premolar to the center of the canine crown. Thus, stabilization of the anterior segment of the upper jaw is created and possible extension of the front teeth forward is prevented;
- The Nanase button is a lamellar element of the base adjacent to the middle of the sky and, when properly fitted, the apparatus lags 0.5 mm behind it;
- As well as two spring modules that distribute molars.
On a note
The devices of this type are made individually according to the model of the patient's jaws in the dental laboratory. The doctor gets the finished design on the jaw model,sucks it in the patient's mouth, corrects, if required, for the device to sit correctly and fulfill its function as much as possible. The doctor then fixes the rings on the teeth with dental cement.
Terms of use of this device on average from three to six months. Then the orthodontist fixes the palatal byugel on the first molars to hold the position reached, and on the remaining teeth a brace system is fixed, which, in fact, completes the started treatment.
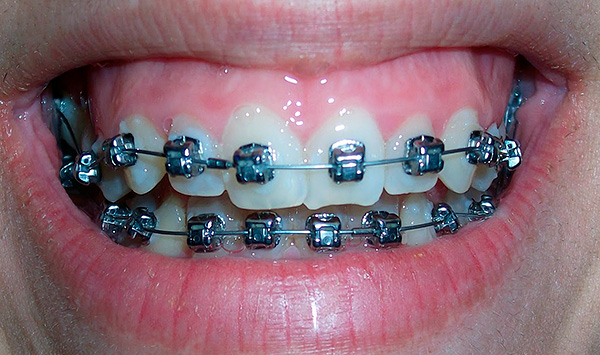
When correcting the distal occlusion, the first and second molars can be displaced without the indicated apparatus, using the bracket system immediately. To do this, at the stage of setting teeth on rectangular arches, the doctor rigidly binds the teeth with a metal ligature and places a spring between 6 and 7 teeth. Springs are replaced by stronger ones every 2-3 weeks.
Another effective way to distalize the teeth is the use of a facial arch with a chin slings and palatine rye. The patient applies the facial arc for 2-3 hours a day and overnight.
The photo below shows an example of such a correction:


For setting the lower jaw in the anterior position using the intermaxillary elastic traction.Subject to the recommendations of the doctor, the result can be achieved in about 3-4 months of treatment.
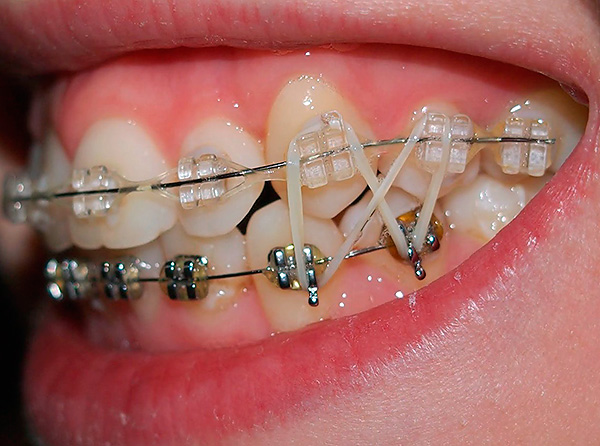
If, however, the desired result was not achieved after the appointment of the maxillary jaws, the doctor fixes the Herbst apparatus described above.
With a severe degree of distal bite, when its cause lies in strongly pronounced developmental anomalies and the ratio of the jaw bones, it is necessary to resort to the help of a maxillofacial surgeon and correct the bite surgically. If the patient agrees to surgery, the orthodontist, together with the surgeon, draw up a joint plan for preparing the patient for surgery and rehabilitation in the postoperative period.
In numerous forums today, one can often find arguments about whether one should or should not agree to such an operation. People often criticize the treatment plan offered to other people, while forgetting that the orthodontist’s treatment plan for a particular patient is based on the medical history, the severity of the disease and the result the patient is aiming for.
On a note
In this case, we are talking about the so-called orthognathic operation, which is carried out in the operating room.The surgeon makes an incision of soft tissue to expose the underlying bone, then the bone is sawn and moved to the desired position, after which the jaw is fixed in the new position using metal plates made of titanium nickelide. In the hospital, the patient spends from 5 days to a week to monitor the condition.
Despite the seemingly rather scary description, in fact, orthognathic operation is today a well-established and safe procedure.
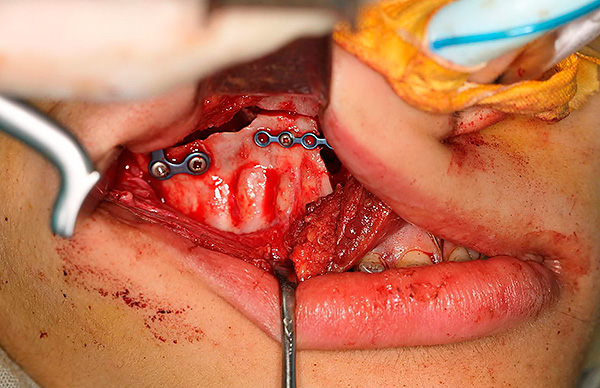
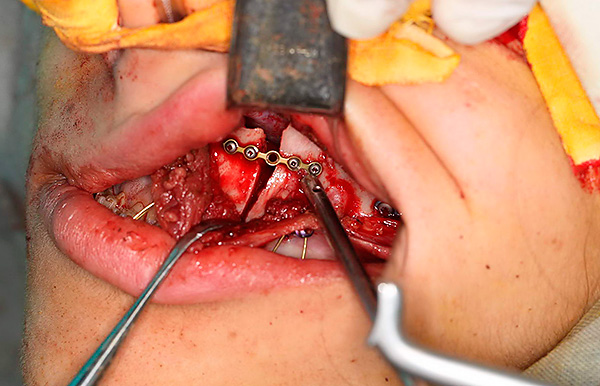
If, in case of a severe degree of distal occlusion, the patient categorically disagrees with the surgical stage of treatment, then the orthodontist corrects the occlusion only partially: so that the dental arches are even. However, the position of the jaw bones relative to the base of the skull remains unchanged in this case, that is, the profile of the patient’s face does not change.
How to prevent the development of distal bite
To prevent the formation of distal bite, first of all, it is necessary to monitor the development of the child from early childhood. Timely wean him off using nipples, sucking his finger, supporting his chin with his fist, injecting fresh (and, therefore, fairly hard) fruits and vegetables into the diet.Adjust other bad habits.
Do not start the state of milk teeth, believing that since they are temporary, then it is not necessary to treat them - in fact, on the contrary, they need to be treated promptly so that there are no problems with permanent teeth. An important task is to preserve milk teeth before their natural change, not leading to their removal due to caries or pulpitis.

It is also useful to visit the orthodontist to control the growth and development of the dental system in general.
So let's summarize. Distal bite is a very frequent pathology of the population of Europe and the European part of Russia. The state of the dental system, which is formed during the distal occlusion, requires treatment, and you should not think that if you do not interfere, then nothing will be wrong and everything will somehow resolve itself. Alas, it will not resolve.
In the future, uncorrected distal occlusion can cause dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint (pain during chewing, regular headaches), abnormal abrasion of teeth (there will be nothing to chew on old age), and in some cases can cause early tooth loss and psychological problems.In addition, many people with distal occlusion do not even realize that they could look more attractive if their profile was not distorted by an occlusion anomaly.
Therefore, if you see signs of a problem in yourself or in your child, then you should not lose time, it is best to solve it in the early stages.
Be healthy!
What are the consequences of an overbite?
Interesting video about the reasons for the formation of the wrong bite

Thank! Everything is very clear.Found answers to all your questions!