Caries is a complex, as a rule, slowly progressive pathological process of destruction of hard tooth tissues due to the complex effect on them of so-called cariogenic factors.
When, for the first time in the Roman Empire, the surgeon Archigen “drilled out” a tooth to a patient and successfully treated caries, his experience was gradually forgotten and remained only in historical documents. It would take more than a century for the caries to be remembered again.

In the Middle Ages, people were very interested in the causes of caries and pain arising in the teeth. However, the fact that caries - this disease became known much later.
By the way, back in the 1st century AD Roman doctor Scribonius tried to suggest that tooth decay is associated with "bad juices" that get into the mouth with food. Since then, several dozens of theories have emerged about what caries is and what are the causes of its occurrence and development, some of which have survived to this day.
Bacterial nature of caries
Miller's chemical parasitic theory on the development of dental caries dates back to 1884 and is still considered the best interpretation of the current understanding of the causes of this pathological process. With minor corrections, it is actively used today.
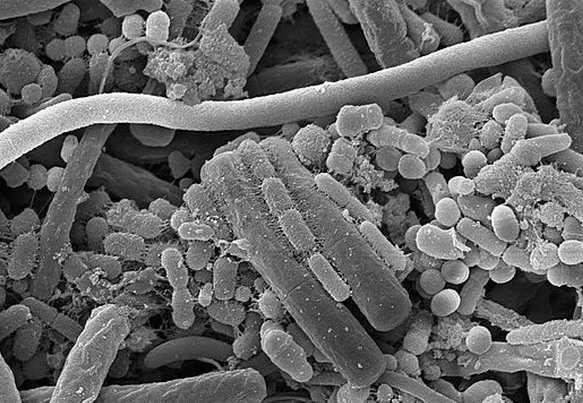
Thanks to this work, mankind has learned that the main cause of caries is the waste products of microorganisms that are released during the fermentation of carbohydrates in the oral cavity, in particular, on the surface of the tooth enamel. In other words, food sugars are a breeding ground for bacteria (for example, for anaerobic Streptococcus mutans), which are found in large quantities in plaque.
Isolation of organic acids, which are products of fermentation of carbohydrates, determines the main cause of dissolution of tooth enamel with leaching of compounds of fluorine, calcium, phosphorus from it, which, in turn, leads to a gradual destruction of the crystal structure.
It is interesting
Even then, Miller recognized the existence of certain factors, such as the amount and composition of saliva, the nature and diet, the composition of drinking water, as well as the effect of heredity and enamel maturation conditions on which the possibility of caries directly depended.
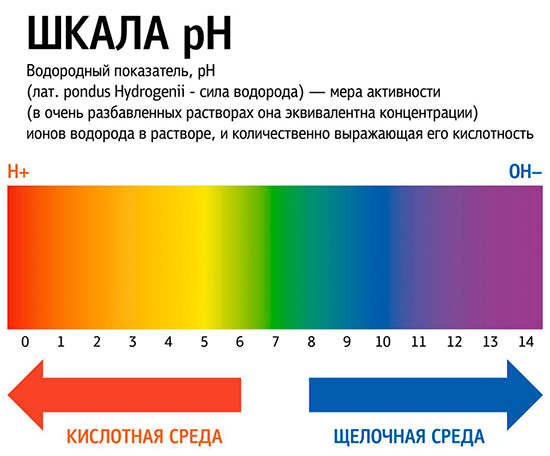
It has been established that usually just a few minutes after ingestion of carbohydrates is enough to lower the pH level in the oral cavity from 6 to about 4. And the lower the pH (in other words, the higher the acidity of the medium), the higher the rate of enamel destruction, the faster caries.
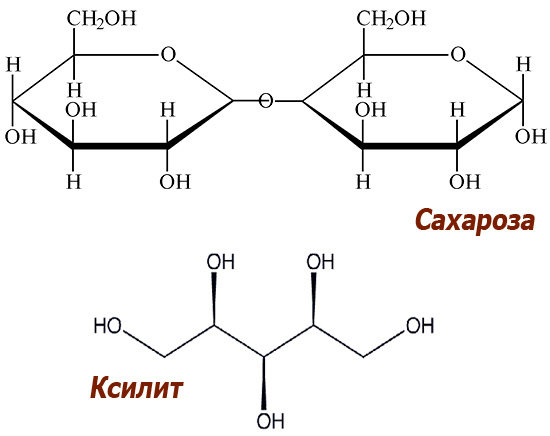
Among the acids formed in plaque, lactic acid was found, as well as formic, propionic, butyric and, in smaller quantities, some others. It is interesting to note that the main carbohydrate required by the bacteria in our oral cavity for the formation of these acids is sucrose. Significantly less intense cariogenic acids are formed during the fermentation of fructose and glucose.
But xylitol or sorbitol, for example, is practically harmless from the point of view of factors provoking caries: the enzymatic system of plaque microorganisms is not capable of converting these substances into acids at any significant speed.
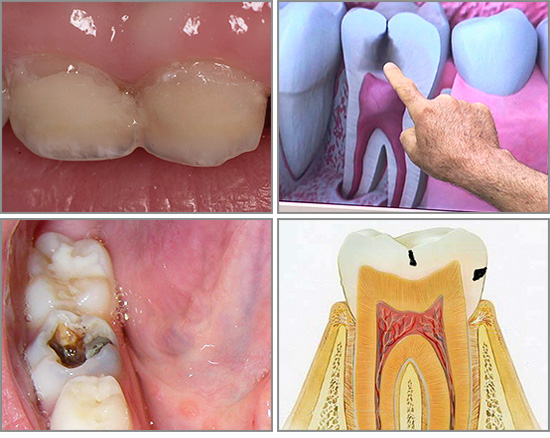
Today, thanks to numerous additional studies, we can argue that dental caries is a local pathological process, which manifests itself only after teething and is associated with focal demineralization of enamel withthe subsequent softening of hard tissue leading to the formation of a cavity.
From this follows a number of important points:
- Dental caries is a pathology that requires timely treatment, so that the destruction does not lead to a carious cavity.
- Caries is a local pathological process, that is, one tooth cannot “infect” another.
- Caries never occurs before teething. This means that the disease develops on the tooth surface against the background of the action of cariogenic factors.
The etiology of caries continues to be studied (in particular, issues related to the influence of heredity, various environmental factors, etc.).
Disease of modern society
Caries on the teeth appeared in ancient times, but there is reason to believe that this problem was not widespread, and the treatment was reduced to the banal tooth extraction. However, in the Middle Ages, caries became a problem for most people. Scientists attribute this to changes in the human diet, as well as environmental and living conditions.
Starting from about the XVIII century, the frequency of occurrence of caries inexorably begins to grow, and today its prevalence in some regions of the planet reaches 100%.At the same time, the incidence of caries in the countries of Western Europe is relatively small, while in Africa and Asia these figures reach 80-97%.
Such statistics is explained by a whole range of complementary factors:
- The nature of the diet (in particular, an excess or lack of carbohydrates);
- Fluorine content, as well as other micro and macro elements in drinking water;
- Social and climate-geographical conditions (the level of dental care to the population, the consumption of drinking water containing fluoride, etc.).
According to a number of authors, carious lesions are observed in about 80-90% of children with milk teeth, and at the time of graduation from school, about 80% of children also have caries - already on permanent teeth.
As for adults: in developed countries, about 95% of them have at least one filling in the tooth.
Classification of caries
For practical use, perhaps the most convenient is the classification of caries by the depth of the process. At the same time caries is divided into two large groups: uncomplicated and complicated, the latter of which includes various types of pulpitis and periodontitis.
As for the actual uncomplicated caries, it is classified into the following types:
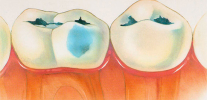
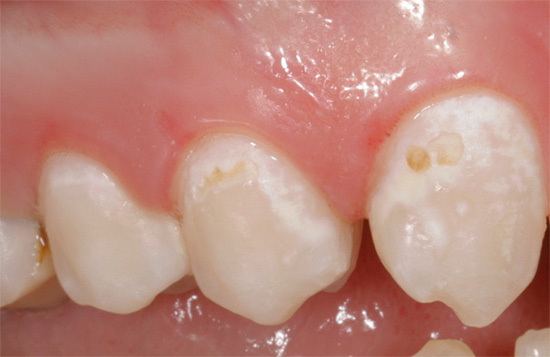
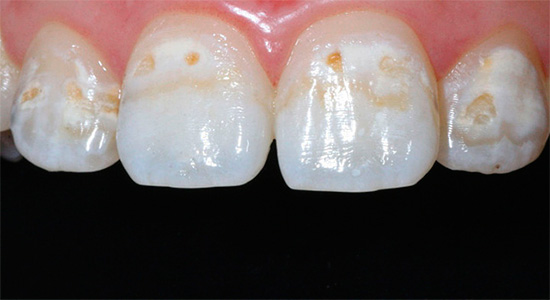
- Caries in the staining stage (the enamel is locally demineralized, as a result of which its color changes, and its hardness and smoothness can also decrease; as a rule, pain is absent at this stage. diagnosis of caries in the staining stage it is important to differentiate it with non-carious lesions of the teeth - for example, with hypoplasia and fluorosis).
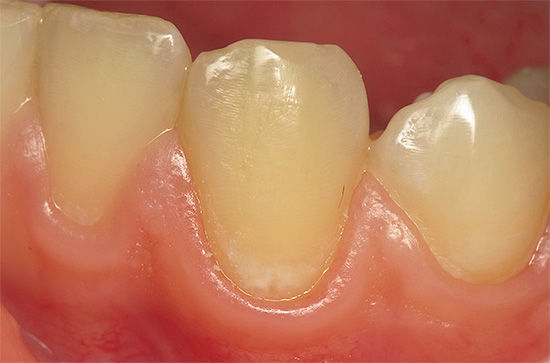
- Superficial caries (white or chalky spot at this stage becomes rough, can begin to pigment. A characteristic feature of the clinical picture with superficial caries is the appearance of pain from sour, sweet, cold. At this stage, it is not always possible to do without installing a seal).
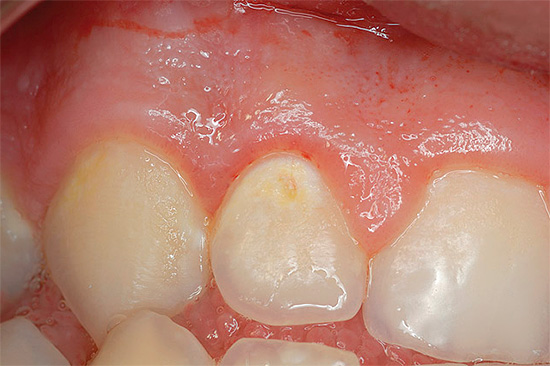
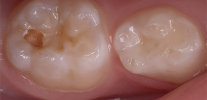
- The average caries (the area of destruction penetrates deeper into the tissues of the tooth with dentin damage, pain from irritants becomes more pronounced and intense).
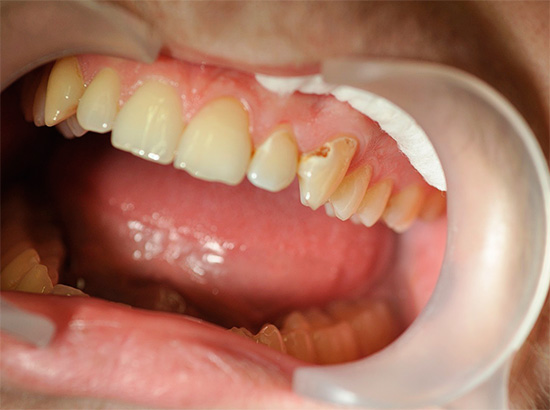
- Deep caries (the affected area reaches the pulpar dentin. If you do not start the treatment at this stage, then the pulp chamber will be affected later and with a high probability you will need depulpation - removal of the “dental nerve”.With deep caries pain can be very strong and prolonged).
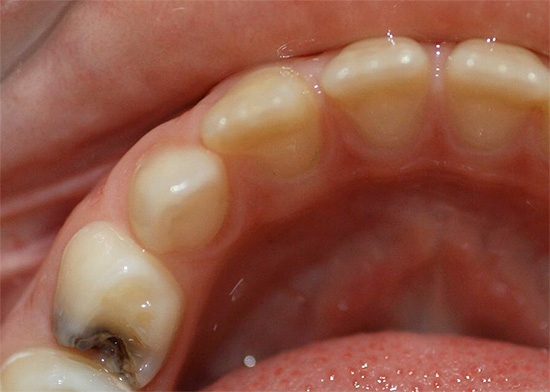
There are other types of caries classifications (by the severity of the process, by localization on the teeth, by the duration of the course, according to WHO, etc.)
What is dangerous caries
Currently, acute and chronic caries teeth. In a chronic course, caries can be very long at the same stage of development.
For example, the appeared white carious stain on the tooth surface may gradually become pigmented due to dyes from food, but for a long time not lead to the destruction of the upper layers of enamel. In chronic form, the transition to surface caries can occur only many years after the start of the process of demineralization.
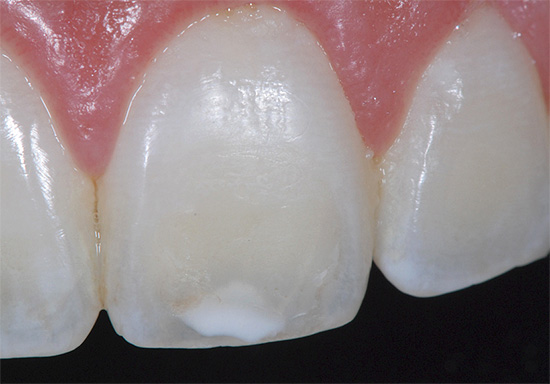
Why not tell about acute caries, when, in a matter of weeks or months, a superficial defect develops first from a pigmented or white spot, and then a cavity of the type of medium or deep caries. Without treatment, such a rapid process usually leads to complications of caries: pulpitis and periodontitis.
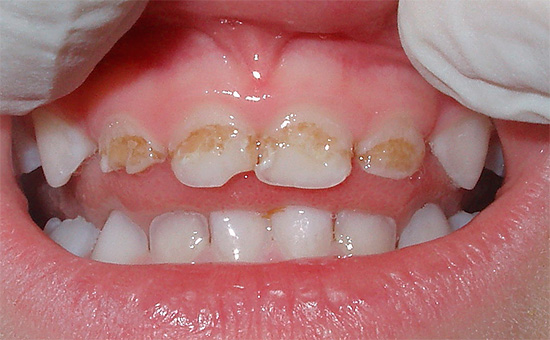
In the treatment of pulpitis is the so-called depulpation - removal of the dental nerve.A dead tooth in most cases will last less than a living one.
Removing teeth as a result of periodontitis is the worst option for occlusion: in the absence of one or several teeth, the others often begin to gradually shift relative to their original normal position. That is why timely treatment is so important already at the initial stages of the development of pathology (caries spots) when it is possible to do with conservative methods of therapy.
Often, great difficulties arise in case of multiple lesions of the so-called “bottle-shaped” caries of milk teeth in young children from 2 to 3–4 years of age.
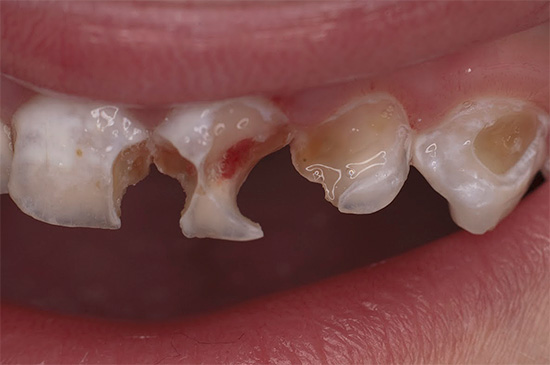
On a note
As a rule, bottle caries occurs in children with reduced immunity, various concomitant pathologies, however, it is not uncommon to develop it in healthy children due to the defective tissue structure of enamel and other factors causing caries. These include, mainly, the wrong mode of feeding and the lack of proper oral hygiene after it. Food remnants after feeding (especially at night) with weak salivation and (or) insufficient mineral content of saliva allow microorganisms of plaque forming on the teeth to quickly lead to tooth decay.
The photos below show some examples of bottle caries:
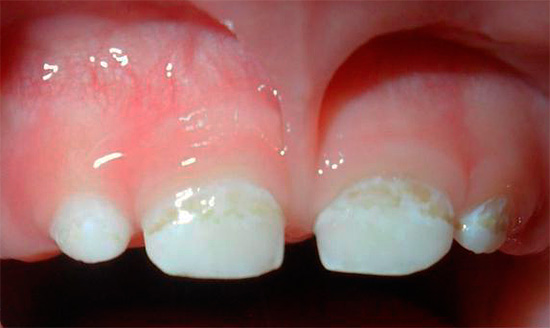
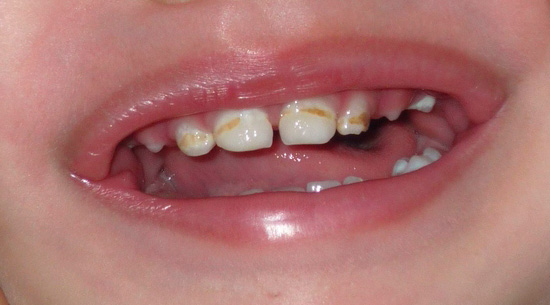
It all starts with ordinary zones of focal demineralization or spots in the cervical area, and then the onset of destruction can turn into a severe form of cervical caries - circular caries, right up to the part or all of the tooth crown. At the same time, the teeth may not hurt for a long time due to the protective capabilities of their forming replacement dentin, which saves from accidental opening of the pulp (“nerve”).
If time does not begin to heal, then the effects of bottle caries can be very serious. No one knows for sure on what day the pains of decaying teeth will begin, but it is at the most inopportune moment that the baby will refuse to eat normally and even sleep.
Incorrectly chosen painkillers can damage the overall health of the child, and stopping the pain for a while is not a positive result, but imaginary well-being. After some time, serious inflammatory processes can occur on the roots of milk teeth (often manifested by "flux" on the gums), leading to the need to remove a tooth.
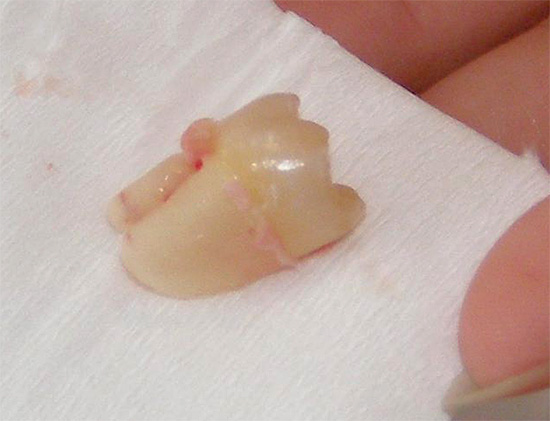
Multiple removal of milk teeth entails a violation of the milk bite. Caries infection, inflammation, premature removal of milk teeth - all of this directly or indirectly affects the normal development and eruption of permanent teeth. In order to prevent such terrible consequences, it is required to timely treat caries even on baby teeth, without justifying inaction by the fact that they will soon fall out.
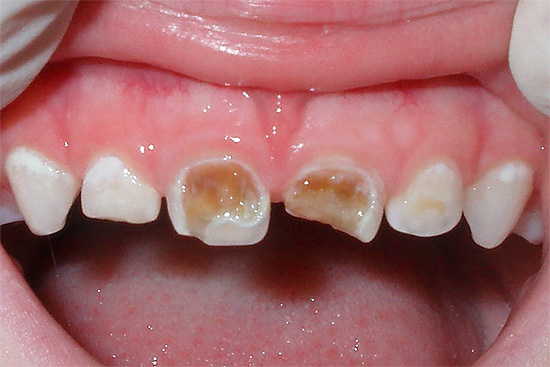
Do not underestimate the effect of diseased teeth on the quality of human nutrition. With deep caries, food intake and its normal chewing can be significantly complicated, and over a long period of time this usually has a general negative effect on the body.
In addition, rotten teeth in the smile area often lead to psychological complexes, especially in children. Fear of smiling broadly, the constant covering of the mouth with your hand while the man laughs can all be attributed to a kind of psychological dangers associated with the presence of caries.
Dental caries
Caries in the stage of white spots is the most favorable for conservative treatment in dentistry without the use of a drill.For this, various drugs and technologies can be used.
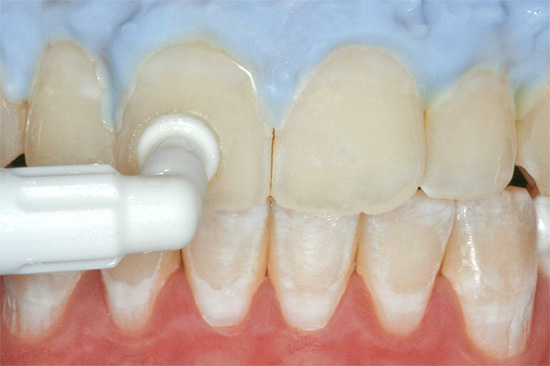
Popular treatment options for the enamel demineralization focus are remineralizing drugs and deep fluoridation agents:
- Gluftored;
- Remodent;
- Enamel-sealing liquid;
- Belagel Ca / P, Belagel F, etc.
The action of these drugs is based on the fact that the enamel demineralization during initial caries is reversible. Moreover, the process of its recovery is normal in a healthy person constantly: all the mineral components necessary for this are already contained in saliva (for this reason, saliva is even called “liquid enamel”).
The concentration of mineral components in remineralizing preparations is hundreds of times higher than in saliva, therefore, in a short period of time, they are able to fill tooth enamel with all necessary components in quantities sufficient for intensive regenerative processes. However, such a restoration is not always possible: the criterion of the reversibility of the destruction of enamel caries is the preservation of the protein matrix, which determines the orderly arrangement of mineral particles in the tissues of the tooth.If the collagen fibers of the matrix are destroyed, then conservative methods of treatment will not be enough, and installation of a seal will be required.
The above preparations are intended exclusively for professional use, but they can be fully combined with the treatment of caries at home - with toothpastes and remineralizing gels:
- GC Tooth Mousse Remineralizing Tooth Cream;
- Remineralizing gel O.C.S. Medical Minerals;
- Toothpaste with active fluoride Fluoride;
- Another fluoride toothpaste is the New Pearl Fluoride;
- Colgate Maximum;
- Lacalut Fluor;
- Pepsodent
And etc.
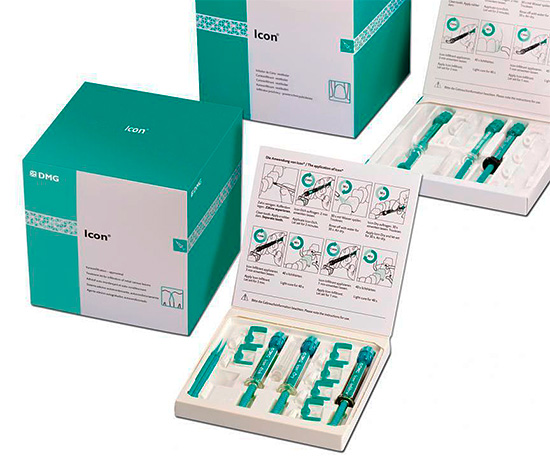
Among the modern technologies for the treatment of caries in the staining stage, the non-invasive ICON technique is becoming popular - caries treatment without a drill, which involves the infiltration of the polymer resins of the preparation into the zone of prepared and treated pre-enamelled enamel.
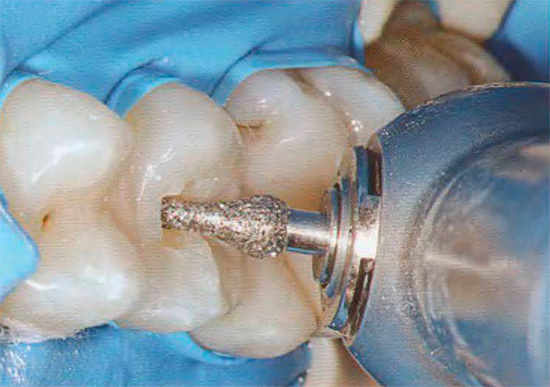
Treatment of superficial, medium and deep caries most often does not do without the use of a drill and consists of several stages:
- Pain relief (general or local anesthesia according to indications);
- Removal of plaque (stone) from the surface of the teeth;
- Isolation of the surgical field with a cofferdam or ordinary cotton swabs;
- Dissection using turbine tips or tips for micromotor with mandatory air-water cooling;
- Expansion of the cavity with the removal of softened and pigmented (in some cases) dentin and incomplete enamel;
- The formation of the cavity under the material chosen in advance for filling;
- Stamping according to its instructions;
- Finishing.
The following are some of the modern materials from the arsenal of a professional dentist:
- Composites;
- Glass ionomer cements;
- Compomers;
- Ormockers (organo-modified ceramics).
Means of prevention: separating truth from advertising
Most commercials lead to believe that the use of toothpastes containing high concentrations of fluoride, will lead to a reliable disposal of caries. The same applies to rinses with fluoride.

You always want to believe in a miracle, especially when dentists advise from the screens, explaining their experience in using these hygiene products. In fact, the mere use of a paste with fluoride or rinse will be extremely insufficient, since the implementation of the tasks of preventing the onset and development of caries requires an entire set of consecutive events:
- Restriction of the use of carbohydrates (any confectionery);
- Mandatory consumption of solid foods, such as fruits and vegetables;
- Mandatory oral hygiene after every meal (at least you need to rinse your mouth after eating);
- Performing proper toothbrushing - all available surfaces.
It is interesting
In a number of industrialized countries, babies under 1 year old already have carious tooth decay. By the end of 2 years of life, the number of children with caries is approximately doubled. At 5 years of age, caries is diagnosed in about 75% of children.
Caries of fissures predominate in milk teeth, and the proportion of approximal (contact) caries increases with age. This is largely due to the culture of nutrition and the predominance of high culinary food processing in developed countries.
Although advertisements are silent on many things, they are far from always lying: fluoride toothpaste will be especially useful if used in conjunction with fluoride mouthwash and also when using dental floss to clean interdental spaces.

It should be borne in mind that the composition, quantity and bactericidal properties of saliva in each person are individual.Not everyone is lucky with high remineralizing indicators of oral fluid, but there are also those who are all right with this. This means that there are a lot of people who, although they regularly use sweets, may not brush or follow the technique of brushing their teeth, but they also have no problems with caries.
However, in any case, you should not rely only on the capabilities of your body, without making any efforts to maintain the health of your own teeth. Regular prevention of caries requires not so much effort to neglect it, so take care of your teeth from youth and be healthy!
What is caries and how to protect against it
When fluoride toothpastes can be detrimental to health
How to keep your teeth healthy until old age: practical advice