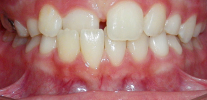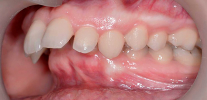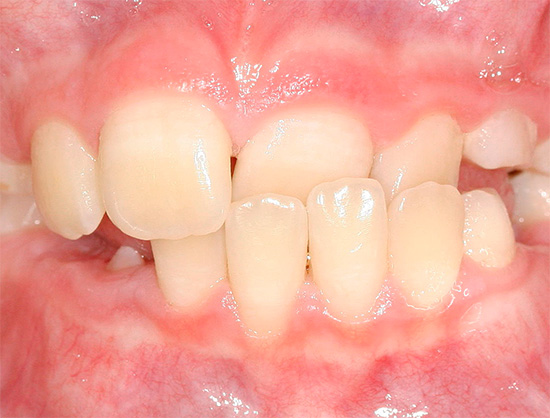
Anomalies of the bite are various kinds of deviations from the normal arrangement of the tooth rows relative to each other. Such deviations can occur both in adults (for example, after the eruption of wisdom teeth or as a result of injury), and in children during the period of growth and the formation of the dentofacial system.
The severity of abnormal occlusion can vary significantly - depending on the severity of the pathology, I, II and III degrees are distinguished. However, even quite insignificant malocclusion sometimes create very serious problems for a person’s normal life, ranging from psycho-emotional to eating problems.
Therefore, let's talk about what kind of bite anomalies are in general and what methods of treatment modern dentistry offers in a given situation. And, importantly, We'll see what preventive measures parents can take to protect their child from biting problems in the future..
What are bite anomalies?
Orthodontists in their practice use the classification of Angle.He singled out 3 types of bite, depending on how the first molars (that is, so-called molars) join together.
The first class of Angle is considered the norm of occlusion, a kind of standard, which the orthodontist tries to achieve, if there are any deviations from the normal ratio of teeth. It was revealed that it is precisely the closing of the teeth according to the first class of Angle that is the most physiological for the entire dental system of the person.
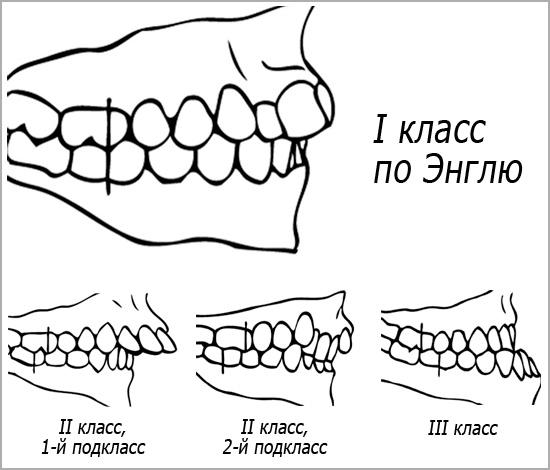
The second and third classes of Angle bite anomalies will be discussed in detail below.
On a note
Today, orthodontists classify the closure abnormalities in the lateral part of the teeth as sagittal anomalies, and the deviations in the anterior part of the dentition as vertical bite anomalies.
Such pathologies are also attributed to anomalies of occlusion, when, during the normal closure of teeth, the following defects are present in the lateral part:
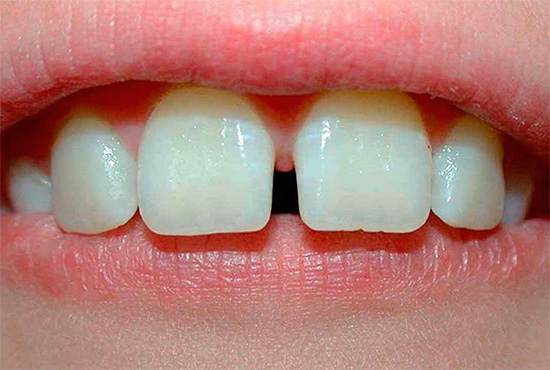
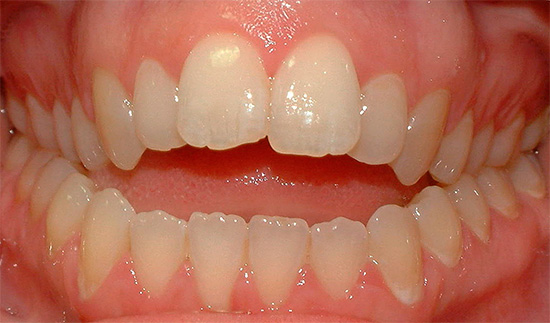
- Middle diastema - the gap between the first incisors of the upper jaw. In the early interchangeable bite (2.5 to 4.5 years), the diastema is a normal physiological condition when the bridle of the upper lip passes between the temporary central incisors.During normal development during the eruption of the lateral incisors and canines, this gap closes, and the attachment of the bridle is shifted and interwoven into the mucous membrane of the upper lip. In some cases, the cause of diastema may be the presence of a supernumerary tooth in the region of divergence of the central teeth of the upper jaw (this pathology can be identified by X-ray examination).
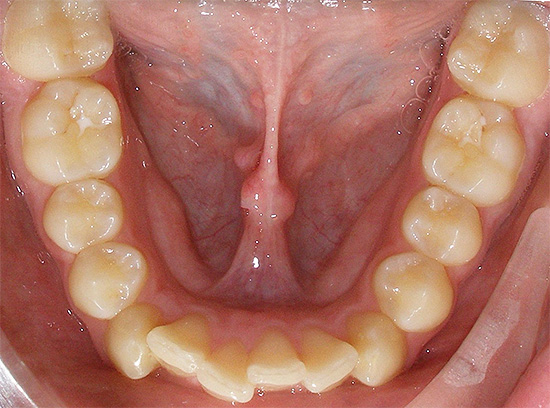
- The crowding of the teeth - this anomaly of the bite occurs when the size of the teeth and dental arches do not match. Approximately 60% of children in the European population show some degree of crowded teeth. In such a situation, the loss of a permanent or temporary tooth can cause the adjacent teeth to shift to the area of the defect in order to fill the void. The crowding of the lower teeth in adolescence is mainly due to the eruption of wisdom teeth and the pressure they have on the dentition.
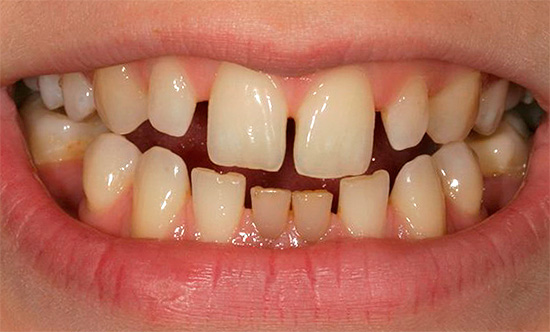
- Tremes - gaps between teeth. It is important to understand that in the replaceable bite, the presence of three is a normal phenomenon, caused by the fact that the milk teeth diverge and prepare a place for permanent larger teeth.Trems can appear with microdentia - the small size of the teeth themselves. In any case, the parents of the child should pay attention to such gaps between the teeth, as the food gets clogged up in them, which, with poor hygiene, can lead to caries and inflammation of the gums.
- Transposition or dystopia of the teeth - these similar terms refer to the eruption of a tooth in an unusual place for it. There are several reasons for this phenomenon. For example, this may be the abnormal position of the dental germ due to hereditary factors, fetal abnormalities during pregnancy, maternal illness during the first stages of pregnancy, childbirth trauma, imposition of forceps during obstetrics, etc. The reason for dystopia of the teeth may be different - lack of space in the dentition causes them to erupt outside the dental arch: cheeks, lips, causing injury to the child during chewing and forming a center of inflammation, because sometimes it is rather difficult to get to such a tooth when cleaning.
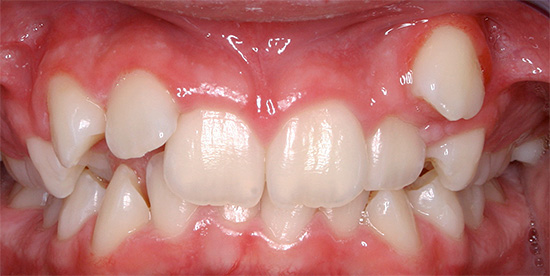
The following bite anomalies will be considered in more detail.
Distal bite
Distal bite is the most common bite pathology among the European population.Many associate its occurrence with the nature of the food intake - we began to eat more soft food, in connection with which the need for chewing and applying efforts disappears. The lower jaw is reduced in size, it is no longer pushed forward, and the upper jaw prevails over the lower jaw. Distal bite is an anomaly of class II according to Engl.
The photo shows an example of the distal bite:
In the distal occlusion, there are two subclasses, depending on the inclination of the incisors of the upper jaw.
Class II, subclass I - the upper incisors are inclined towards the upper lip. The reasons for the formation of this phenomenon may be the habit of thumb sucking, prolonged nipple sucking, the habit of keeping the tongue between the teeth, as well as the hyperactivity of the muscles of the upper lip and the circular muscles of the mouth.
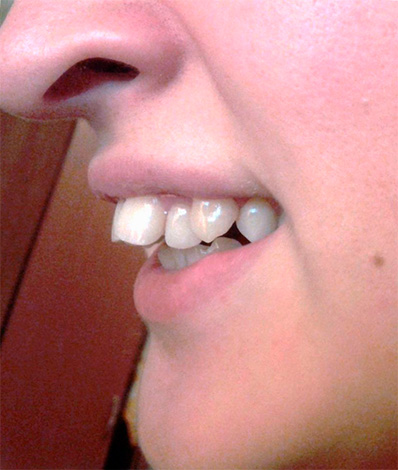
The facial features of this type of occlusion are a concave profile, open lips, compensatory stretching of the lower lip forward and upward. Sometimes there are cases of excessive activity of the lower lip (for example, with the habit of biting the lower lip), then the upper incisors move forward, and the lower ones fall backwards from the normal position.
Class II, subclass II - the upper incisors are inclined towards the sky. The causative factor can be the habit of biting the upper lip, as well as the infantile, that is, the children's type of swallowing with the tension of the muscles of the lips and cheeks. In such cases, when examining a patient, the lips are closed, the lower lip is thickened, a deep crease at the chin is released.
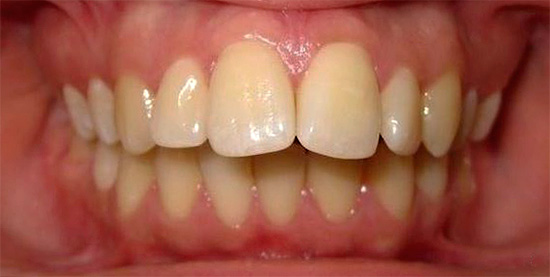
Distal bite is often accompanied by speech disorder, inability or difficulty in biting food, difficulty in breathing, as well as pain and dysfunction in the temporomandibular joint.
Notice how the shape of the jaw changes after the treatment of the distal bite:
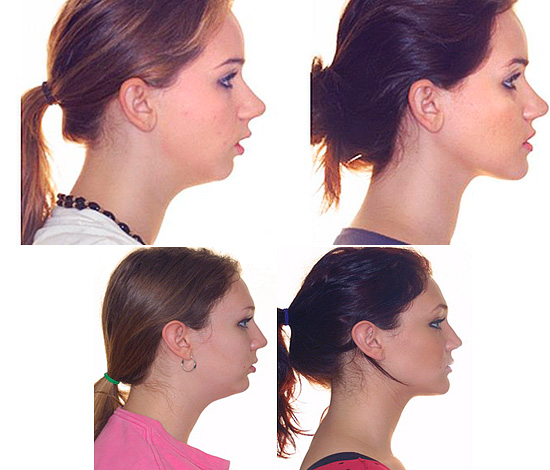
Mesial bite
Compared with the distal bite, the opposite situation is observed in the mesial bite - when the upper jaw lags behind the mandible in size. This is the third class of bite abnormalities according to Angle's classification.
The reasons for the development of mesial bite can be:
- birth injury;
- early removal of the teeth of the upper jaw;
- genetic predisposition - for example, the child got a massive lower jaw from his father and a small upper jaw from his mother.
Often, with this occlusion anomaly, one can see such a phenomenon as periodontal compensation: the teeth on the upper jaw are crowded, while on the large lower jaw they are located exactly, there may be gaps between them (three).
Facial signs of mesial bite: a convex profile, prominently protruding chin, drooping of the upper lip and protrusion of the lower lip.
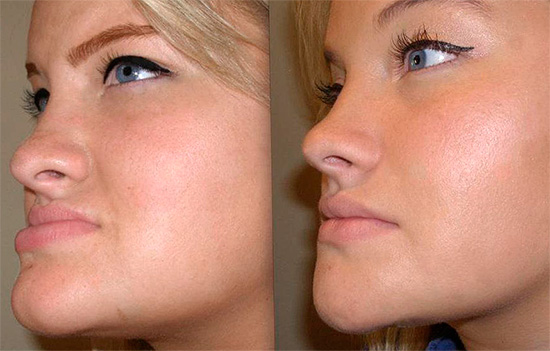
Mesial bite contributes to the development of temporomandibular joint disorders - due to the anterior position of the head of the maxilla in the articular fossa, a constant sprain of the temporomandibular joint, tension of the temporal and masticatory muscles, and the development of pain as well as headaches may occur. Sometimes patients complain of injury to the upper lip with the teeth of the lower jaw during meals.
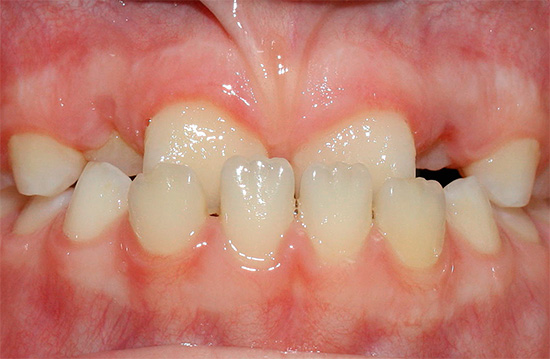
Open bite
An open bite is the non-clogging of the teeth in the anterior region, which causes a gap between them. Normally, the upper incisors should overlap the lower incisors by one third of the crown. With the open bite overlap is absent altogether, or minimal.
There are the following types of open bite:
- front open bite - no overlap in the anterior part of the dentition with closed lateral teeth;
- lateral open bite - when the teeth overlap in the anterior section, the lateral teeth do not close.
Among the causes of this anomaly describe:
- hereditary factor;
- mouth breathing - in this case, the child needs to consult an ENT doctor, because it is important to understand why the child breathes through the mouth. Perhaps there was an injury and there is a curvature of the nasal septum, or the presence of adenoids. Sometimes weakened immunity and frequent colds can also impede the nasal breathing of a child;
- finger sucking habit, long sucking nipples and other items;
- the infantile type of swallowing and the habit of laying the tongue between the teeth;
- congenital malformations - cleft of the alveolar process of the lip and sky;
- endocrine disorders;
- maxillofacial tumors.
Facial signs of open bite: the mouth is half-open, but if it is possible to close the mouth, then the face is tense.
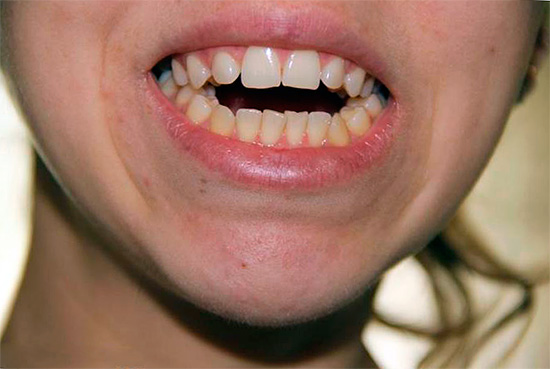
Patients complain about the inability to fully bite off and swallow food, often lisping is observed.
There are 3 degrees of severity of open bite, depending on the size of the vertical gap: I degree - up to 5 mm, II degree - from 5 to 9 mm, III degree - more than 9 mm.
Also pay attention to what teeth are closed in the lateral divisions. This classification by severity is used by dentists in the selection of military servicemen undergoing a medical examination.
Deep bite
Deep bite is called in which the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth. Sometimes the lower teeth rest with cutting edges against the sky mucous membrane, then they speak of a traumatic deep bite.
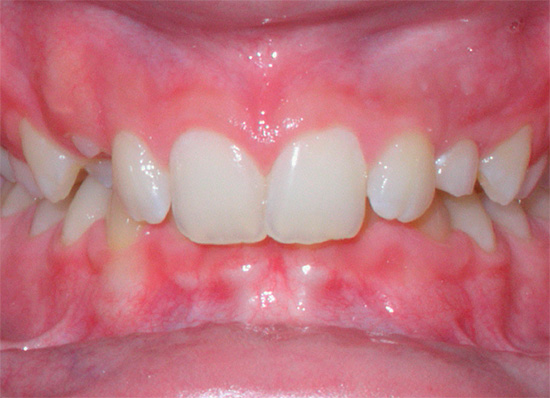
Possible causes (etiology) of the occurrence of a deep bite:
- early loss of chewing teeth (due to trauma or complications of caries leading to their removal, or their primary absence is adentia);
- violation of nasal breathing;
- inappropriate swallowing;
- violation of speech function;
- bad habit of sucking various items;
- violation of the terms of teething, especially in the lateral parts of the dentition;
- early abrasion of temporary teeth.
As in the case of an open bite, three degrees of a deep bite are also distinguished, depending on the severity of the anomaly (that is, the amount of overlap of the lower dentition and the upper one).
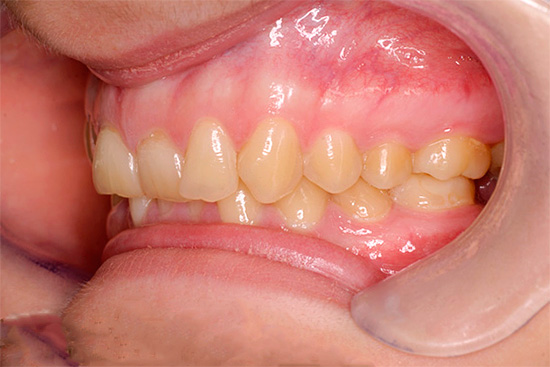
Facial signs of deep bite:
- inversion of the lower lip out;
- the severity of the chin crease;
- shortening of the lower third of the face (sometimes doctors use the term "avian face).
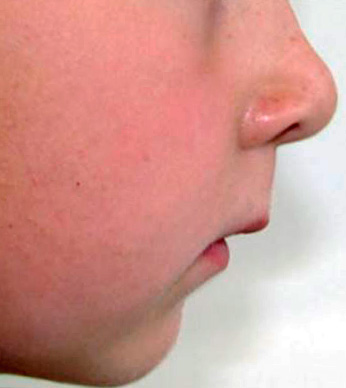
As a rule, with this anomaly of the bite, patients complain of difficulty biting and chewing food, and often there is pain in the temporomandibular joint, and headaches are possible. Very often a speech defect occurs - patients talk through their teeth.
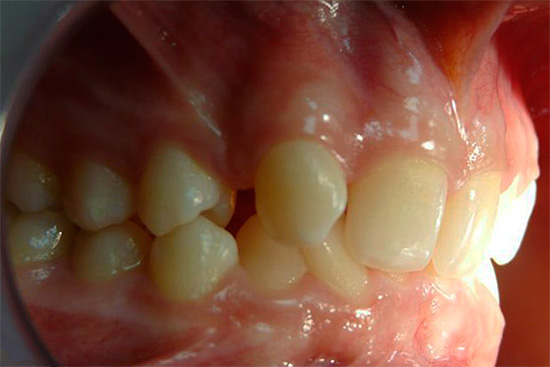
Cross bite
As the name implies, when cross-bite, the teeth intersect with each other.
When cross-occlusion, there is a discrepancy in the size of the jaws in the lateral division. Orthodontists refer this type of bite to transversal anomalies, and the pathology can be one-sided and two-sided.
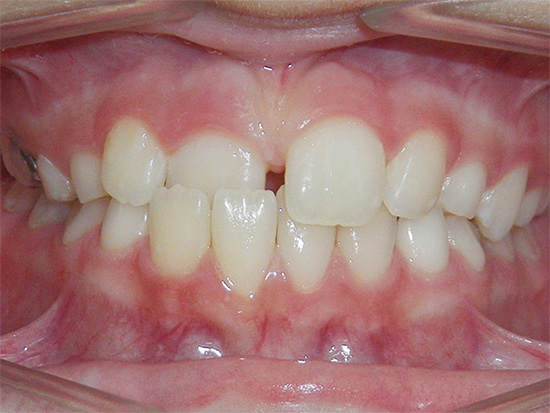
Cross bite occurs in both anterior and lateral divisions.
With the side bite type, orthodontists distinguish the following types of this anomaly:
- with a displacement of the lower jaw in the direction of the tongue - lingual cross bite;
- in the direction of the cheek - buccal cross bite;
- and towards the sky - a palatal crossbite.
Causes of anomalies:
- bad habits (listed above);
- trauma or damage to the jaw, including birth trauma;
- the imposition of forceps at childbirth;
- lack of individual teeth;
- disorders of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) - ankylosis, habitual dislocation of the joint, hypoplasia of the joint on one side;
- the indelibility of the surfaces of milk teeth;
- violation of the sequence and timing of teething.
The photo below shows an example of cross bite in an adult:
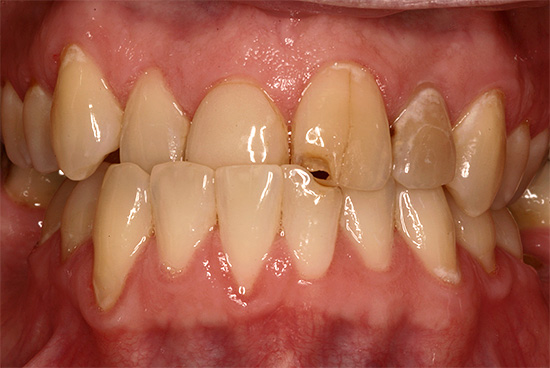
Frequent complaints from patients and parents:
- the presence of aesthetic defect with a noticeable discrepancy between the size and position of the jaws;
- difficulty eating
- violation of sound pronunciation;
- gum disease due to possible injury when chewing and speaking;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
As a rule, vertical occlusion anomalies are combined with anomalies in the sagittal direction.
The first appointment with the orthodontist - as usual
Often, when parents with children come to a consultation with an orthodontist, their first question is something like: “Doctor, are we not late with the treatment?” Indeed, it is very important to arrive on time, since the methods of orthodontic treatment largely depend on the specific age of the child. .

It should also be borne in mind that if the child is disciplined and tuned in for treatment, the bite is usually managed to be corrected faster and more efficiently than in adulthood.
The first method is better to plan in 6-7 years, since at this age the first permanent teeth of the upper and lower jaw erupt. However, you can apply before, if you see that your teeth are growing a little differently than expected - in order to insure yourself and not trigger the situation.
It is important to properly prepare the child before going to the doctor, explaining that the doctor will only look at the teeth (so that the child is not afraid and was willing to cooperate with the doctor).
At the primary consultation from the age of 4-5 years and older, when the children are already more conscious, the doctor can refer you to the orthopantomogram image. This will help to assess the state of the dental system, the presence or absence of a child of the rudiments of all permanent teeth, the location of the roots of the temporary teeth, as well as the stage of development of the teeth.Sometimes temporary teeth linger in the jaw and are an obstacle to permanent exit.
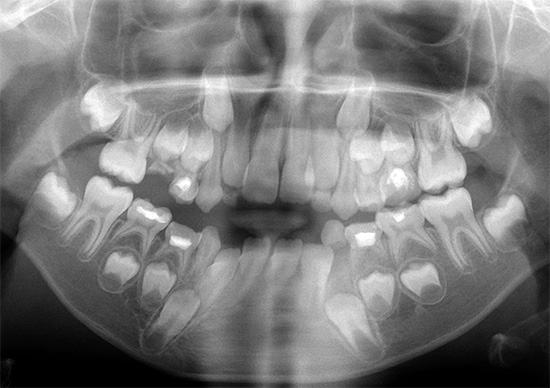
Also, using an orthopantomogram, one can assess the presence of carious cavities, their depth, see the foci of the inflammatory process in the root of the tooth, see the condition of the underlying bone structures of the upper and lower jaw (maxillary sinus, mandibular canal). All this helps to properly plan the course of treatment of bite abnormalities.
At the first admission, the orthodontist can take photographs of the face and dentition of the patient, and may also take pictures from the upper and lower jaw to fully assess the bite of the child.
On a note
Sometimes doctors plan to take the impressions as a separate visit (usually in the morning). The impressions are removed using special dental spoons in size and shape of the jaws.
It is better to carry out this procedure on an empty stomach, or after 2 hours after eating, because a specific foreign body can cause an emetic reflex when in contact with the soft tissues of the oral cavity. This, in turn, will leave an unpleasant impression on the child and may affect the quality of the impression.
What does an orthodontist pay attention to?
First of all, the orthodontist draws attention to the complaints of the child himself and his parents. Also rated:
- harmonious development of the face;
- attachment of upper lip and tongue frenulum;
- depth of the vestibule of the mouth;
- condition of the oral mucosa;
- the patient's speech (perhaps the child will need speech therapy intervention).

Just like all doctors, an orthodontist collects a history of the life and health of a child. The doctor will also be important to know the nature of the course of pregnancy and childbirth. In addition, the type of feeding plays a significant role in the process of formation of dental anomalies.
If there are complaints of pain or muscle tension in the temporomandibular joint, the doctor may prescribe additional studies - a X-ray of the temporomandibular joint when opening and closing the mouth, electromyography is a method to evaluate the coordinated work and tone of the chewing and temporal muscles.
In some cases, computed tomography (for completeness assessment of the structures of the maxillofacial area) is required.
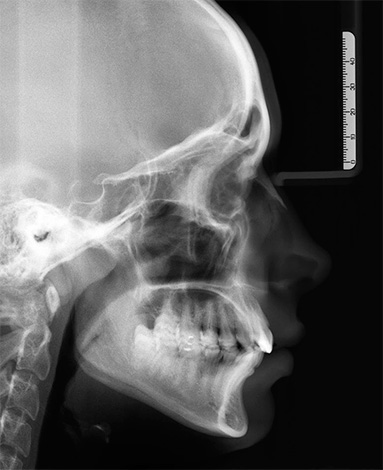
At the age of 12-14 years and later, the main criterion for making a correct diagnosis is the study of the X-ray of the head in lateral projection.This type of research allows the doctor to get an idea of the nature of the growth of the jaw bones relative to each other and the base of the skull. And also about the form of the pathology of the bite - either an anomaly of the bite was formed only due to the lack of space for the teeth in the dental arch, or it is due to underdevelopment and incorrect position of the jaws, which is correctable, but sometimes requires the intervention of the maxillofacial surgeon.
Bite Abnormalities Treatment Methods
In the treatment of bite abnormalities in children, the doctor can use the most diverse combinations of functional devices.
For example, it can be removable plate devices with an expanding screw and combinations of additional elements. The task of these devices is to normalize the growth of the jaws in relation to each other. Plates, of course, exert pressure on the teeth with the help of arc elements or loops (for example, a Reinbach loop to close the diastema), but they cannot act sufficiently on the character of the inclination of the teeth.
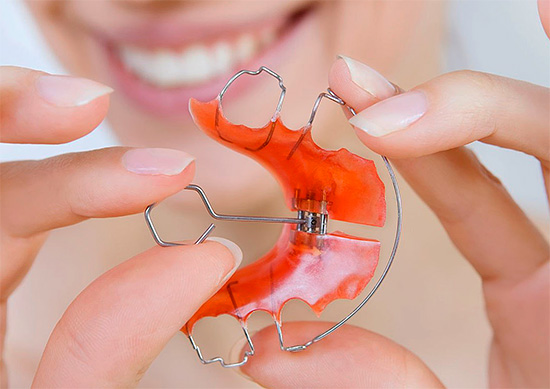
Therefore, with a significant crowding and incorrect position of the teeth, the doctor may recommend the use of a bracket system, since it is the braces that are able to fully affect the position and tilt of the teeth.
Important
The mode of wearing plate removable expanding devices prescribed by a doctor. The main rule is if you want to achieve results from the treatment, then you need to wear the device as much as possible day and night. Sometimes patients, but mostly parents of children, complain that, well, they say, we paid money, but there is no effect. The doctor begins to ask: "How do you wear?". Answer: “Well, after school a couple of hours, at night the child refuses to sleep with a record ...”
There are also removable devices that correct the abnormal occlusion by normalizing the work of the muscles of the maxillofacial region - for example, the functional regulator of Frenkel. Its design includes special elements: side shields for cheeks and labial pellets, fastened together by a metal arc.
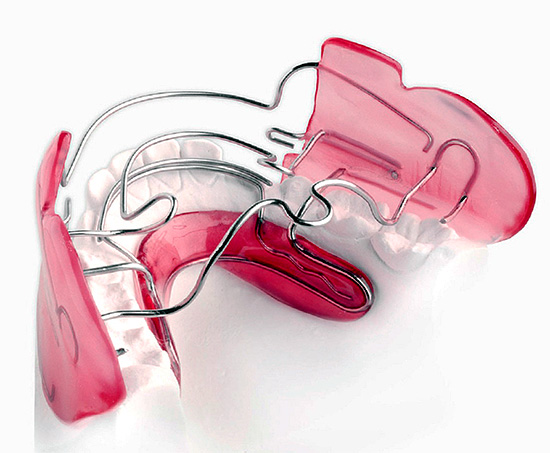

The Frenkel regulator is divided into three types, depending on the child's bite anomaly. It affects the closing of the lips, breathing and the position of the tongue.
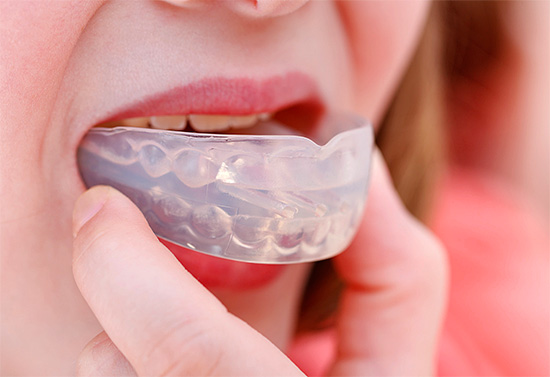
If there are complaints about the temporomandibular joint, the doctor may prescribe the wearing of an articular silicone splint.Now produced a large number of different combinations of these devices, both domestic and foreign manufacturers. The choice of the type of such apparatus also depends on the type of occlusion anomaly and the age of the child.
The task of articular silicone tires is to unload the muscles surrounding the joint and a kind of "reprogramming" their work to normalize the functions of the joint, reduce the load on its structural elements (capsule, ligaments). It is also important to observe the wearing regimen prescribed by the doctor, so that the treatment is not wasted.
On a note
An orthodontist can recommend you myogymnastics - this is a complex of physiotherapy exercises to ensure the coordinated work of certain muscles. The complex can be assigned as a separate treatment option, or with the aim of preventing the formation of improper bite. Myogymnastics requires discipline and interest from the child, as well as visiting the doctor to control the exercise every two weeks, so not all orthodontists use this method in their daily practice, although it is very effective.
The use of a bracket system in the treatment of bite abnormalities is the method of choice (including in adulthood).What is a bracket system? In simple terms, braces are fixed devices that are fixed to the teeth, with locks, which have a special program for moving teeth. The movement is carried out by the arc, which is fixed in these locks, the arc moves and reaches the ideal shape of the dental arch.
The average treatment time on braces is 1.5-2 years.
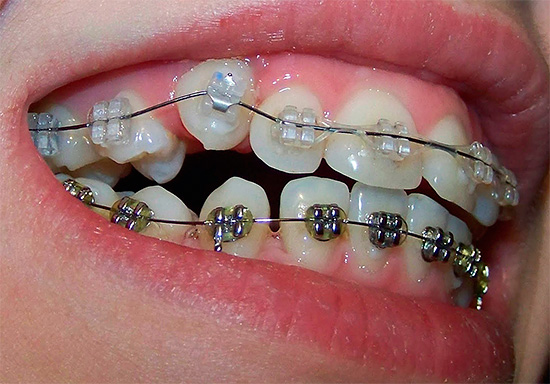
Today there are many modifications of bracket systems. For example:
- ligated braces, that is, the arc is tied to the bracket with the help of special metal or rubber ligatures. Ligatures provide a hard grip arc with a bracket and limit the slip along the dental arch. The disadvantage of this equipment is the need for frequent visits to the doctor - once a month (and some doctors prescribe patients every two weeks). Visits are necessary to replace ligatures, because they tend to weaken.
- Self-ligating bracket-systems differ from the previous ones in that in the design of a bracket there is a lid that keeps the arc inside the lock. This provides a more free sliding of the metal arc along the dentition, which is more comfortable for the patient, reduces the number of visits to the doctor and the treatment time. But such brackets are more expensive than ligature systems.
Bracket systems also differ in the material from which they are made:
- The simplest and most noticeable are metal braces. Plus of them is that they are very durable. If the bracket is peeled off, it can be pasted again. Practice shows that metal braces guarantee a reduction in the terms of treatment of abnormal occlusion.
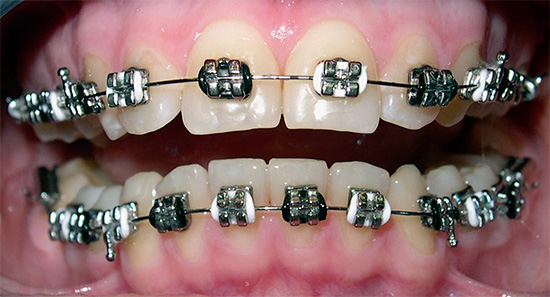
- Plastic braces are more aesthetic, since they coincide with the natural color of teeth. Of the minuses - they are painted from food and are not as durable as metal ones, which sometimes forces the doctor to glue a new bracket because of the initial failure, which is an additional expense for the patient.
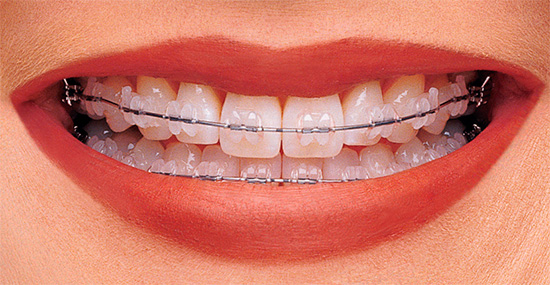
- Ceramic braces - not visible on the teeth, more durable than plastic. Of the minuses - due to the high degree of arc friction in the castle, the total treatment time increases. The cost of such braces is higher than metal and plastic.
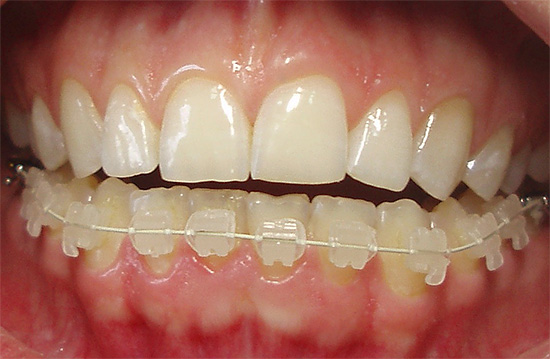
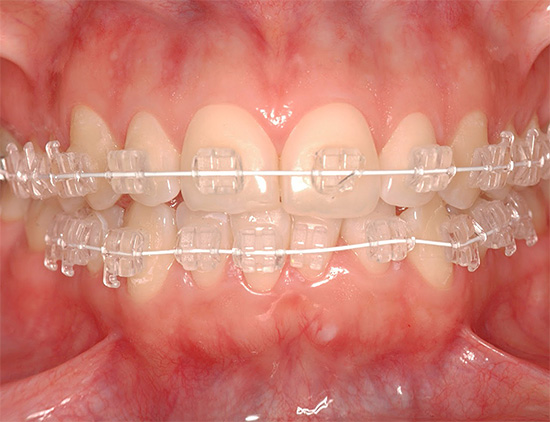
- Sapphire braces - the most transparent and invisible on the teeth, but much more expensive than analogues.
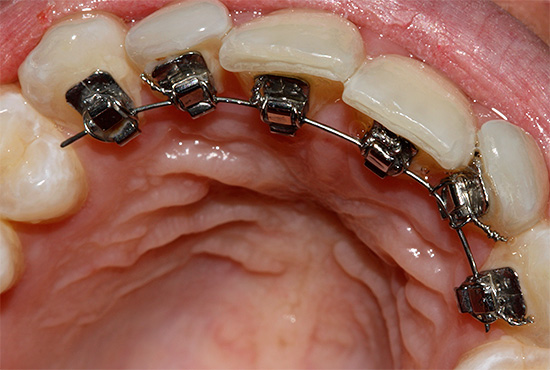
- Lingual braces - the doctor fixes this type of braces on the lingual side of the teeth. Thus, they are not visible to others. However, when wearing such braces, certain difficulties arise: constant irritation of the tongue, disturbed diction.Lingual braces require more thorough care and hygiene than in the case of wearing conventional braces. The doctor orders the whole set individually for each patient and, accordingly, if the bracket or the arc breaks, there will be difficulties with repairing and replacing, as arcs and braces from other systems will not work in this case. The cost of treatment with lingual braces is much higher than on conventional systems.
On a note
It is important to maintain a good level of hygiene when treating with braces, brushing your teeth after each meal, and using brush brushes in addition to the brush to clean the area around the bracket between the arch and the teeth. If we neglect the hygiene, then the formation of white spots on the teeth is possible - foci of enamel demineralization at the place of the braces, such stains do not pass later and require treatment.
Methods for the prevention of bite anomalies
It is well known that it is always better to prevent the development of the disease than to cure its effects.
To prevent the development of malocclusion, you should adjust the bad habits of the child. For example, in time to separate the child from the nipples.If it is impossible to influence a child on your own, then you can buy a special set of devices for the prevention of occlusion anomalies, which is appropriate for the child’s age (for this, it is better to consult a doctor to find the right equipment for you).
Among the set of devices for the prevention of the formation of anomalies of the bite can, for example, highlight the following:
- Karbitz's vestibular plate - it looks like a nipple, it is adjacent to the vestibular surface of the teeth, thereby weaning the child from the bad habit of sucking fingers, pacifier, lips, to lay one's tongue between the teeth, etc.
- Kraus' vestibular plate - shown when the habit of sucking the tongue is present and the function of swallowing is impaired.
- Mulleman's Propsor - this device interferes with oral breathing, is indicated in the treatment and prevention of distal occlusion and open bite, keeps the jaw in the extended position and separates the chewing teeth.
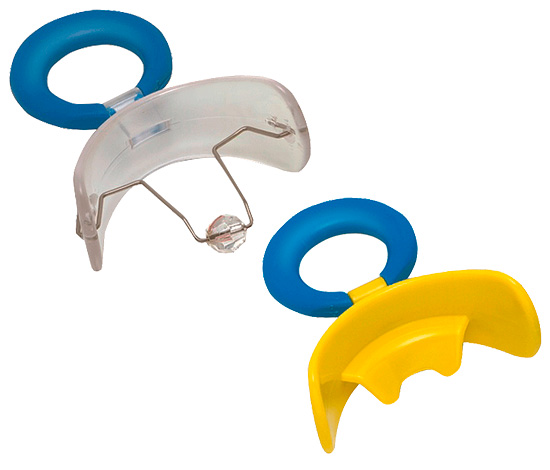

There are other types of devices for the prevention of the formation of bite anomalies, and for each type of occlusion.
Monitoring the health of the child requires the inclusion of both dentists and general practitioners to monitor the proper development of all organs and systems.Regular visits to a pediatrician, general practitioner, otolaryngologist and speech therapist will help notice the problems of the dental system.
Of course, orthodontic treatment is usually not carried out for vital reasons, but depends only on the person’s desire to improve his appearance (or the child’s appearance). But one should not forget about such an important factor as the psychoemotional state of the child with an abnormal bite: even if there is a seemingly insignificant flaw, the child already feels not like everyone else, he often becomes depressed and withdrawn. In turn, this is reflected in his communication with others and self-esteem, which often leaves an imprint on the rest of his life.
Whatever treatment method you choose, a lot depends on the mood of you and your child for long-term treatment in compliance with specific recommendations of the wearing regimen mode, as well as on your trust in the doctor and coordination of your actions with him.
Be healthy and attentive to the health of your children!
Interesting video about the classification of bite anomalies and methods of treatment in appropriate situations
An orthodontist tells about the important nuances of correcting the wrong bite