The teeth can hurt the child at any age, even at the age of 1.5-2, when, it would seem, they only barely had time to erupt. The most common cause of toothache is caries, which often develops unnoticed by the parents of the baby, until one day the child begins to complain of acute or nagging pain.
Often this problem takes parents off guard: sometimes at night, sometimes on weekends, when there is no opportunity to immediately go to the dentist. In this case, it is important to properly provide first aid to the child, it is quite possible to relieve a tooth at home - it is only important to approach this correctly so as not to aggravate the situation.
Depending on the age of the child and the cause of the toothache, the methods of pain relief may vary significantly. Most of the drugs that are good for adults can not be given to children under the age of 12. To alleviate the toothache in babies, special children's medications are used - just below we consider them in more detail.
On a note
Do not underestimate the usual mouthwash - warm clear water.With deep caries, pain syndrome often occurs due to the irritant effect of food debris that enters the carious cavity. It is enough to rinse your mouth thoroughly to substantially alleviate the toothache or even eliminate it completely (if the matter has not yet reached the pulpitis).
Why a child may have a toothache
It is useful to keep in mind that although the most common cause of toothache is caries, however, other pathologies can also cause pain in the baby’s mouth:
- Chip and destruction of tooth enamel (if the baby has recently fallen and one or even several teeth could be damaged);
- Pulpitis and periodontitis (usually accompanied by acute spontaneous pain, which can not be removed only by rinsing the mouth);
- Flux (purulent inflammation in the periosteum of the tooth - visually looks like a bump on the gum);
- Abscess (can swell up the whole cheek);
- Complications after tooth filling (if you recently visited a dentist who prepared a tooth) ...
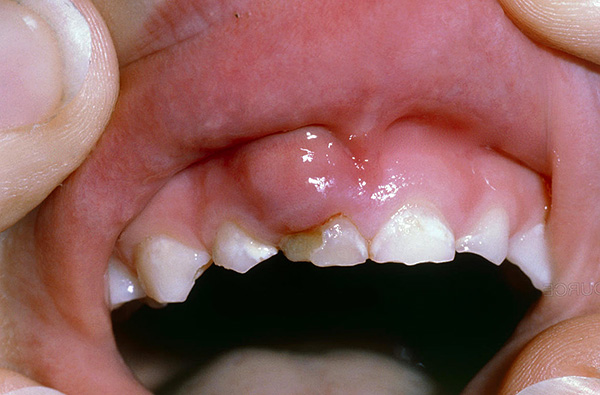
As well as the eruption of a new tooth, gingivitis, stomatitis and other factors.
As for caries, it causes aching or sharp paroxysmal pain.At first it appears as a reaction to cold, hot or sweet, and subsides in a couple of minutes (for example, a child’s tooth may ache immediately after eating, and then the pain goes away on its own).
With deep damage to the tooth, pain can appear regardless of the action of irritants and does not go away for a long time.
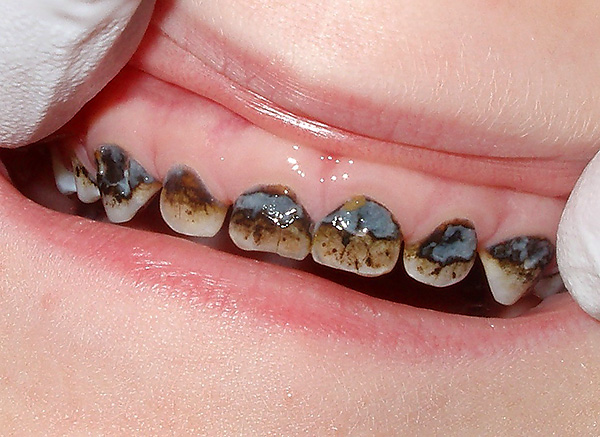
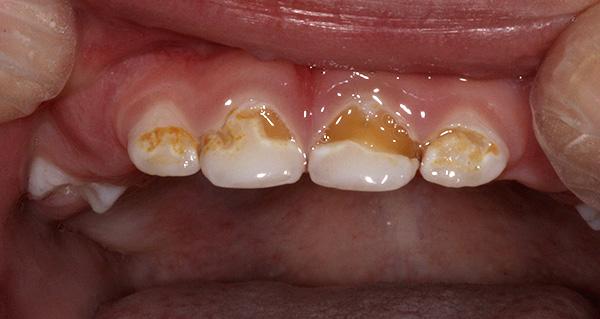
Carious tooth lesion can be recognized by the characteristic dark (yellow, brown, black) spots on the teeth. Even if the dark point looks small, there may well be an extensive carious cavity that reaches the pulp chamber of the tooth (there is a dental “nerve” in this chamber), which causes severe pain.
The photo below shows an example of a deep caries in a child:
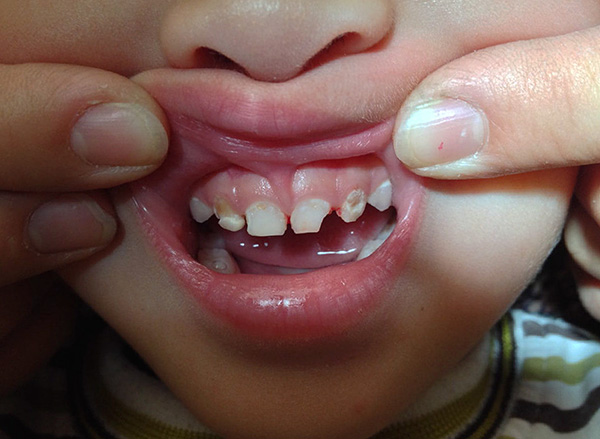
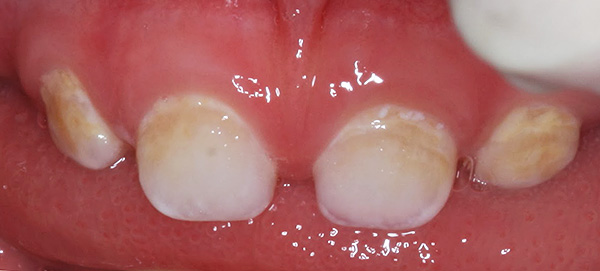
Caries can develop on baby teeth, even in infants. The so-called "bottle" caries occurs in children aged 0 to 4 years due to inadequate oral hygiene. It begins with white spots at the base of the tooth (at the gum) and quickly spreads to all teeth.
The photo below shows how bottle caries may look like at the initial stage:
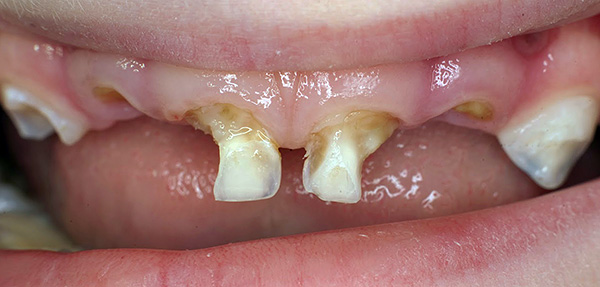
And so the baby's teeth can look if the situation start:
On a note
Caries on baby teeth usually develops much faster than on molars (permanent). In just 2-3 months, surface caries can go deep.
Deep caries, if not cured in time, can lead to the development of pulpitis - inflammation of the soft tissues of the tooth. If the infection is not eliminated even at this stage, then it can go to the root of the tooth with the development of periodontitis. Both of these diseases are accompanied by very strong acute, pulsating pain that can spread to the entire jaw, larynx and ear. Also characteristic reaction to temperature stimuli and exacerbation in the evening and at night.
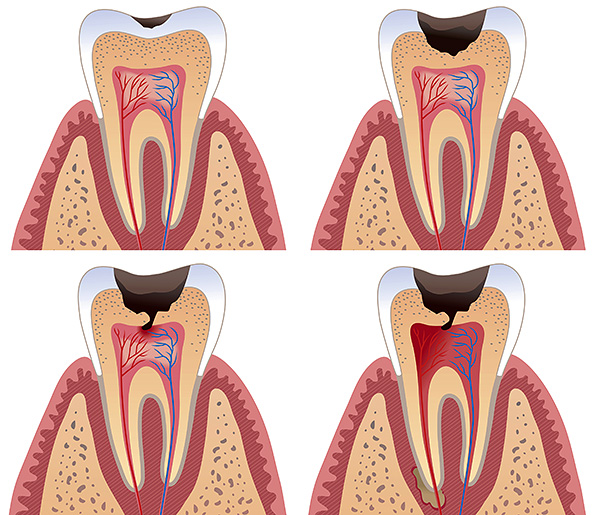
Sometimes pain in the tooth appears after treatment at the dentist. The reasons for this may be several, and the most common ones:
- Damage to the tooth pulp (for example, overheating during preparation, although this is very rare today);
- Allergy to filling material.
In some cases, the pain may go away by itself in a few days or a week, in others it may be necessary to re-open the tooth and replace the filling. Therefore, if positive dynamics are not observed, then it is important to re-show the child to the doctor.An x-ray may be required to clarify the diagnosis.
Also, purulent diseases - flux, abscess - can provoke strong toothache. They are easily recognizable by swelling of the gums and the formation of cones near the diseased tooth. In severe cases, the baby's face may become asymmetrical, the body temperature rises - in such a dangerous situation it is important to see a doctor immediately.
On a note
If a child has a cheek that is swollen, but not a single tooth has become ill, this can be a symptom of gingivitis, lymphadenitis, inflammation of the facial nerve or salivary glands, an allergic reaction, and some other diseases. And here, too, it is important to quickly refer to the pediatrician.
About the danger of such states
Contrary to popular belief, caries on baby teeth should be treated, even if they should fall out soon. First, the carious process can deepen and reach the “nerve” - this will lead to severe pain. Secondly, an infection (with periodontitis, for example) can spread to the rudiments of the molars that have not yet erupted and irreversibly damage them.
In addition, the premature loss of milk teeth leads to tears in the dentition and can provoke the formation of abnormal bite.Do not forget about the accompanying psychological problems, often accompanying children with bad teeth (the kid is shy of his "rotten" teeth, fears to smile for years, his peers are constantly teasing him).
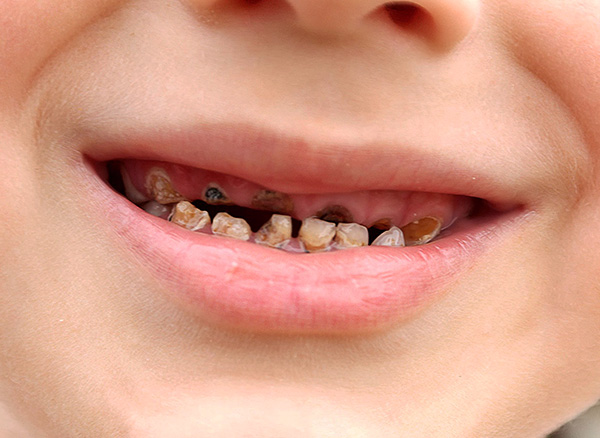
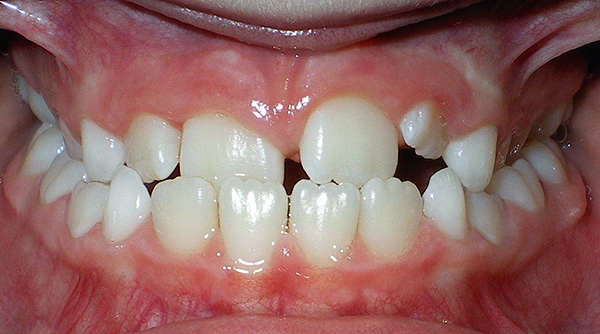
The easiest way to cure caries at the initial stage of its development. With deep caries and, especially, pulpitis and periodontitis, more complex treatment is required.
With purulent pathologies (flux, abscess, phlegmon) without treatment, the disease can spread to neighboring healthy teeth, leading to their mobility. In severe cases, this can lead to tooth loss.
On a note
If a toothache tormented a child for several days and then stopped abruptly, this does not mean that the illness has passed. As a rule, relief is due to the fact that the pulp of the tooth (“nerve”) dies - therefore, sensitivity disappears. It is important to understand that the infection has not disappeared anywhere - the necrotized neurovascular bundle inside the pulp chamber begins to decompose with the formation of pus, which will form the focus of inflammation on the tooth root.
No less dangerous is a disease such as gingivitis (gum disease). When symptoms appear, many consider the problem insignificant and refuse to visit the doctor, preferring to treat the child at home.With the wrong treatment of gingivitis, it can turn into a chronic form, causing the formation of abscesses in the gums and jaw bones. Meanwhile, with proper treatment, the disease disappears in 1-2 weeks.
Below are the situations when the baby must be shown to the doctor:
- The apparent destruction of the teeth caries;
- Acute pain in the tooth or gum;
- Aching pain in the tooth, which does not pass for a long time;
- Swelling of the gums or the appearance of cones on it;
- The appearance of ulcers in the mouth;
- Cheek swelling (even without pain).
You should not delay with a visit to the doctor, believing that you only need to wait a bit - and the baby teeth will fall out themselves. In children, tooth enamel is thinner than in adults, and, moreover, is less mineralized, so tooth decay often develops rapidly, quickly leading to complications. Therefore, already when the baby’s teeth appear white spots or small brown dots, it is imperative that you see the dentist.
The photo below shows the caries of milk teeth at the initial stage:
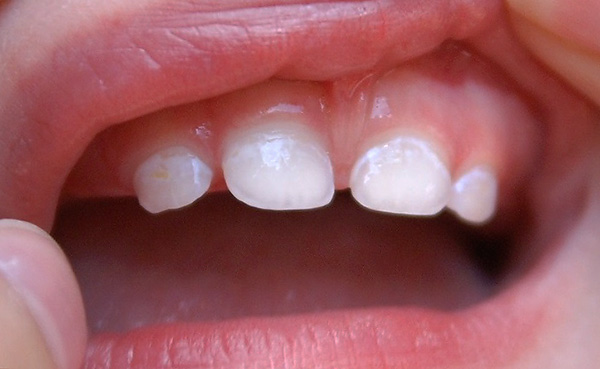
Practice shows that sometimes parents give an anesthetic drug to the child with the expectationthat the medicine will relieve pain and eliminate the need to visit the dentist (after all, it is a strong stress for the child). After taking the medicine, the baby can really get better, however, painkillers do not cure the disease, but only temporarily reduce the severity of the symptoms.
Therefore, if the baby's teeth react to hot and cold, or he often complains of pain in one tooth, then the trip to the dentist is better not to postpone. In the initial stages of caries, it is much easier to treat than when its complications appear.
First aid for a child with a toothache
At home, it is impossible to cure caries or pulpitis, but it is quite possible to reduce the accompanying pain syndrome. The choice of means depends on the child's age - some drugs are suitable for children from 3 months, while others are contraindicated up to 12 years.

It is worth noting again that often toothache can be removed by rinsing the mouth with warm clean water. When a child gets older and can rinse your mouth, you can use special solutions.
When choosing a painkiller, you need to carefully study the instructions for its use, pay attention to contraindications and side effects.If it is not possible to immediately take the child to the reception, then, if possible, it is better to consult a doctor at least by telephone.
So, consider the drugs that are commonly used to relieve toothache in children ...
How to help a child from 3 months to 12 years
For toothache and gum disease in children aged 3 months to 12 years, ambulance measures are usually used as:
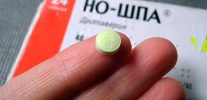
- Paracetamol-based preparations: Panadol, Efferalgan, Cefecon and some others;
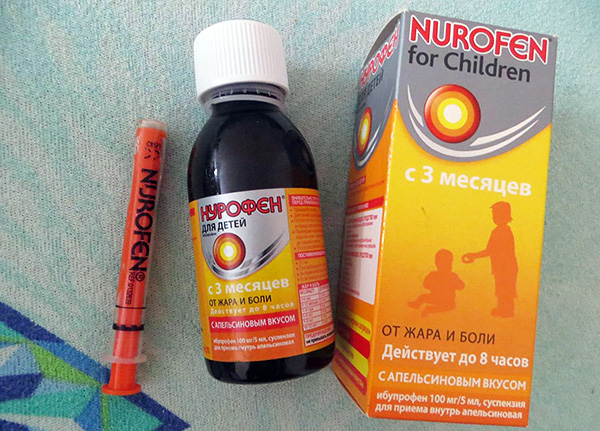
- Ibuprofen-based preparations: Nurofen (in syrup and suppositories), Ibuprofen.
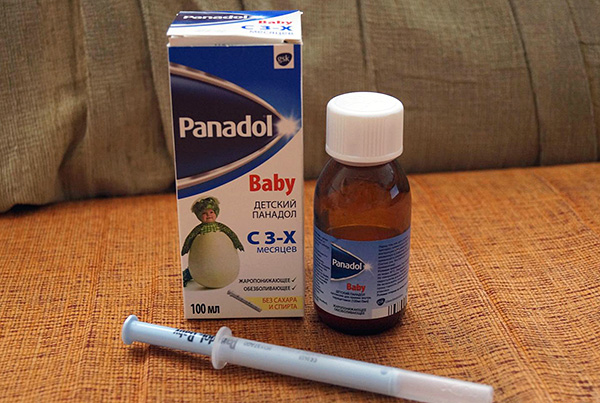
Paracetamol provides analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. It takes effect after about 20 minutes, and the effect lasts up to 6 hours.
Ibuprofen-based medications are also popular. For example, children from 3 months with no contraindications allowed Nurofen in syrup or suppositories (Nurofen tablets are used in children over 12 years old).
It is very important to observe the dosages recommended in the instructions and not to exceed them, even if the toothache does not pass. It is also impossible to use in parallel different means based on the same active ingredient, as this may provoke an overdose.
On a note
In children, only 20 milk teeth grow.The first appear after 6 months, and the last - by 3-4 years. Stagger and fall out they begin in 5-6 years. This age accounts for the largest number of cases of toothache, caries and visits to dentists.
A lot of trouble can also cause painful teething in a baby. In this case, commonly used:
- Dental ointments and gels based on lidocaine: Kamistad, Kalgel and others;
- Homeopathic gels: Holisal, Traumel-S, etc .;
- Dental drops for children: Dantinorm Baby, Fenistil etc.

Some gels and ointments are suitable for children from 3 months, they are used to relieve aching pain when teething. In the case of caries or pulpitis, they are ineffective, although in the presence of lidocaine they help to slightly reduce acute pain. - The effect usually persists for half an hour. Such gels are sometimes used to quickly help your baby before visiting the dentist.
With painful teething for infants, Kamistad gel is suitable. Its main components are lidocaine and chamomile extract. It is used in diseases of the oral cavity and teething. Apply the gel on the gums can be 3 times a day.
In inflammatory diseases of the gums in children over 3 years of age, the dental gel Holisal, whose active ingredient is choline salicylate, is popular. Due to its thick consistency, it lasts longer on the gums, wilts deep into the tissue and provides an analgesic effect for about 2 hours. You can apply it up to 3 times per day. With toothache against caries or pulpitis, Holisal is absolutely ineffective.
Dantinorm Baby Tooth drops are a homeopathic remedy. Used for painful teething in babies, but they do not relieve pain during caries or pulpitis.
When choosing the optimal drug is recommended to consult a doctor.
Toothache relief in children over 12 years old
After 12 years, children can take many drugs for adults, only at a lower dosage. For example, when toothache is commonly used: Nurofen (in tablets or capsules), Nise (tablets), Tempalgin, Ketanov, Ketorol, the same Paracetamol (tablets). Ibuprofen et al.
Sometimes, when a weak aching pain is used, Analgin is still used, although in many countries of the world this drug is prohibited for use because of the possibility of serious side effects.Be that as it may, do not apply the tablet Analgin to the patient's tooth, as advised in folk medicine, because the drug can destroy the enamel (the same applies to Aspirin).
Aspirin and Baralgin help with weak or moderate aching toothache.
Paracetamol is often used in children, it has fewer contraindications, and also has anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. However, it is worth noting that, as an analgesic, paracetamol is not very effective, and, for example, in acute tooth pain on the background of pulpitis, the effect may be clearly insufficient.
Ibuprofen-based drugs are very popular today: Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Solpaflex and others. They have a quick and strong effect, but have a fairly wide list of contraindications and side effects. In children, these tools and other drugs based on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be used with great caution.
Drugs based on nimesulide also help to relieve toothache quickly: Naiz, Nimesil, Nimid and others. They are produced in the form of tablets and sachets, which are dissolved in water.These drugs provide a significant reduction in even severe pain in about half an hour. Allowed to children from 12 years.
Ketanov (or its analogue Ketorol) also helps well to get rid of intense pain, but it is contraindicated for children under 15 years of age. Ketanov begins to act for 1 hour, and the effect lasts up to 6 hours, and it exceeds all the means listed above in its effect. In addition to the analgesic effect, it also has an anti-inflammatory effect. The recommended dose for adults is 1 tablet per day; in case of severe pain, the administration can be repeated one time 6 hours after the first one.
On a note
It should be borne in mind that due to the individual characteristics of the organism and the specifics of the pathology, sometimes, it would seem, a strong drug may not relieve pain, and a weaker one, on the contrary, is more effective. This happens rarely, but if the drug is clearly not working, then you should not increase its dosage and try to use it again and again - it is better to try another remedy.
Sometimes gels and lidocaine ointments help relieve a toothache - they have a very fast analgesic effect, but it does not last long (usually no more than 30 minutes).Lidocaine is also released in the form of a spray that is sprayed around a sore tooth or applied onto a piece of cotton and applied to the gum or tooth (depending on what hurts). It is important to take into account that the child may be allergic to lidocaine, therefore, it is necessary to use such agents, especially for the first time, with the utmost care.
What is useful to consider when using folk remedies
There are many traditional medicine recipes that are used to reduce toothache. Some tools are really effective, while you can hardly expect results from others.
In case of toothache and inflammation in the oral cavity, it is really possible to alleviate the condition by rinsing with herbal decoction. In the absence of allergies, they can be used in children from an early age. The main thing is that the baby knows how to rinse his mouth and does not swallow the solution. The very same little children can be given to hold warm water in their mouths. As noted above, it often helps soothe the pain.

The classic mouth rinse solution is made from water and salt (less commonly baking soda). A teaspoon of salt should be stirred in a glass of warm boiled water.This means (warm) rinse the oral cavity about once every half hour. Salt has an antimicrobial effect, helps reduce inflammation and prevent the spread of bacteria.
In traditional medicine also use sage, chamomile, oak bark or aspen. Herbal remedies doctors are allowed to use in young children, if not allergic. Before you prepare one or another decoction, you need to read the instructions for the use of herbal. It is also worth considering that these funds do not relieve an acute toothache, they are more often used in complex therapy for the treatment of inflammatory processes in addition to other means.

On a note
It may seem surprising, but for some reason, some doubtful folk methods of alleviating toothache are still popular. For example, it is recommended to put a plantain root into the ear, lay a piece of propolis into the carious cavity, tie a clove of garlic to the wrist, etc. Needless to say that in practice such methods do not work. And also do not expect to cure the tooth of a child with plots - a visit to the dentist will be a much more correct and effective option.
What not to do with a toothache
Despite the fact that in most cases the teeth hurt in children because of caries, but many other diseases can also cause pain. Accurately determine the cause at home is quite problematic, so this should deal with the doctor. And the task of the parents is to help the child at home before visiting the dental clinic, while not allowing gross errors, which not only can increase the pain, but also can provoke further development of the disease.

So, with a toothache:
- Do not lie on the side of the sick tooth;
- Do not lie on your swollen cheek;
- Do not warm the sore spot outside (warm rinses are permissible, but it is strongly not recommended to apply a heating pad to the cheek on the part of the patient's tooth);
- You should not give your child too hot or cold, sweet and hard food. It is better to feed the baby with soft food at room temperature;
- It is forbidden to give small children Analgin, Citramon, Ketanov and other drugs that are contraindicated up to 12 years;
- You can not give the child an anesthetic for a long time, hoping that the tooth will soon fall out by itself;
- You can not postpone the visit to the dentist,if the child’s acute toothache has decreased or even disappeared. Caries itself does not pass, and inflammatory diseases can become chronic.
What awaits the baby at the reception at the dentist
It is known that children, when visiting doctors, often behave far from the way their parents would like: a child can cry, scream, break out, bite ...
Some techniques can reduce the level of stress in the baby and prevent the formation of psychological trauma.
Before visiting the clinic, the baby needs to be told that the doctor will examine the teeth, clean them and treat them, but it is better to omit all the details. Needless to say, it will not hurt, because even an injection of anesthesia may seem painful to the child, and then he will feel deceived.
It is imperative that you lead a child to a pediatric dentist who knows how to find an approach and calm the baby (although even this does not always work). In his office can be a lot of toys, and on the wall in front of the chair - a screen with cartoons. To allay the anxiety of the child, usually the reception does not begin immediately with treatment. The kid has the opportunity to look around and meet with the doctor.
It is important to know
If a child starts to act up and cannot calm him down, then it is not necessary to forcibly carry out treatment, so that psychological trauma does not arise and a steady fear does not form. It is better to leave, and then make an appointment for re-admission.
In some children's dental clinics psychologists work who can help a child morally prepare for dental treatment.
In difficult cases, when the child is very restless or there is a long and difficult treatment to be done, it can be performed under general anesthesia or sedation.
Sedation is carried out, for example, using a mixture of oxygen and nitrous oxide, which is inhaled through a mask. With mild sedation, the child remains conscious, but relaxes and calms down, and with deep sedation, he sinks into sleep. Sedation is used for children from three years.
If sedation is not appropriate, general anesthesia may be given to the child if indicated. Modern drugs have much less contraindications and side effects than those used before. The use of anesthesia or sedation does not affect the physical or psychological health of the baby. He regains consciousness immediately after the procedure.
Anesthetics are used for local anesthesia. Moreover, before the injection the doctor can anesthetize the child's gums with a spray or gel of novocaine, in order to exclude any painful sensations even from the introduction of the needle.
On a note
Silver teeth are sometimes used on milk teeth. Silvering does not cure caries, but this prophylactic procedure at the initial stages helps to some extent prevent the spread of caries over the enamel surface or between adjacent teeth. The tooth is treated with a silver nitrate agent, with the result that it becomes gray or black. The procedure is repeated 3-5 times.
Silvering is painless and easily tolerated by children, but with an insufficient level of oral hygiene, this procedure will have virtually no effect - the teeth will continue to actively deteriorate.
Prevention of caries in children
Care for the health of the child's teeth should be immediately after their eruption. Without proper care, babies develop very quickly “bottle-in” caries, which actively progresses and often spreads to all teeth. To prevent this, you need to wipe your teeth with a special fingertip (sold in a pharmacy).
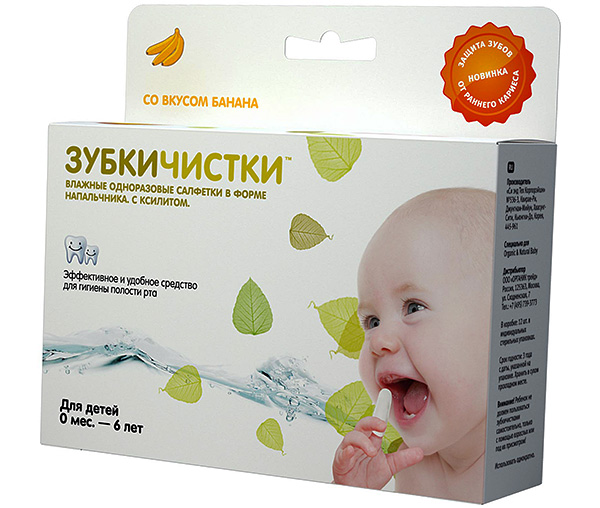

It is very important to teach a child to brush teeth from an early age.Today there are many children's toothbrushes and toothpastes with different tastes, and the whole procedure can easily be turned into a fun game. The child should brush the teeth twice a day, and rinse the mouth with clean water - after each meal.
In the opinion of many parents, it is possible to teach a child to brush their teeth independently and to introduce it into a habit already from 2-4 years old.

To clean the gaps between the teeth need a floss or irrigator. There are special children's threads, which the baby will be easy to use on their own.
Do not forget that the health of teeth is important not only their hygiene, but also proper nutrition. With a lack of vitamins and minerals, tooth enamel can become thinner, which leads to the appearance and development of caries.
As a preventive measure, you need to visit the dentist with a child every 6 months. In the initial stages of caries, its foci on the enamel can be seen only during a professional examination. Therefore, the sooner the child visits the dentist, the less will be the risk of developing severe pathologies.
Be healthy!
How to prepare a child to visit the dentist
Useful video: why it is so important to treat milk teeth in time