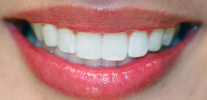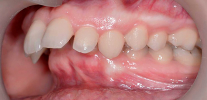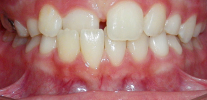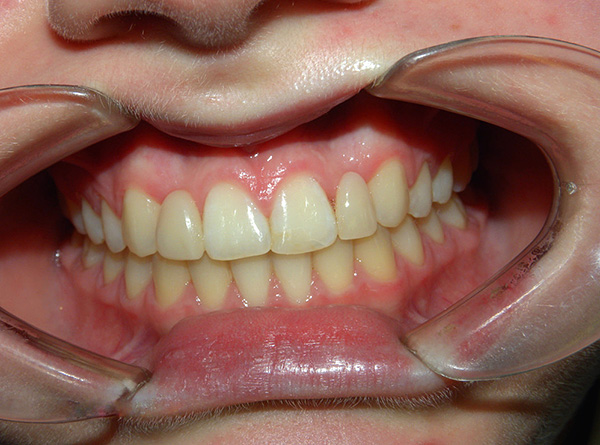
Permanent bite is the relationship of the dentition of the permanent teeth with the upper and lower jaws fully closed. If it is simpler to say, this is a fully formed bite, when all milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones.
Compared with a temporary bite, a constant is characterized by a number of important features - then we will consider in detail the stages of its formation, interesting nuances of the transition from a milk bite to a permanent one, as well as modern techniques for the treatment of bite anomalies and a situation when such treatment is difficult ...
Important nuances of the transition from a milk bite to a mixed
Orthodontists pay special attention to the period of late milk bite, when preparations are made for changing temporary teeth to permanent ones. Already at this time, when examining a child’s oral cavity, for a number of signs (not always obvious), future problems with the position of teeth can be suspected.
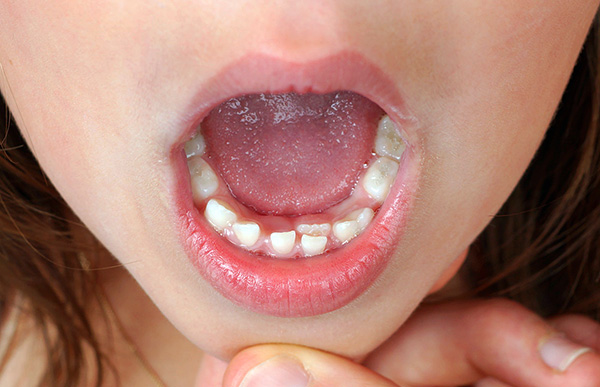
Normally, the shape of milk teeth coincides with the shape of the teeth in the permanent dentition, but the crowns of the temporary teeth should be proportionally wider, especially in the area of temporary molars (i.e., chewing teeth with numbers 5 and 6). In this case, wide crowns prepare a place at once for two future permanent teeth - premolars.
In turn, temporary incisors (front teeth) have more prominent outlines and are normally slightly inclined to the palate, as the roots of permanent teeth located in the bone exert pressure on their roots.
The size of the teeth and dental arches of the child is much smaller than in the period of constant bite. In children under 4 years old, the lower jaw occupies a posterior position, but when the period of active growth of the jaws and heads of the temporomandibular joint begins, the lower jaw moves forward (to some extent this is due to the nature of the child’s nutrition - the cessation of sucking and active chewing of food). With the normal growth of the jaws, gaps (tremes) appear between the temporary teeth of the child - this indicates the proper development of the dental system, and in no way should parents be considered a pathology (as sometimes happens).
On a note
If there are gaps between the teeth in an adult or adolescent, this is indeed a sure sign of pathological bite or diseases of the oral cavity tissues (for example, gingivitis or periodontitis).
The roots of milk teeth dissolve with time, and they fall out, giving way to new permanent teeth. But sometimes it happens that the milk teeth remain in place, and despite the fact that the child grows, the change of individual teeth does not occur.
This may be due to several reasons:
- The child may be missing the germ of a permanent tooth in the bone. In practice, when interviewing parents, it is usually possible to find out that there is such a pattern in the family, and the relatives may not have separate teeth or even groups of teeth. Obviously, in such cases, the pathology is associated with heredity;
- Either a permanent tooth cannot come out of the bone due to its incorrect position or interference from adjacent teeth.
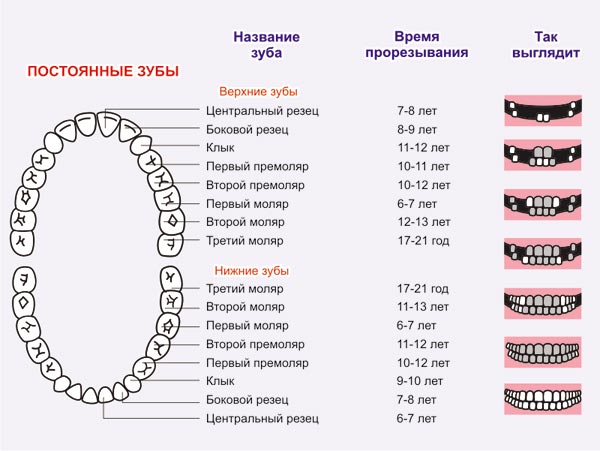
On the X-ray picture below, permanent teeth in the bones, formed under the milk teeth and ready to push them out, are clearly visible:
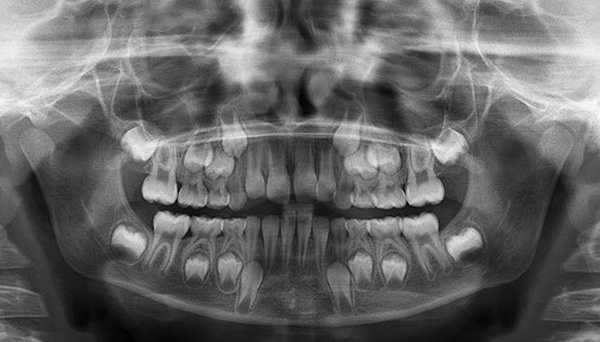
In any case, only the dentist after the examination can understand the reason for the delay in changing temporary teeth - an X-ray image will be taken.After evaluating the snapshot, the orthodontist discusses treatment options.
For example, if there is no primordium, then after fixing the bracket-system, the neva milk tooth is retained until the orthodontist creates enough space in the row for further prosthetics of the desired tooth.
If there is a permanent tooth in the bone, but there is little space for teething, or it is too deep, or lies in the wrong position, then after fixing the bracket system and creating space for the desired tooth, after it is opened by the surgeon, the tooth is gradually “pulled”, fixing on it first orthodontic button, and then tying to the orthodontic arch.
Characteristics of permanent bite and what factors may affect it
An important stage in the formation of permanent bite begins long before the beginning of the eruption of permanent teeth - even at the stage of mineralization of their buds. Mineralization with the formation of high-grade hard tissues occurs inside the gums, therefore, it is only a doctor who can assess how this process goes, after a radiological examination of the child. Salinity begins in the first months of the baby’s life, and even after the tooth appears, this process does not end immediately, but it continues for another 1–1.5 years to fully “ripen” the root of the permanent tooth.
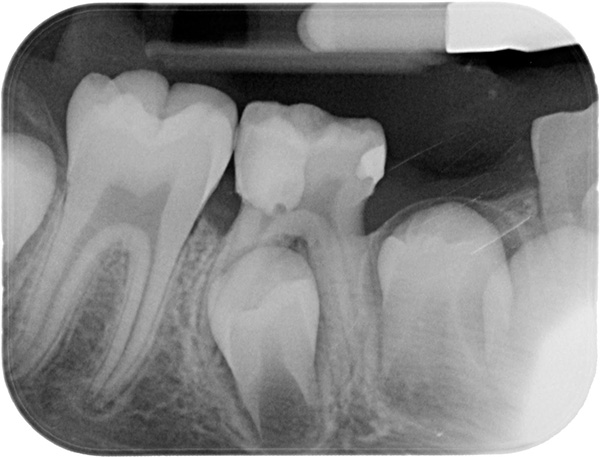
The period of mixed bite begins with the eruption of the first permanent tooth. There is a certain order and terms for the eruption of permanent teeth:
- as a rule, molars erupt first - 6 teeth at the age of 5-6 years;
- between the ages of 6-8 years, incisors alternately erupt (first the first incisors on the lower jaw, then on the upper ones);
- soon the lateral incisors of the lower and upper jaws appear.
The upper incisors are usually located with a slight lingual inclination, and they are larger than temporary teeth. Their appearance coincides with the period of growth of the upper jaw, and initially they are located in their place tightly and without gaps.
When the lateral incisors erupt, they put pressure on the central upper teeth that have already appeared, which is why the central incisors diverge, forming a physiological diastema (groin) and leaning towards the lips. However, normally, after the eruption of permanent canines in the upper jaw, the diastema closes itself. This stage of development of the dentition is often called the stage of the "ugly duckling", but after the eruption of the canines in a child, the teeth of both the lower and upper jaws are aligned.
After the appearance of incisors in both jaws, a period of physiological rest begins, lasting 1-1.5 years.
Between the ages of 9 and 12, the second stage of the eruption of permanent teeth begins. At this time, canines are replaced, premolars appear - “fours” and “fives” on the lower jaw (the order of eruption is 3-4-5, and on the upper jaw, on the contrary, first appears 4 teeth, followed by a canine, and after 5 tooth).
The penultimate second molars appear - 7, and behind them wisdom teeth (third molars, that is, 8-ki).
It is important to understand that although there are more or less definite periods of teething in the permanent bite, they are relative, and in practice there may be some deviations from them that do not lead to serious consequences.
The figure below shows the age characteristic for the eruption of certain teeth:
Thus, in the permanent dentition, a person has 28-32 teeth, the shape of which resembles that of a milk teeth. In addition to the main groups of teeth already present in the temporal bite, 4 new ones appear - premolars.
We should also talk separately about the latest “eights”, often causing a lot of trouble because of the negative impact on the bite ...
About wisdom teeth and their possible impact on bite
Since wisdom teeth appear most recently in the oral cavity, they can, with eruption, change the position of the remaining permanent teeth, pressing down on their “neighbors” and displacing them, thus ensuring a place for themselves.
On a note
The nature of human nutrition since the times of primitive ancestors has changed significantly. Molars, especially wisdom teeth, were needed by man earlier for grinding hard bones and chewing hard raw meat. The load on the chewing apparatus was very significant, and because of this, the size of the teeth and jaw bones was greater. Today, people mostly eat soft, thermally processed foods, the chewing load has become smaller, so the size of the jaw bones has decreased. As a result, there is initially not enough space in the jaw for wisdom teeth.
Knowing this fact, many pediatric dentists and orthodontists, recommend removing wisdom teeth even before their eruption begins, so that they may spoil the teen's permanent bite in the future. Statistics of studies on this topic shows that the eruption of wisdom teeth causes such problems as crowding, turning of teeth, displacement of the first molars and the formation of a pathological bite in 35-40% of cases!
However, the removal of innocent and even “eights” that have not yet erupted is a controversial issue, and some experts do not approve of this practice. Indeed, for many people, wisdom teeth do not lead to problems, they regularly perform their chewing function and, moreover, in old age they come in handy when needing prosthetic teeth.
Anyway, the decision to remove wisdom teeth should be made by the orthodontist together with the patient after the examination. Even at the stage of drawing up a treatment plan, the doctor discusses the issue of removing “eights” - it is often better to start at this stage, and after healing and recovery, proceed to level the bite.
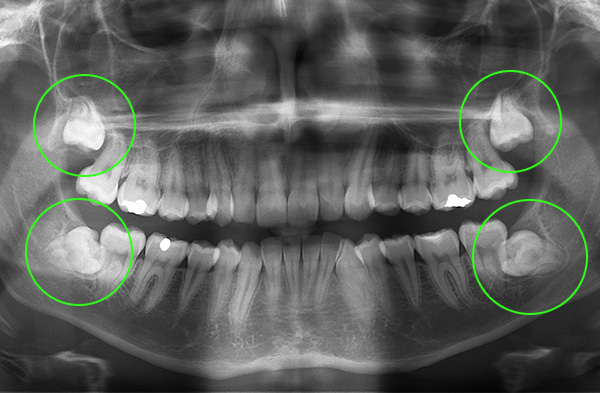
On the other hand, it happens that already in the process of treatment the orthodontist, seeing the dynamics, recommends removing wisdom teeth. There is a technique for removing the rudiments of still unformed wisdom teeth - this option is in many cases less traumatic than the removal of already fully formed teeth, but requires some skill from the surgeon.
On a note
The unequivocal indication for the removal of wisdom teeth is their improper location in the jaw bone - when they are tilted towards the roots of the adjacent permanent teeth or cheeks,because of what can not cut through, and often at the same time cause inflammation of the surrounding tissues.
How to understand that there is something wrong with the G8? The process of their appearance, even normal, can bring certain inconveniences: the gums itch (especially at night), salivation increases, some adults complain of slight pain in the area where the tooth is cut. All these phenomena are a variant of the norm.
But there are also disturbing symptoms that should not be ignored:
- Persistent temperature rise above 37.5 degrees;
- Swelling and redness in the area of the cutting tooth;
- Intense pain, difficulty chewing and swallowing.
In all these cases, especially if the dynamics are negative and only get worse over time (the pain is stronger, the temperature is higher), there is no need to wait - contact your doctor as soon as possible! In advanced cases, inflammation in the face of obstructed wisdom tooth eruption may threaten the patient’s life.
Types of permanent bite: what is considered the norm, and what is pathology?
It is customary to distinguish several types of physiological occlusion, that is, allowing to fully perform the chewing function:
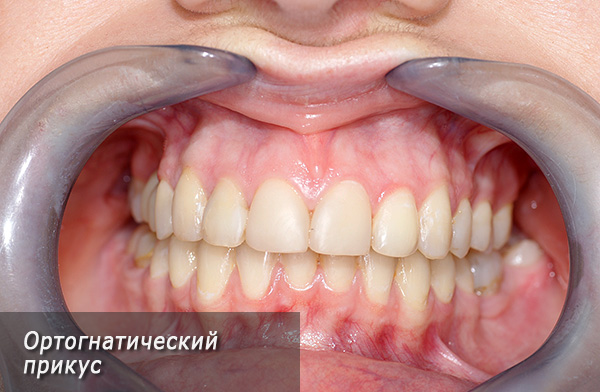
- Orthognathic bite is considered the most aesthetic and most favorable for maintaining the healthy state of the soft tissues of the oral cavity and temporomandibular joints. The orthognathic bite possesses the following features: the teeth in the lateral part are closed according to the 1st class of Angle, namely, the anterior-buccal tubercle of the upper “six” is located in the inter-tubercular fossa of the lower 6th tooth. The front teeth of the upper jaw overlap the incisors of the lower jaw by no more than one third. All teeth on both jaws are in close contact with each other. At the same time, they have a certain slope, ensuring their even and correct position;
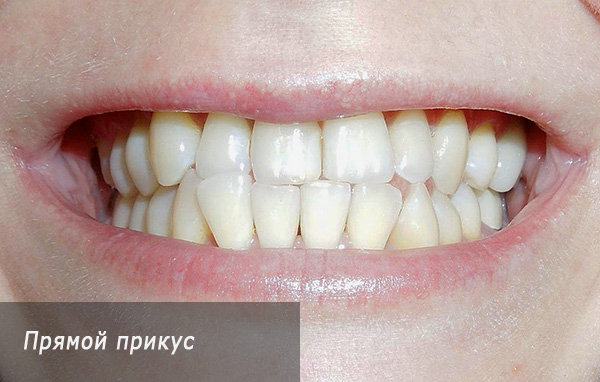
- Direct bite - in this case, the ratio of the posterior teeth is preserved in the first class of Angle, and the teeth in the anterior part of the joint join into the joint (with time, this may lead to their erasure);
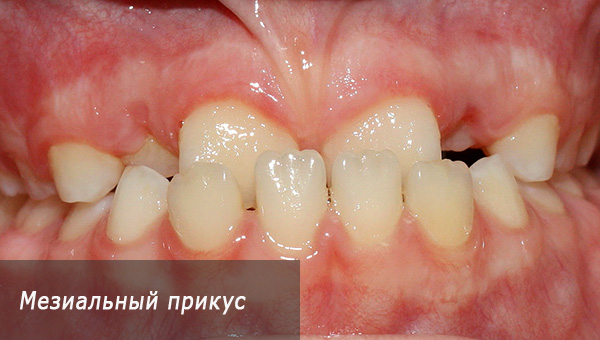
- Previously, a progenic bite was also attributed to the physiological (pro - forward, genus - chin). That is, with this type of bite, the chin is pushed forward. In the anterior part of the dentition, there is a reverse incisal overlap, that is, either the lower jaw is pushed forward, due to which an anomalous ratio of standing molars is observed, or the teeth of the lower jaw themselves are inclined towards the chin.However, at the same time, this position of the jaw bones can be called abnormal, corresponding to the mesial bite;
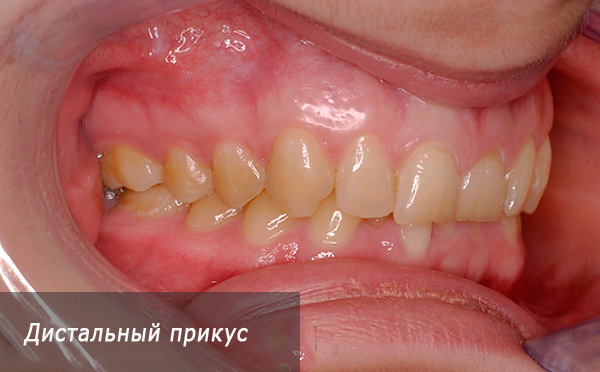
- Prognathic bite - in this case, the upper jaw is located in front of the lower jaw, the incisors of the upper jaw are tilted forward with their cutting edges because of which the incisors of the lower jaw join with them at the most posterior point, the side teeth are closed abnormally: the anterior cheek side of the first upper molar of the upper jaw is located ahead of the interdubral fossa of the molar of the lower jaw. This ratio of the first molars can also be called abnormal - it corresponds to the distal bite;
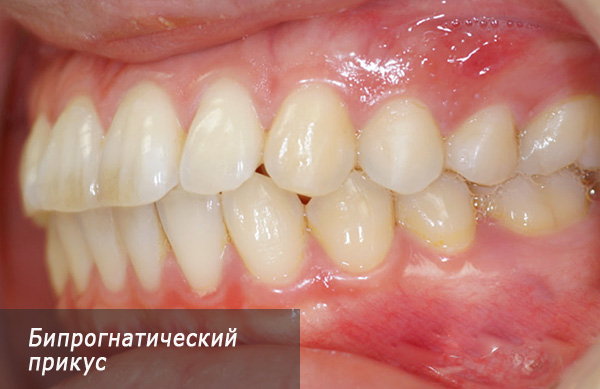
- Biprognatic bite - both jaws are displaced forward relative to the base of the skull, in the anterior section the incisors are closed by cutting edges, and to achieve this closure, the incisors of the upper and lower jaws lean forward.
On a note
With progenic, prognathic and biprognathic bites, the chewing function may be quite normal, although the bite is pathological and may lead to additional problems later - therefore the orthodontist may suggest correcting it.
When assessing a permanent bite in an adult patient, an orthodontist pays attention to how a person closes his teeth during a conversation, when the lower jaw is moved to the side and forward. This closure of the teeth with different movements of the lower jaw relative to the upper one is called occlusion.
Allocate anterior and lateral occlusion. Assessment of occlusion is important to understand whether there are malfunctions in the normal chewing process. This allows you to anticipate early erasing of teeth, overstrain of the muscles of the maxillofacial area, loosening and, in severe cases, loss of teeth.
The photo below shows what causes erasing of the teeth due to improper occlusion in the anterior region:
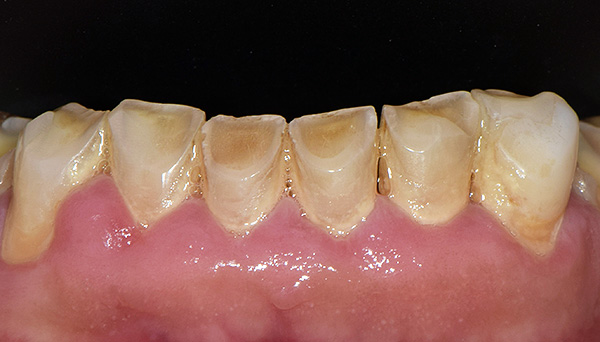
Normally, the lateral teeth of the upper and lower jaws should not remain in the same plane when closing. That is, the molars should have a certain inclination so that with different movements of the lower jaw the side teeth do not lose contact with each other. In the presence of the correct inclination of the teeth, conditionally drawn lines are formed - occlusal curves:
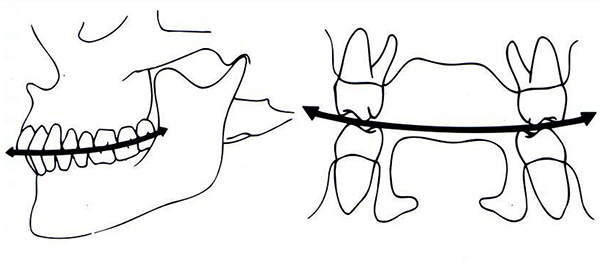
Taking into account the shape of the occlusal curves, the orthodontist can reveal signs of an abnormal permanent occlusion upon careful examination of the patient’s dentition.
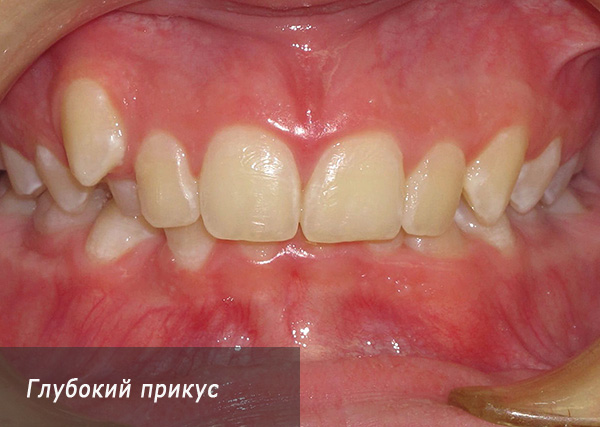
The front teeth can also close incorrectly. For example, it is not uncommon for the incisors of the upper jaw to overlap the incisors of the lower jaw excessively - sometimes so much so that the lower teeth cut their edges into the palate, injuring it. Such an overlap in the anterior section is called a deep bite:
The opposite situation - when in the front section the teeth do not close at all, or their overlap is minimal. Such a bite is called open:
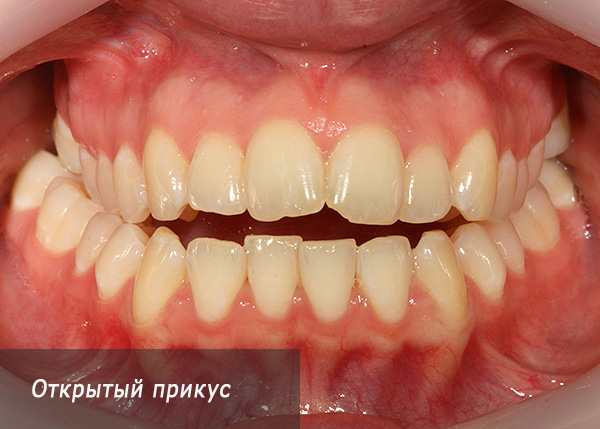
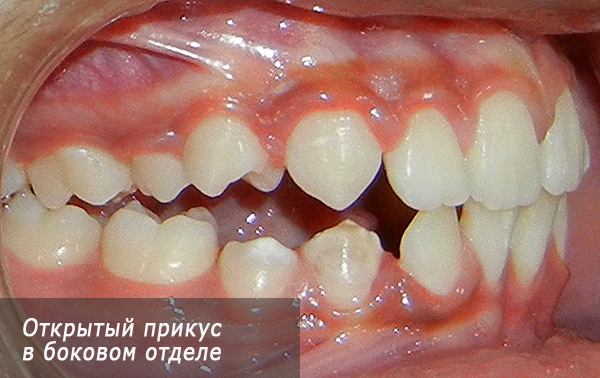
Open bite is often found in the lateral part of the dentition:
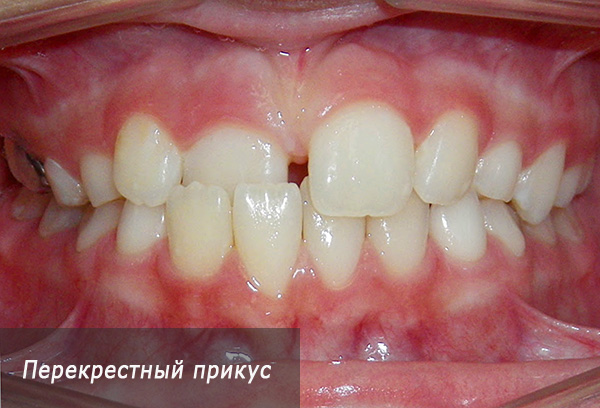
Another type of irregular permanent bite is a cross bite, and the cross closure can be either in the front or in the lateral division. This anomaly occurs due to inconsistencies in the sizes of the upper and lower jaws or their individual segments:
As a rule, the wrong bite combines the pathological closure of the side and front teeth, therefore drawing up a treatment plan for a particular patient sometimes becomes a difficult task for the doctor.
Formation of bite in adolescence
Adolescence is a test for the whole body of a child, and the dentofacial system is no exception.Under the influence of sex hormones, a natural surge of body growth occurs, after which growth slows down and gradually stops.
Puberty in boys and girls goes differently:
- Girls start growing up about two years earlier than boys. The start of puberty in girls is the beginning of breast formation and the appearance of the first pubic hair. Peak growth in girls is observed 1-1.5 years after the first signs of puberty appear. After another year and a half, the final stage of maturation of the girl begins — the beginning of the menstrual cycle, after which the growth slows down and ends in another year and a half;
- Boys, unlike girls, do not have such a clear separation of the changes taking place. It is known that active growth in boys begins about 3-3.5 years later than in girls, and also ends later. The first sign of the onset of puberty in boys is considered to be a rapid weight gain. The growth spurt begins a year after gaining weight - at this time the boy is losing weight, his hair appears in the groin area. At the third stage of maturation, in 8-12 months the growth of muscles and bones takes place, the body shape changes.Two years later, the last stage of maturation occurs, growth stops, the first hair on the face appears.
All these changes, one way or another, affect the formation of a permanent bite, and not always for the better.
Experienced orthodontists usually try to start the bite treatment during the peak of the child's growth, because the growth of the jaw bones as a whole coincides with the growth stages of the entire skeleton, and at the peak of growth the treatment is most effective and the result can be achieved faster.
On a note
In order to understand how a child is formed and whether he has a growth stock, an orthodontist can direct him to an x-ray of a hand to see whether the so-called growth zones on the arm have closed or not.
Thus, if there are problems with a bite in adolescence, then you should not delay the visit to the orthodontist - it is better to start solving the problem during this period.
Bite correction in adult patients
Adult patients have their own specifics, and this may be associated not only with the physiology. For example, adults want to have a beautiful smile, but at the same time, they often do not want others to see braces and any other devices on their teeth.Although recently there has been a fashion for braces - their presence is perceived not as a sign of imperfection, but as a sign of well-being and prosperity.

To date, there are three areas of aesthetic orthodontic appliances, allowing to correct the anomalies of permanent bite in adults.
The most popular option is vestibular braces (that is, pasted on the teeth from the side of the lips), made of materials similar in color to the tooth enamel, which makes the bracket system unobtrusive.
Aesthetic vestibular braces are made of three types of materials:
- Plastic;
- Ceramics;
- Sapphire.
On a note
Plastic braces are the least expensive, but they are fragile, break easily, tend to be painted. So, for example, if you like tea, coffee, cigarettes, then these braces will quickly turn yellow.
Compared to metal braces, aesthetic braces are more demanding from the doctor precision fixation. Sticking or peeling the locks during the treatment process can damage the grille, which ensures the adhesion of the bracket to the tooth, and it will not hold, which means that in any unusual situations the patient will have to pay for the new bracket.
In addition, such systems are more expensive than metal counterparts by about 20-30 thousand rubles. For example, a set of “simple” metal braces, which are tied to the arch with ligatures, costs an average of 20 thousand rubles, and the aesthetic option, depending on the material used, can cost 40-50 thousand rubles.
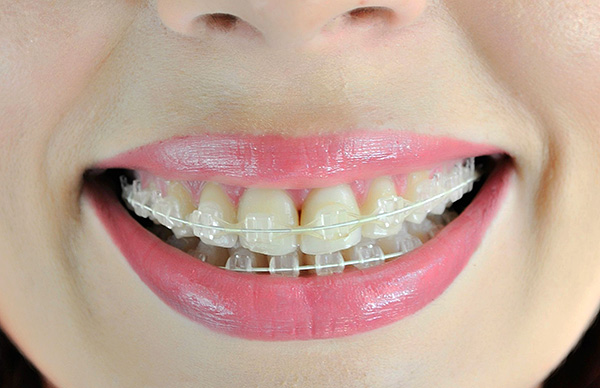
It should be noted that sapphire braces are the most durable and do not lose their aesthetic and functional properties, ceramic ones behave a little worse - in some cases they can be painted.
The photo below shows sapphire braces:
For those who, when correcting bite at all, do not want others to see braces in their mouths, there are 2 system options.
The first option: lingual braces - an orthodontist sticks them on the teeth from the side of the palate and tongue and, thus, others do not suspect that the person is wearing braces.
There are two types of such systems - standard lingual braces, the so-called 2D-systems. They are manufactured by the factory, have a standard shape and size, are able to move teeth in a two-dimensional space.The doctor ties up the arc that moves the teeth to the locks with metal or rubber ligatures.
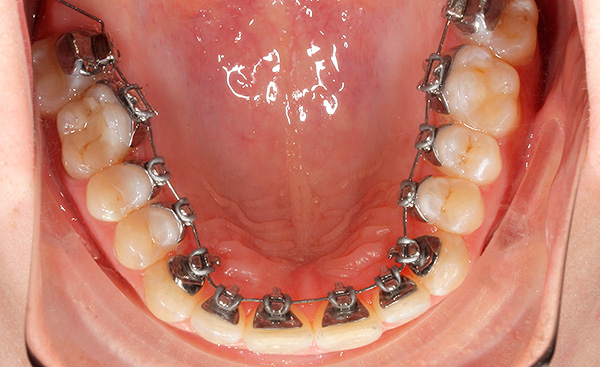
From the practice of the orthodontist
Opportunities for the movement of teeth using such systems are limited due to their standard convex shape and incomplete fit of the active arc. As many orthodontists, who use these braces, say, when treating complex orthodontic pathologies, it is difficult to achieve an ideal bite, since the effect is mainly on the crown part of the tooth, and the position of the roots remains almost unchanged.
The second option: individual 3D-lingual braces - made of gold alloy in the laboratory individually for each patient, taking into account the shape of each tooth and its inclination. Together with braces, the doctor orders a set of active arcs for the entire period of bite correction. This approach provides a snug fit of the arc to the teeth and the ability to adjust their position along with the roots.
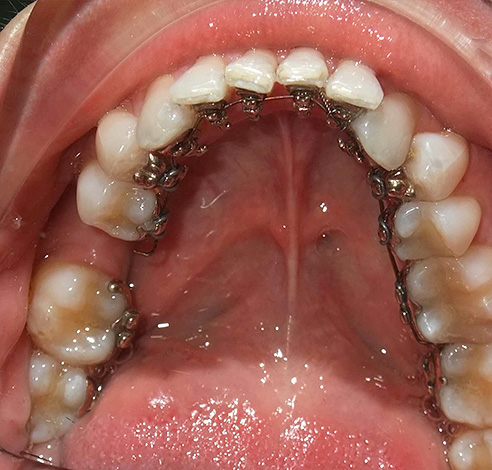
On a note
When an individual lingual braces arc breaks, and this sometimes happens in patients, the orthodontist is forced to order a new one, since arcs from other systems are not suitable.This stretches the treatment time, since braces and arcs are made in Germany or in the USA (depending on the specific system). Otkleyki braces and breakdowns of arcs are poured into additional costs for the patient with so pretty impressive system costs - in some clinics the cost of individual lingual systems reaches 150 thousand rubles and above (this is the cost of the system and its installation).
Another option for leveling permanent bite in adults is the use of orthodontic caps (aligners) - unlike braces, these are removable devices.. They are made individually after receipt of the impression of the teeth and the casting of the plaster model. Then a set of transparent caps is prepared, which must be worn sequentially, one after the other, replacing as the required intermediate result, controlled by the doctor, is achieved.

The greater the sequence number of the cap in the set, the closer it corresponds to the correct location of the teeth in the bite. Read more about this in the article. Orthodontic caps for bite correction
In general, it is worth noting that the timing for the correction of permanent bite in adult patients is on average 2-2.5 years, sometimes longer (depending on the complexity of orthodontic pathology).Approximate terms for each specific case can be called by an orthodontist only after a full examination of the patient. The treatment plan may include the stage of removal of individual teeth - molars or premolars, to create the necessary space in the row.
Treatment of patients with "difficult" condition of the oral cavity
Sometimes adult patients complain not only about the “curvature” of the teeth, but also about other problems of oral health. For example, persistent odor from the mouth, bleeding and swelling of the gums. These symptoms are the first signs of gingivitis or periodontitis.
With periodontitis, there is a recession (decrease) of the gum tissue, because of which the tooth root is gradually visible. The teeth themselves acquire mobility, diverge among themselves.
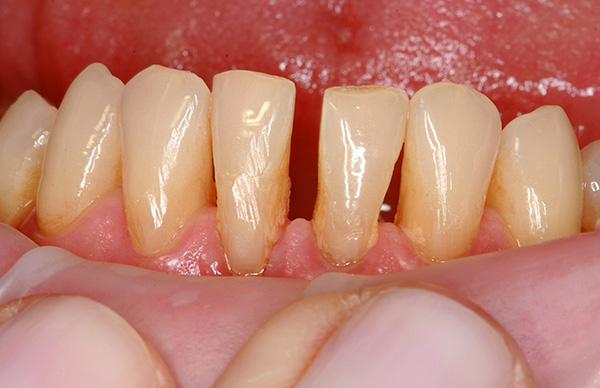
Bite correction in patients with gum disease is not an easy task for an orthodontist, because orthodontic treatment can only aggravate the situation. Such patients necessarily need a consultation from a periodontist who will assess at what stage the process of inflammation and select the necessary treatment. Treatment may take from 3 to 6 months, depending on the severity of the disease, and until then the orthodontist cannot start working with the patient's bite.
In addition, a common problem for adult patients is the absence of some teeth. When planning bite correction in such cases, the orthodontist can offer two solutions to the problem:
- Prosthetics of a missing tooth on an implant (titanium implant plus, for example, a zirconia crown);
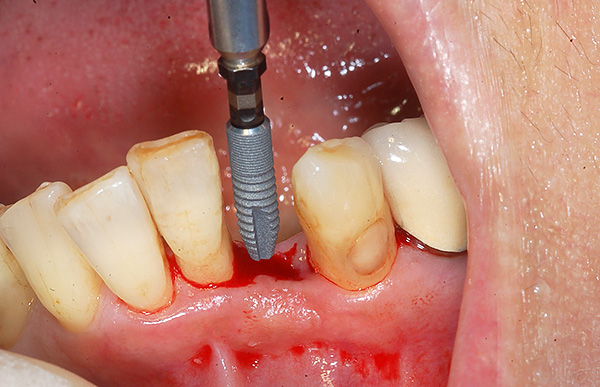
- Or you can use your braces to move your existing teeth in the direction of the defect, thus closing it.
In both cases, the patient should be orthodontic prepared: enough space should be created in the dentition for the implant to be implanted, and to close the gaps in the row, the teeth should be aligned in an arc.
It is interesting
After the start of orthodontic treatment, the teeth become mobile, and in patients with gum disease, this mobility may be excessive. Therefore, before starting the treatment, the orthodontist can remove the so-called “blocking” contacts, which create an unnecessary burden on talking and chewing. This procedure is called selective grinding. After the contacts between the teeth are normalized, their mobility should decrease.
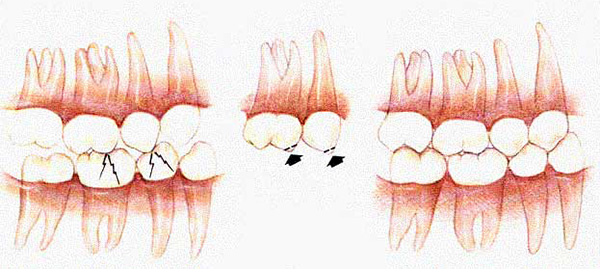
Orthognathic surgery as a permanent occlusion treatment
Sometimes, to achieve the perfect orthognathic bite, the efforts of an orthodontist alone are not enough. When preparing a treatment plan, the orthodontist can immediately tell his patient that he will need an interventional maxillofacial surgeon. If the patient agrees to this stage, then the treatment plan is adjusted accordingly to exactly what the surgeon needs for the operation. Then these doctors work together, together, and when the orthodontist creates all the necessary conditions for the operation, then the surgeon performs the surgery.
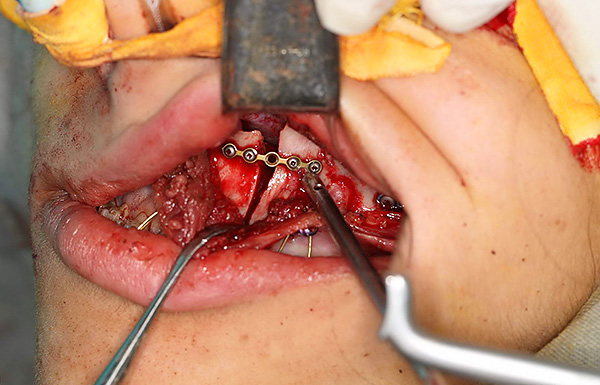
Indications for surgical treatment are severe skeletal forms of bite abnormalities. That is, when the causes of bite problems are not only the incorrect position of the permanent teeth, but also the incorrect position or size of the jaw bones relative to the base of the skull.

However, for obvious reasons, many patients are categorically against surgery. Then the orthodontist conducts orthodontic camouflage of the wrong bite, that is, puts all the teeth exactly along the arc, plans to remove individual teeth and shifts the rest towards the removed ones, seeking an acceptable option for the bite.At the same time, pathological contacts between the teeth can be maintained, and the patient's profile according to the facial features usually still gives an abnormal position of the jaw bones.
In fact, do not be afraid of orthognathic surgery. The surgeon makes all cuts and bone cuts only in the mouth, that is, there are no scars on the face. After surgery, the surgeon prescribes the wearing of special elastic strands to secure the new position of the jaw bones and give the muscles to get used to the changes.
The recovery period after orthognathic surgery is approximately 1 month. During this time, the patient must follow a strict diet, not to eat solid food (the first two weeks, all food should be liquid). In the hospital after surgery, the patient spends 5-7 days, then he is allowed to go home, and after 2 weeks the person can return to work, following the instructions of the doctor.
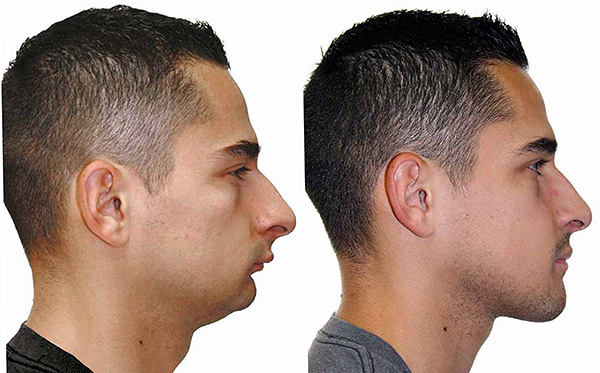
After 3-4 weeks, the orthodontist, together with the surgeon, examines the patient, and if the result is satisfied with the doctors, the removal of the bracket system is appointed.
Possible complications of orthodontic treatment
Any treatment is an intervention in the work of the human body, the same applies to the orthodontic treatment of permanent bite.It may seem strange to some, but the most important step in this is the initial preparation of a treatment plan for a particular patient. For this:
- The orthodontist conducts a detailed analysis of diagnostic models of the patient's jaws, meticulously calculates the available space deficit;
- Examines a panoramic picture of the jaws to assess the position of the teeth, the inclination of the roots of the teeth, assesses the state of the adjacent tissues - the maxillary sinus, the alveolar process of the maxilla, the mandibular canal, is also important analysis of the bone plate, which is a layer between the teeth and jaw bones;
- Analyzes a snapshot of the skull in the lateral projection - telerogentogram, according to a certain method, the orthodontist can estimate the length of the jaws and their position relative to the base of the skull, assess the type of jaw growth, the inclination of the front teeth and understand what is the root cause of the abnormal bite.
After the orthodontist compares all the information received, he must describe in detail the plan for further action. Depending on the diagnosis of the patient and the characteristics of his bite, the orthodontist chooses braces with a specific dental program,selects certain arcs and involves the use of additional elements - bends on the arc, connecting additional devices at specific stages of treatment to achieve the best possible bite.
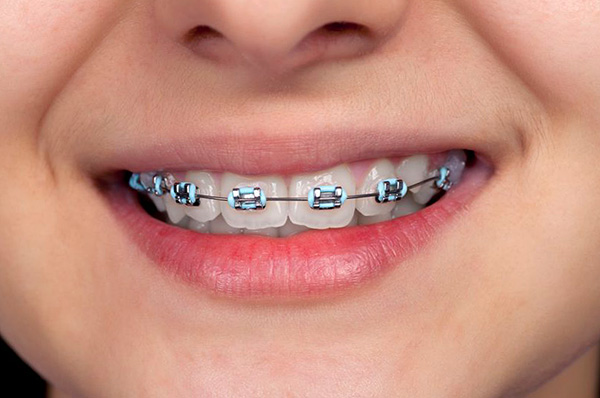
Sometimes, patients complain that time is ticking and the bite does not even out, or they notice that their teeth have bent excessively in one direction or another. In addition, for gum diseases after fixing braces, excessive mobility of the teeth may appear.
The reasons for all these phenomena can be miscalculations from the orthodontist, which consist in the wrong choice of braces, or incorrect positioning of the braces on the teeth, or setting too strong an arc at the very beginning of treatment, which can cause overload of the teeth and the tissues holding them.
To prevent such complications, it is important to choose the right doctor. Many patients visit different orthodontists and collect their opinions about their problem before making a choice, trusting a specialist and starting a long-term treatment. This is the case when it is better to look for not a clinic, not “where is cheaper”, but it is worth looking for a highly professional experienced doctorwhich, step by step, together with you, will go all the way to beautiful teeth, the duration of which can be several years.
Useful video: stages of changing milk teeth to permanent ones
What is a correct and incorrect bite in a child and why it is so important to consult an orthodontist in time