Cross bite is considered, which is characterized by the intersection (crossing) of the dentition when the jaws are closed. This pathology is often quite difficult to treat, and the duration of the necessary procedures and their success is largely determined by the severity of the clinical case and the reasons that, in fact, led to the occurrence of cross-bite.
Be that as it may, it is important to understand that this bite anomaly requires adequate and timely treatment, because without the appropriate orthodontic intervention, very unpleasant and sometimes dangerous consequences are possible (we will also talk about them a little later).
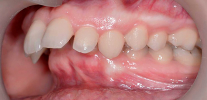
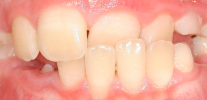
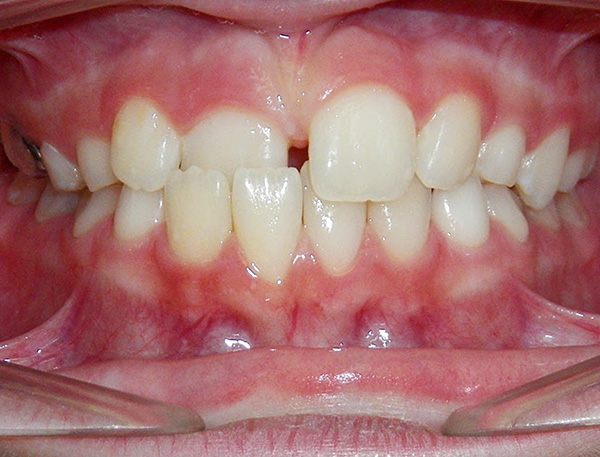
The photo below shows examples of cross bite in a child and an adult:
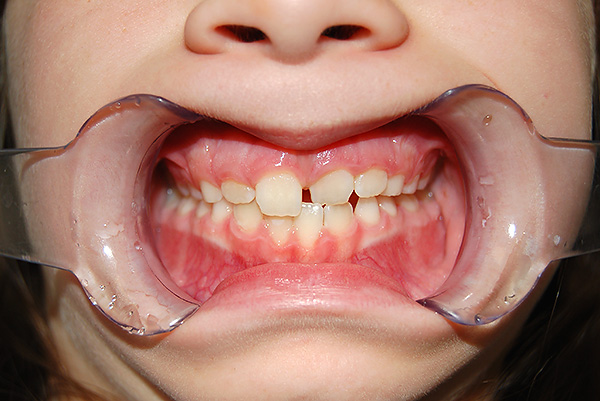
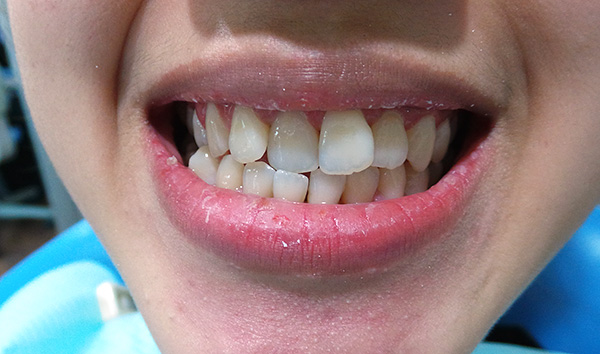
Types of cross bite, allocated by orthodontists
There are several types of cross bite, and depending on the type of this pathology, the plan for the corresponding treatment can also be different.
So, let's see what types of cross-bite doctors today identify.
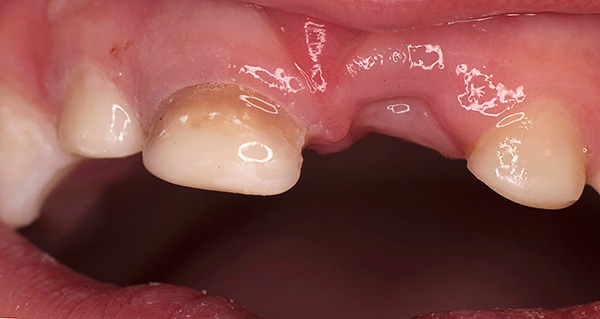
Cross bite in the anterior section - it is diagnosed when one or several teeth are in an abnormal position, most often tilted to the side of the tongue, thereby creating a reverse overlap. For example, one or two cutters may cross.
The photo below shows an example of anterior cross bite:
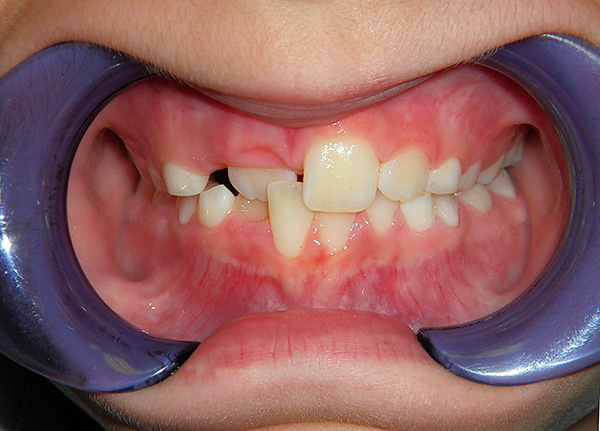
As a rule, the cross bite in the anterior section is combined with an abnormal mesial bite in the lateral part of the dentition, or with the habitual displacement of the lower jaw forward and the formation of a false cross bite. In the second case, it is important to understand the reason why it is more convenient for the patient to push the lower jaw forward.
Cross bite is also distinguished in the lateral part - pathology is characterized by improper closure of premolars and molars (that is, 4, 5, 6 and 7 teeth, as well as wisdom teeth). As in the frontal section, with the cross-bite of the posterior teeth, the anomaly can affect only one tooth, several, and even the entire lateral segment.
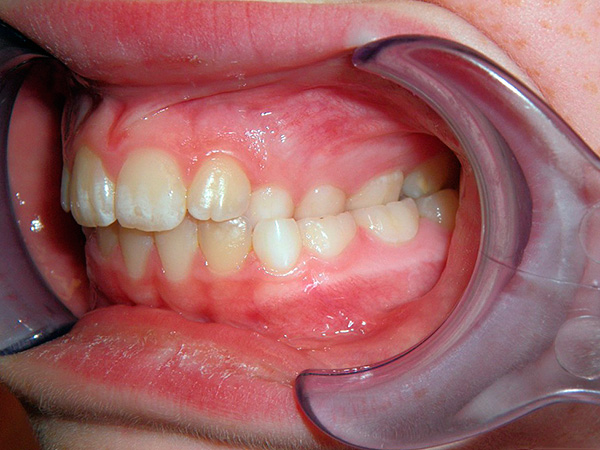
When diagnosing cross bite in the lateral section, it is important to clarify which way the lower jaw is displaced,and also whether there is an offset from only one side of the dentition, or from both. Depending on this, orthodontists secrete a unilateral and bilateral lateral cross bite.
In turn, one-sided cross-sided bite may manifest itself in different ways, namely:
- Unilateral cross bite with a shift towards the tongue (lingual bite). This type of cross-bite often occurs due to crowding of the teeth, as a consequence of the lack of space in the dental arch. Either in children with a delay in changing milk teeth in the milk bite;
- Unilateral cross bite offset cheek (buccal bite). This type of anomaly is quite rare, it can be, for example, due to improper insertion of tooth germs, which causes teeth to erupt outside the dentition in the direction of the cheek. However, the more teeth are in such an abnormal closure, the more likely it is that the reason for this type of cross bite is asymmetry in the development of the jaws;
- And, finally, one-sided cross bite with an offset to the side of the sky (palatinal bite).It is diagnosed when one or more teeth in the lateral segment are tilted towards the sky. The causes of this type of occlusion can be macrodentia (excessively large teeth) and the absence of individual teeth. As a rule, pathology is more common in congenital malformations, or injuries and diseases of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
An example of unilateral cross bite in an adult:
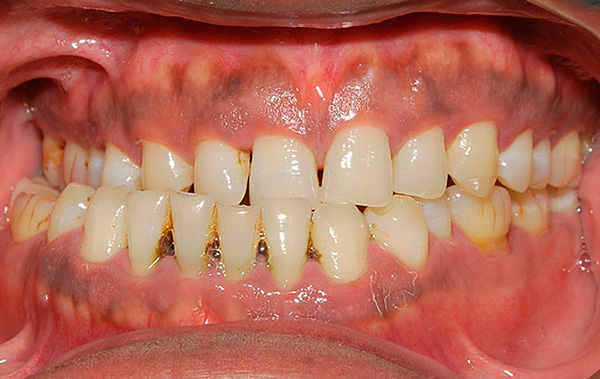
With regard to bilateral cross-bite - the most common cause of this pathology is the discrepancy between the size of the dental arches. Often this is combined with a pathological bite of Class II Angle and the anterior position of the upper jaw, which sometimes requires treatment for treatment to the maxillofacial surgeon for the complete correction of the pathology.
On a note
Cross bite is true and false. In the case of a true cross bite, the doctor makes this diagnosis taking into account the information obtained during the main and additional examination methods. False cross bite occurs when the patient, for whatever reason, pushes the lower jaw to its usual position, thereby creating cross blocking contacts.
Therefore, when examining a patient, it is very important to determine the position of the so-called central occlusion, that is, the position of the teeth, which is convenient for a given person at rest. To do this, the doctor asks the patient to open his mouth and, by relaxing the lower jaw, quietly close the mouth, without intentionally correcting the position of the jaws (which is interesting, not everyone can do it the first time).
The second way to determine the central ratio is that the doctor puts his thumbs on the skin reference points of the corners of the lower jaw, the patient opens his mouth, slightly tilting his head, the doctor asks the patient to relax the jaw, and slightly shaking it and feeling the muscles relax, quickly and without effort directs the jaw up. This procedure is also usually repeated several times to ensure that the central ratio is reached.
The causes of the pathology
As a rule, cross bite is formed in childhood. The reasons for this may be several - let's consider the main ones in more detail.
- Bad habits in early childhood. In the child, the structures in the body are more malleable than in the adult, and the maxillofacial region is no exception. Even the slightest regular pressure sometimes contributes to the development of deviations. For example, the habit of sleeping on one side with your hand under your head, the habit of biting your lip, sucking fingers and other foreign objects, the habit of propping up your cheek with your hand - all these daily repeated actions often contribute to the displacement of the lower jaw, individual teeth, and in some cases even violate normal growth. jaws;

- Ankylosis and arthritis of the TMJ. Ankylosis refers to the pathological accretion of joint elements between themselves, which in the case under consideration limits the mobility of the mandible. This process can be the result of long-term arthritis, that is, an inflammatory process, or a consequence of an injury — for example, obtained by applying forceps during labor. Ankylosis treatment is usually very laborious and requires long-term orthodontic treatment in a team with a maxillofacial surgeon. Sometimes the treatment takes 10 years or more - respectively, and the cross bite will be corrected gradually, as the patient matures. An example of a patient with ankylosis is shown in the photo below:
- Violations of the timing and sequence of teething.Every tooth in the normal should erupt in the dentition at the definition time and at the place determined by this tooth. If, for example, for some reason a tooth does not erupt for a long time, the teeth that are already in place often shift to fill the void (to compensate for a defect in the dentition) - as a result, pathological contacts are created, which is the reason for the development of cross bite. And if the teeth erupt much later, when the dentition is already formed, then the “belated comrades” have to literally find a place for themselves. For example, a tooth may erupt in the area of the transitional fold of the gum, in the direction of the lip, cheek, or palate;
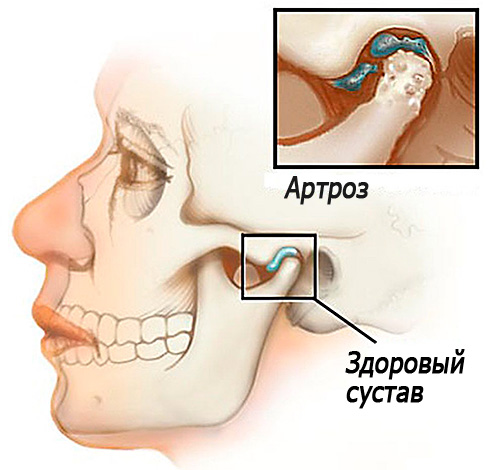
- Diseases of upper respiratory tract (frequent colds, nasal congestion, tonsillitis, adenoids). The fact that the pathological enlargement of the tonsils often leads to obstructed nasal breathing, forced mouth breathing, which is directly related to the formation of the pathological bite. The inflammatory processes of the ear can affect the temporomandibular joint, as it is in close proximity to the ears, and the partitions separating one formation from another are rather thin.Accordingly, inflammation in the middle ear can provoke arthritis, or, in more severe cases, ankylosing of the joint. That is why, in otitis, patients sometimes notice difficulty in opening the mouth painfully and swelling just below the earlobe;
- Early loss of milk teeth. Removal of temporary teeth due to caries and its complications quite often leads to the formation of cross and other types of abnormal bite. As they say, nature does not tolerate emptiness, and if an empty seat appears, the remaining baby teeth will fill it with themselves, leaning and shifting towards the defect, forcing the already permanent teeth to cut out beyond the dentition, or with an inclination or rotation along the axis;
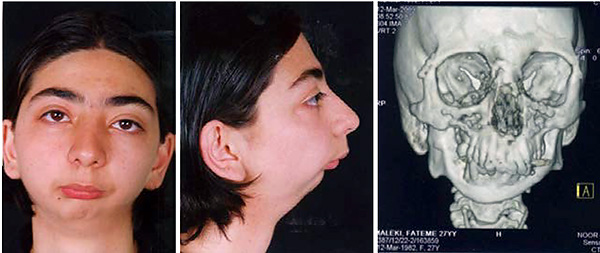
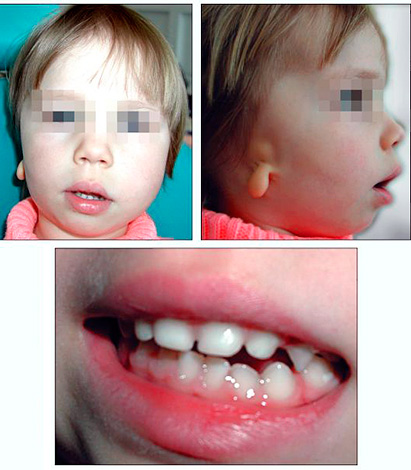
- Congenital malformations (various syndromes). An example is the syndrome of the first and second gill arches - this disease is hereditary, based on violations of the formation of these formations in a human embryo in the first weeks of its development in the womb. And as you know, it is from the gill arches that the structures of the maxillofacial region, the upper and lower jaw, are formed.The appearance of the patient with hemifacial microsomia (the scientific name of the disease) is presented in the photo below:
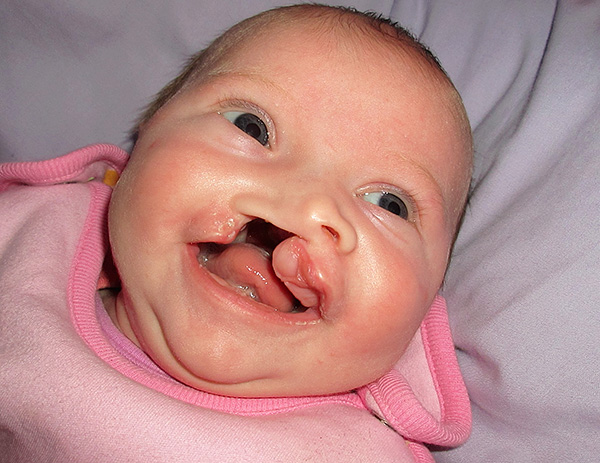
- Cleft lip and the alveolar process of the sky can also cause the formation of cross bite. These congenital malformations of the child are characterized by the presence of fistula between the oral cavity and the nasal cavity, which greatly hampers the normal development of the child, his feeding, speech and the formation of the bite. Treatment of children with cleft lips and the alveolar process of the palate is a complex and lengthy process, planned from the moment the pathology in the fetus is detected. After birth at certain stages of growth, the child undergoes operative treatment to correct the defect and close the fistula.
As usual, the diagnosis of cross bite
Diagnosis of cross-bite in a child begins with a routine external examination. In addition to the initial examination, the orthodontist must carefully collect a history of the child’s life, find out how the pregnancy and childbirth proceeded from the mother.
It is also important to clarify whether there were any serious injuries, strikes, falls, that is, factors that could affect the development of the maxillofacial area.
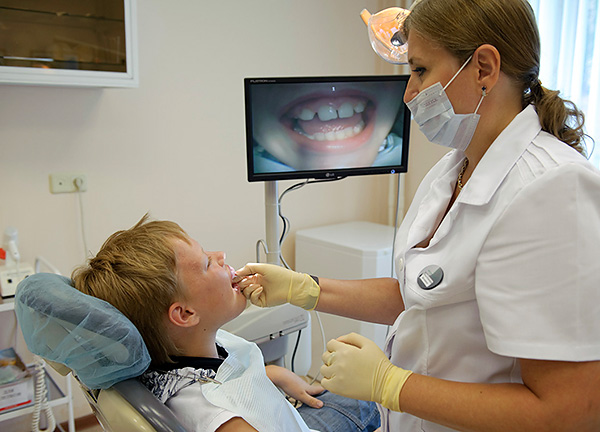
The second important point of diagnosis is to determine the position of the central occlusion using the methods described above, or using other methods, for example, using wax bite patterns (orthopedists use this method for prosthetics in patients with complete or partial tooth loss to properly make a prosthesis).
It is interesting
In rare cases, after dental prosthetics (that is, after orthopedic treatment), patients notice that their bite has become abnormal - for example, there may be signs of cross bite. In other words, when using the prosthesis, contacts blocking the normal jaw closing appear, which cause discomfort when talking and chewing food. This may be a sign of the so-called artificially formed cross-bite, and is a consequence of the fact that the doctor incorrectly determined the central ratio of the patient's jaws.
Other mandatory methods for the diagnosis of bite abnormalities, including cross bite, include carrying out functional tests. For example, a sample can be carried out according to Ilina-Markosyan - this test allows you to assess the degree of pathological displacement of the lower jaw:
- First, the doctor assesses the patient's face at rest and during a conversation (to identify imbalances in the muscles and their excessive tension);
- Then the patient is asked to close his mouth and clench his teeth, without opening his lips. This technique allows us to estimate the habitual displacement of the lower jaw in one direction or another;
- Next, the patient is asked to open his mouth wide and pay attention to how this mixes the lower jaw relative to the midline of the face;
- After determining the central ratio, the doctor assesses how aesthetically the patient's face would improve in this position compared to his usual occlusion.
Of the additional diagnostic methods, radiographic examinations are mandatory:
- Orthopantomogram (in children over 5 years). Allows you to assess the asymmetry of the bony structures of the jaws;
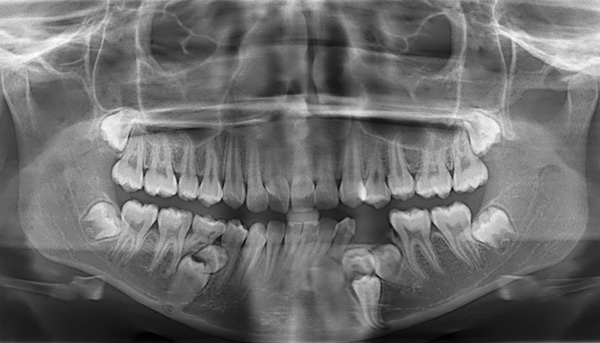
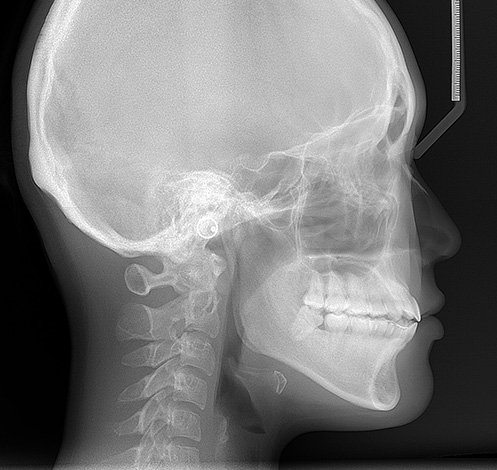
- Telegentogram. Allows you to evaluate the patient's skull as a whole and see which fragments of the jaw bones are shorter than the others;
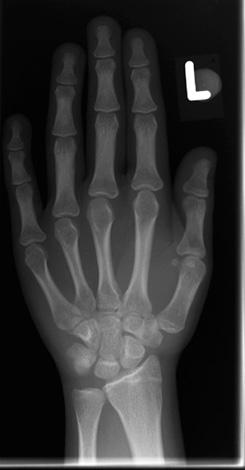
- X-ray of the child's hand - is carried out during adolescence in order to understand at what stage of bone growth the child is now (this is important for choosing the best treatment plan);
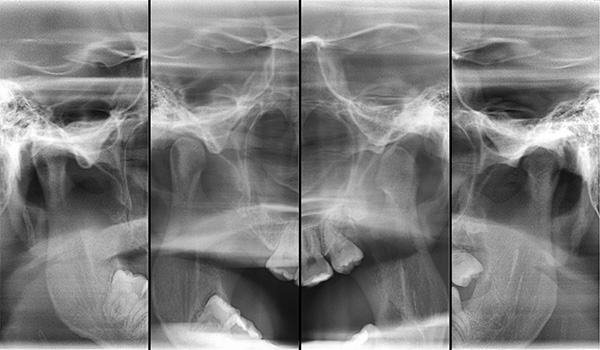
- X-ray of the temporomandibular joint in the open and closed mouth of the patient - it is necessary to make sure that the temporomandibular joint is not the cause of the cross bite.
What problems may arise in the presence of cross bite
Teeth erupted outside the dentition and create cross-contact can seriously injure the oral mucosa during a conversation and meal. Patients often complain of biting their cheeks, lip trauma - in such cases, you should seek help from an orthodontist as soon as possible, as permanent injury to soft tissues is dangerous and can lead to ulceration of wounds and their suppuration. Moreover, if this process is long (chronic), then such injuries can degenerate into malignant tumors of the oral cavity.
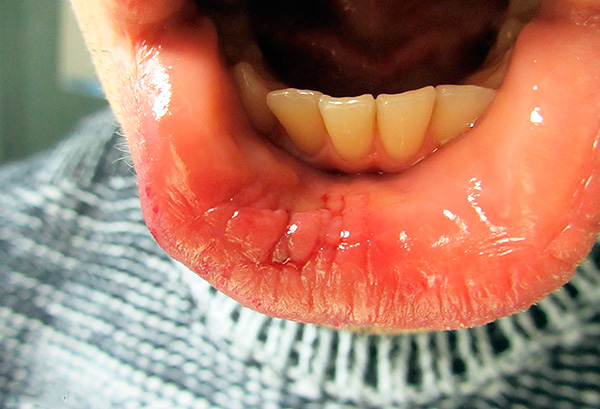
Further. Due to the excessive pathological load on the teeth in the cross-bite, there is a danger of increased abrasion of the teeth, for example, the cutting edges of the incisors. Sometimes this problem is very acute, when a kind of hemp remains from the teeth.
In severe cases, patients may experience severe facial asymmetry, pain in the area of the TMJ and difficulty opening the mouth, and regular headaches.

If you examine the reviews of adult patients, among other problems described, people sometimes note the impossibility of taking solid food and problems with the gastrointestinal tract (as a result of an unbalanced diet).
Parents of children with pronounced crossbite often note their excessive shyness, isolation, problems with communication, low self-esteem, because in childhood any aesthetic defects very often attract ridicule from peers. In some such cases, to achieve the best effect of treatment, the orthodontist may additionally recommend classes with a qualified psychologist who will improve the emotional status of the child.
Approaches to the treatment of pathology in children
Depending on the severity of cross bite and on the age of the child, the treatment of the pathology may differ markedly.
In the early replaceable bite (but usually not earlier than 5-6 years of age of the child), the method of choice will be treatment on removable laminar apparatus with an expanding screw and a sectoral saw cut. That is, the screw will expand exactly the segment of the dentition that needs such a correction.
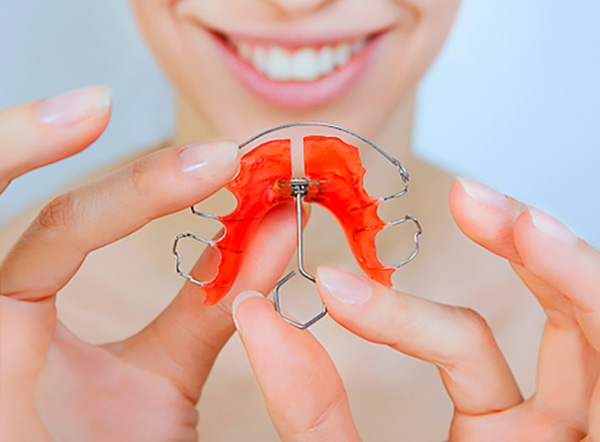

In addition, the doctor may include additional elements in the design of the apparatus for correcting cross bite - cheek and labial pilots for normalizing the muscles in this area, as well as for moving soft tissues away from the teeth - to prevent unwanted pressure that tissues can exert on the teeth.
Generally speaking, an experienced orthodontist may include in the design of a removable apparatus a wide variety of additional elements to increase the effectiveness of the treatment.
Functional devices, such as the Frenkel function regulator, work well when correcting cross bite: this device normalizes the natural myodynamic balance of the maxillofacial region.
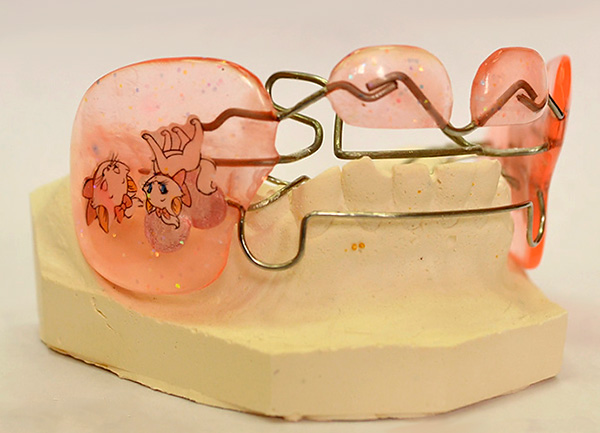
In addition, the cross bite is often combined with improper closure of the first molars, so the orthodontist may suggest the use of such devices as the activator Andrezena-Goyplya and Persin activator for the treatment of anomalies of classes II and III.
On a note
From the age of 10-12 years old, if the removable equipment failed to achieve the desired effect, you can use frame devices,manufactured individually on the model of the jaws of the child. The skeleton apparatus is soldered to orthodontic rings, selected by the orthodontist in advance. The doctor adjusts the device so as to increase its impact on the desired side of the dentition.
With a significant narrowing of the upper jaw, the doctor can use for the treatment of cross bite extender structures such as the Biedermann apparatus for rapid palatal expansion (also with a screw, the doctor sets the activation mode). Activation is made by either the parents or the patient himself, on average once every 7-10 days.
An example of such a device is shown in the photo:
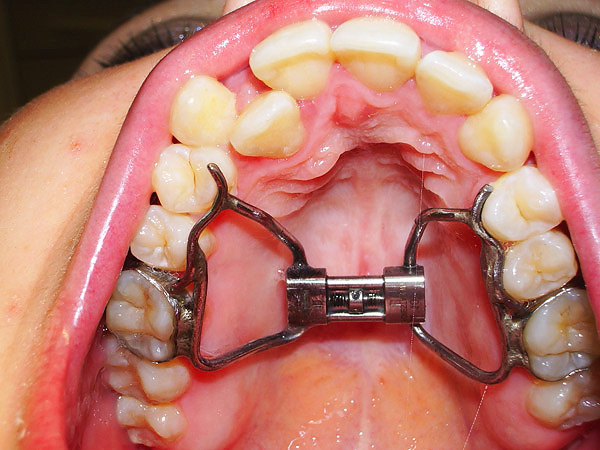
Sometimes the correction of cross bite is carried out in two stages, that is, treatment with the help of devices is a preparatory stage for treatment on the bracket system, which works directly with the angles of inclination of the teeth, corrects unnecessary turns and places each tooth in its place in the maxillary arch.
Treatment of cross bite in adults
In adult patients, the treatment of cross bite usually begins on the bracket system. It is also possible to use the frame expanding devices described above - in conjunction with a bracket system, or before preparing for fixing braces.
To correct the actual cross overlap at the stage of wearing rigid rectangular arcs, the doctor additionally connects elastic cross cravings in the lateral and anterior parts of the dentition, which the patient wears 12 hours a day and overnight, removing during meals.
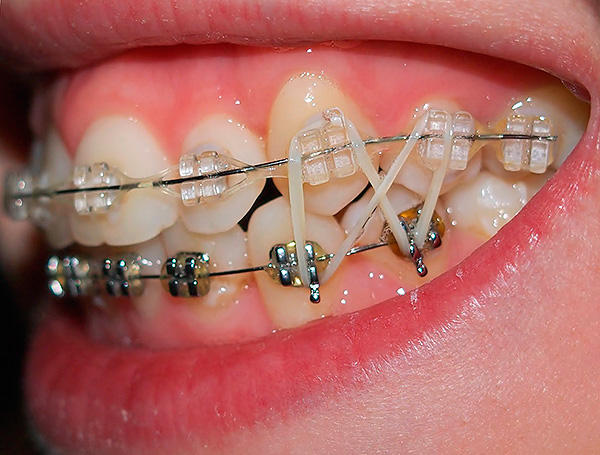
Sometimes you can limit the partial fixation of braces only to those segments of the dentition that need treatment.
On a note
In case of severe severity of the pathology, the orthodontist negotiates with the patient the possibility of using orthognathic surgery. If the patient agrees to surgery, then the treatment plan is adjusted accordingly to exactly what needs to be achieved to complete the work of the surgeon.
Often, patients immediately abandon this method of treatment because of fear of surgery on the maxillofacial area. Then the orthodontist, as far as possible, corrects the pathology only with the help of bite correction, however, the jaw bones remain in the wrong position.
Preventive actions
For the prevention of the development of cross bite in a child, it is important from infancy to fight the bad habits of the baby,regularly visit a pediatrician and a dentist (caries on milk teeth must be treated in a timely manner).
At the age of 5-6 years, it is advisable to go to a consultation with a doctor orthodontist to hedge yourself and start treatment in time, if necessary. It is very important to monitor the formation of the correct posture of the child: many scientific studies have been conducted that prove the relationship between persistent violation of posture and pathological bite.
Exercise, attend a course of therapeutic massage. This will help to avoid many health problems, and not only with a bite, because our body is a single whole, and everything in it is closely interconnected.
Be healthy!
(If you have personal experience of correcting cross-bite in your child or child, be sure to leave your review at the bottom of this page in the comments field. Such information will be of great interest to those who are in a similar situation, but are just beginning their the way to a beautiful smile ...)
Useful video: a girl talks about her case of correcting cross bite
What you should know about bite correction at different stages of its formation