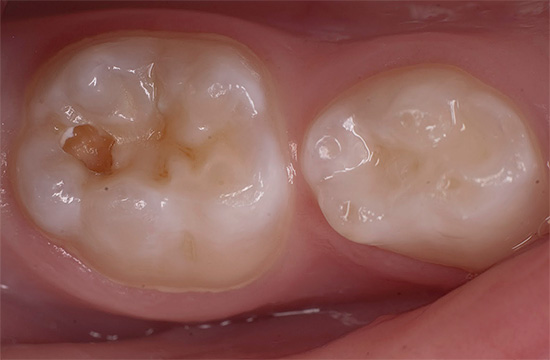
Most people more than once thought about what the word "caries" itself means, even despite a more or less clear understanding of the processes occurring in a tooth when it is destroyed. But one usually wonders about what dentin caries is only after visiting the dentist’s office, when the doctor suddenly suddenly “pleases” you with a message about the need to put a seal.
On a note
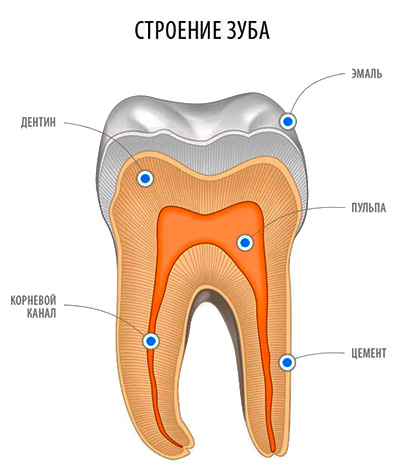
“Caries” is the Latin name for the rotting process. And the word "dentin" comes from the Latin "dentis", which means "tooth." In essence, dentin is the basis of the tooth and is under enamel.
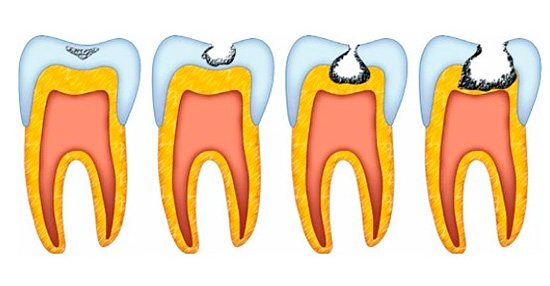
Given the current classification of carious lesions by WHO (World Health Organization), the following types of caries are distinguished:
- Enamel caries;
- Dentine caries;
- Cement caries.
Further we will be interested only in caries of dentin, acquaintance with which let us begin with a detailed consideration of the reasons that cause this pathological process.
The main causes of dentin caries
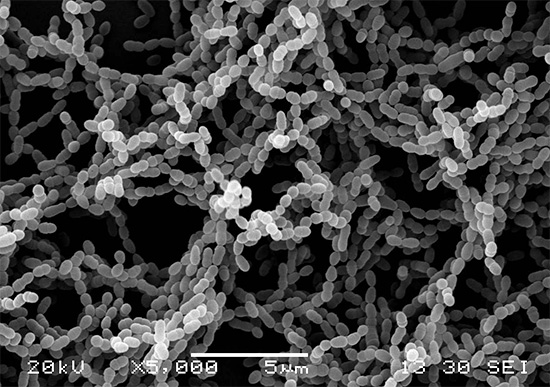
As a result of the vital activity of the bacteria Streptococcus mutans and several other species, organic acids are formed on the surface of the plaque due to the enzymatic decomposition of carbohydrate residues, for example, sugar. It is these acids that cause the “washing out” of the main mineral components from the crystal lattice of the tooth enamel (calcium, fluorine, phosphorus).
On initial stage of caries The specified process of demineralization occurs only within the subsurface layer of enamel. As a result, as a result of the active leaching of minerals and the slow return of them back, the formation of a carious stain occurs. It can be white or pigmented as a result of staining of the “voids” of the enamel with food dyes and drinks.
Caries in the staining stage - this is not caries of dentin. At this stage, the pathological changes on the tooth surface are still reversible, if measures are taken in time.
According to numerous researchers, carious stain in most cases can be cured with remineralizing drugs, without using a drill.Such drugs include various fluorinating varnishes, gels, calcium preparations and combined formulations.
However, if you overlook the stage of damage to the enamel in the early stages, then there is already an irreversible process - dentin caries. At this stage, the mineral components are washed out from the dentin itself, which, as you remember, is the basis of the tooth.
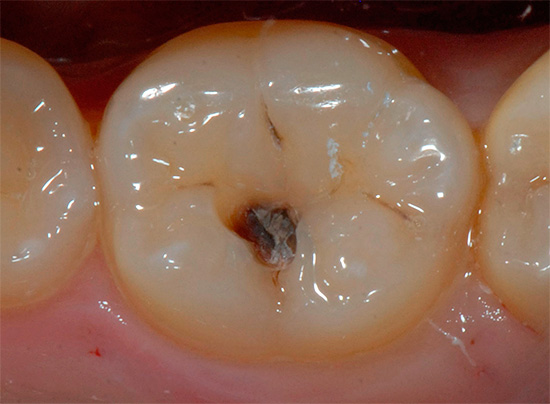
It is interesting
Dentin is significantly different in its chemical composition and structure from tooth enamel. It is much less durable and consists of organic compounds by 20%. The thickness of the dentin in the tooth reaches an average of 2 to 6 mm. At the same time, dentin is penetrated almost all its thickness by dentinal tubules containing nerve endings.
Clinical picture
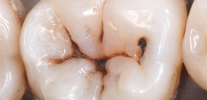
Dentin caries is accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the tooth with the formation of a cavity. However, do not think that a hole in your tooth will definitely be visible: often the carious cavity is not visualized and can only be detected at a dentist’s appointment when probing a tooth with a special tool for diagnosing caries.

However, there are quite common cases when the patient himself sees the cavity formation in the tooth, since the clinical picture is rather rich with accompanying symptoms in case of dentin caries. These include:
- Discomfort when chewing;
- Toothache from temperature irritants (cold, hot food or drinks), sweet;
- Aesthetic imperfection, especially when the front tooth begins to collapse.
A pain symptom may occur from one or several irritants at once, but quickly passes after the source of irritation is eliminated.
Sometimes caries dentin does not manifest itself, but only few are so lucky. With the appearance of at least one or several of the above symptoms, most people are already ready to sign up for a dentist's treatment in order not to delay or aggravate the process.
Features of diagnosis of carious lesions of dentin
Diagnosis of dentin caries in most cases is not difficult, even for an ordinary person. An important characteristic of caries at this stage is the occurrence of pain, which quickly disappears after the removal of the stimulus. For example, when eating candy in a problematic tooth, severe pain may occur, which quickly passes as a result of rinsing the mouth cavity with ordinary warm boiled water.
Methods for diagnosing carious lesions of the dentin at the doctor are different, ranging from subjective to objective and instrumental. From the point of view of your symptoms, a doctor, like you, cannot always establish a diagnosis immediately and accurately. However, even at this stage, you can formulate a preliminary diagnosis and go to the objective methods of research.
To clarify the diagnosis in this situation are used:
- Cavity sounding technique;
- Tooth percussion (tapping);
- Palpation of the transitional fold near the patient's tooth;
- Thermometry.
Probing of the carious cavity is performed by a dentist with the help of a probe - a special tool pointed at the end. Where there is a softening of tooth tissues, the probe will fall or get stuck. It may feel sore.
With percussion, the doctor can determine the state of the peri-root zone, the presence of inflammation in it, which does not happen with dentin caries. Pain when tapping on a tooth (especially sharp) usually indicates the passage of an infection deep into the tooth: into the root canals or into the surrounding root tissue.
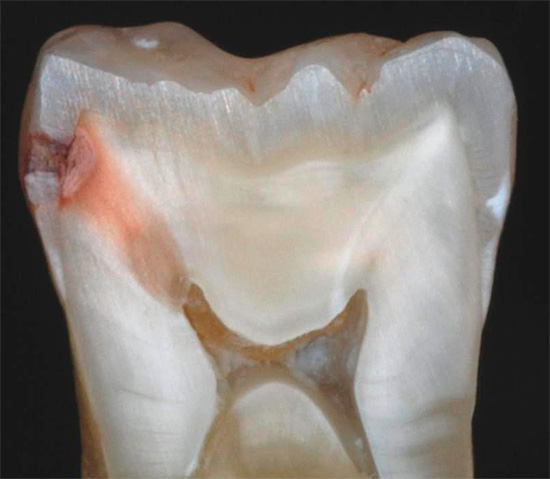
In this case, no longer talk about the average caries.If the pain is absent, it means that the diagnosis of dental caries is confirmed.
On palpation of the transitional fold, it is possible to determine the presence of overt or covert foci of infiltration of the exudate or, in other words, the state of “swelling” of the tissues surrounding the tooth. If there are no signs of infiltration, then, most likely, we are not talking about the complications of caries.
Thermometry can help determine the causative tooth causative for patient complaints of cold, warm or hot. You can always take some water into the syringe and rinse the alleged aching tooth. If signs of pain appear, the causative tooth is found, and the diagnosis is practically made.
There are also reliable additional and special methods of examination, when using data from electroodontometry for accurate diagnostic caries. Unfortunately, this technique did not take root in most medical institutions.
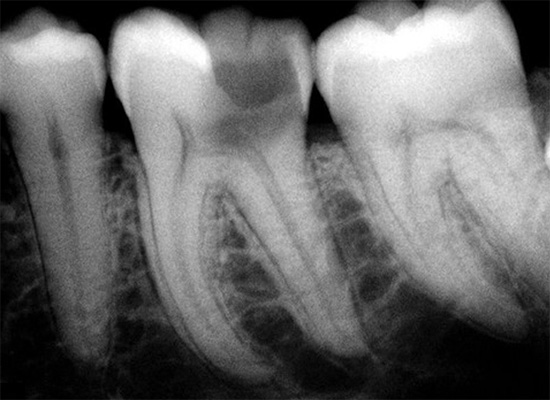
With the help of radiological methods of investigation, it is possible to determine the severity of the carious process and the level of its complication. At the root there can be various manifestations of inflammation, and their obvious presence will deny the diagnosis of dentin caries.
Sometimes dentinal caries is masked by its complications (for example, chronic forms of pulpitis or periodontitis). Unfortunately, in such non-standard situations, the symptoms may be similar in some aspects. Only a dentist at the reception can determine the final diagnosis.
Dentin caries treatment
If caries reached the dentin of the tooth - it means that you have already missed the moment when the treatment of pathological changes could be carried out without using a dental drill. At this stage, a visit to the doctor usually does not do without drilling the teeth and installing fillings.
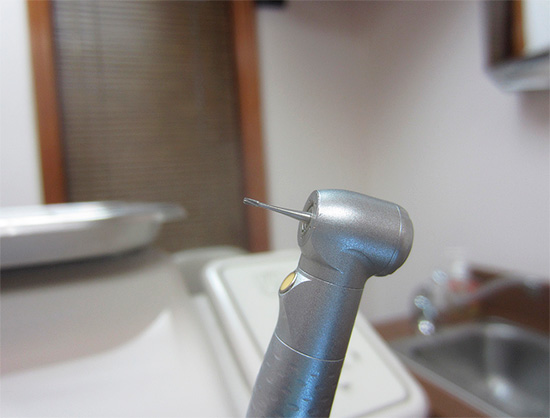

At the dental admission, measures will be taken to preserve not only the tooth, but also the pulp (“nerve”) inside its roots. To do this, the doctor will consistently conduct the following stages of treatment:
- Adequate anesthesia, so that you do not experience pain;
- Treatment of the tooth from carious and infected tissues (using a drill);
- Washing the cavity formed with antiseptic solutions;
- Laying lining and seals of the price level, which will be discussed in advance.
It should be noted that, at present, modern filling materials are being produced that allow gentle treatment of the tooth without cutting out healthy tissue, unlike Soviet filling materials (cements, amalgams, etc.). This is due to the possibility of high-tech fillings to enter into chemical bonds with the tissues of the tooth, forming durable and inseparable compounds due to special adhesive systems (or "adhesives").
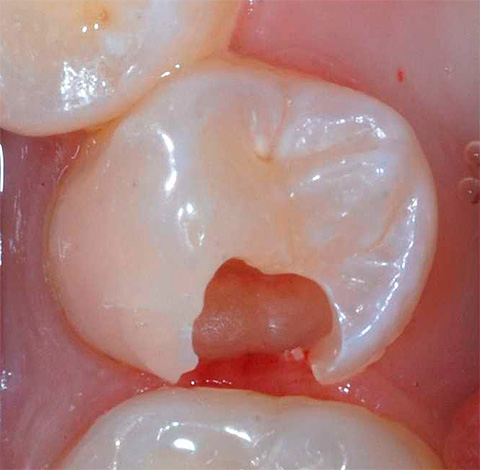
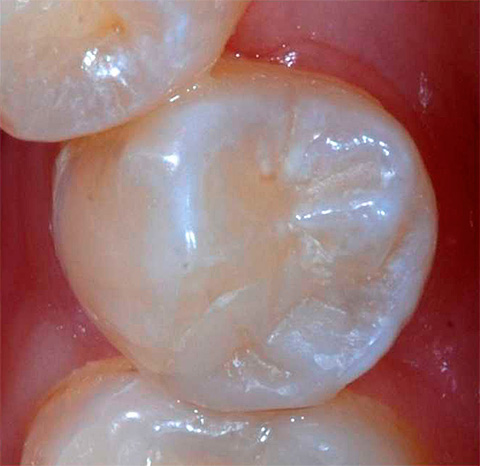
Dentin caries prevention
Modern methods of prophylaxis make it possible to recognize caries in the staining stage at an early stage and begin treatment with non-invasive methods, that is, without the use of dental machines. The simplest and most common way to determine the presence of a carious stain is staining with a 2% solution of methylene blue. Only in the presence of a hidden carious process, it is possible to persistent staining of the tooth enamel even after prolonged washing of the dye solution with a stream of water.
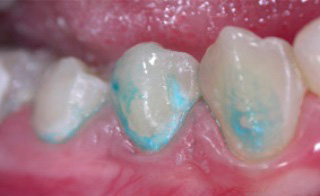
After diagnosing a carious stain, you should contact your dentist for help. At the reception, you will be given a number of preventive procedures that will stop the development of caries in the early stages and prevent the destruction process from affecting dentine. Such preventive measures include the following:
- Conduct professional oral hygiene (removal of tartar and plaque).
- Remineralizing therapy: coating with fluoride varnishes, gels or special solutions of the surface of the affected enamel of the problem tooth and still healthy teeth to strengthen them. For each drug has its own instructions and course of application (from 1-2 times to 10-20 visits).
- The course of home remineralizing and strengthening therapy (according to the situation).
Carrying out the above recommendations, caries in the staining stage will not turn into a more severe form - dentin caries. The course of preventive measures will allow to achieve excellent results without the use of a drill, it is important only to consult a dentist in time.
Take care of your teeth and be healthy!
Interesting video: the structure of the tooth, caries and its complicated forms
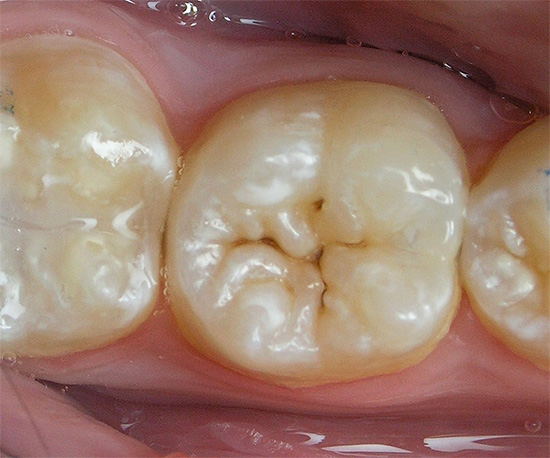
Examples of carious lesions of the teeth, their drilling and subsequent filling

Very useful article. Thanks you!